The following are the technological achievements developed by our laboratory since 2012, including research paper publications, technical reports, patents, products, and other information. The majority of the data is arranged based on the completion year at the time of development.(2026/01/18 Updated)
2026Y’ achievements
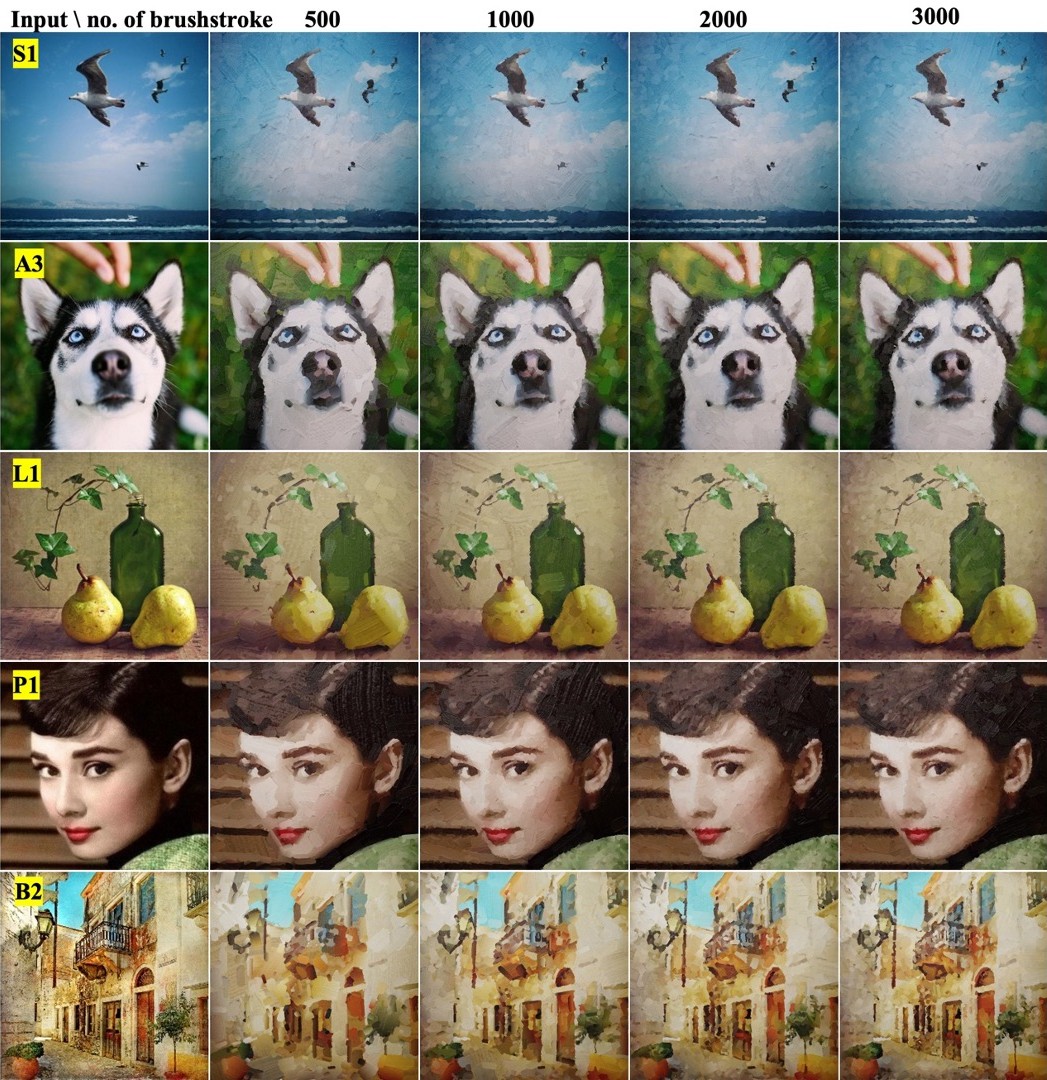

Oil painting styled texture generation with accompanied normal maps and stroke-based rendering
Existing techniques for generating oil-painting textures often lack realistic surface details and accurate shading, especially in 3D contexts. Addressing these deficiencies, this study proposes a stroke-based rendering (SBR) framework employing a dual-neural network to synthesize synchronized color and normal maps. The model was trained on 47 photometrically scanned brushstroke samples spanning ten brush types to capture authentic structural data. Unlike traditional color-only methods, our approach simulates physical surface reflections, ensuring consistent shading and enhanced textural realism when applied to 2D images or 3D models via Blender. This method effectively extends artistic stylization to complex 3D scenes, offering significant potential for digital art, gaming, and virtual reality applications requiring high-fidelity, stroke-based representations.
2025Y’ achievements
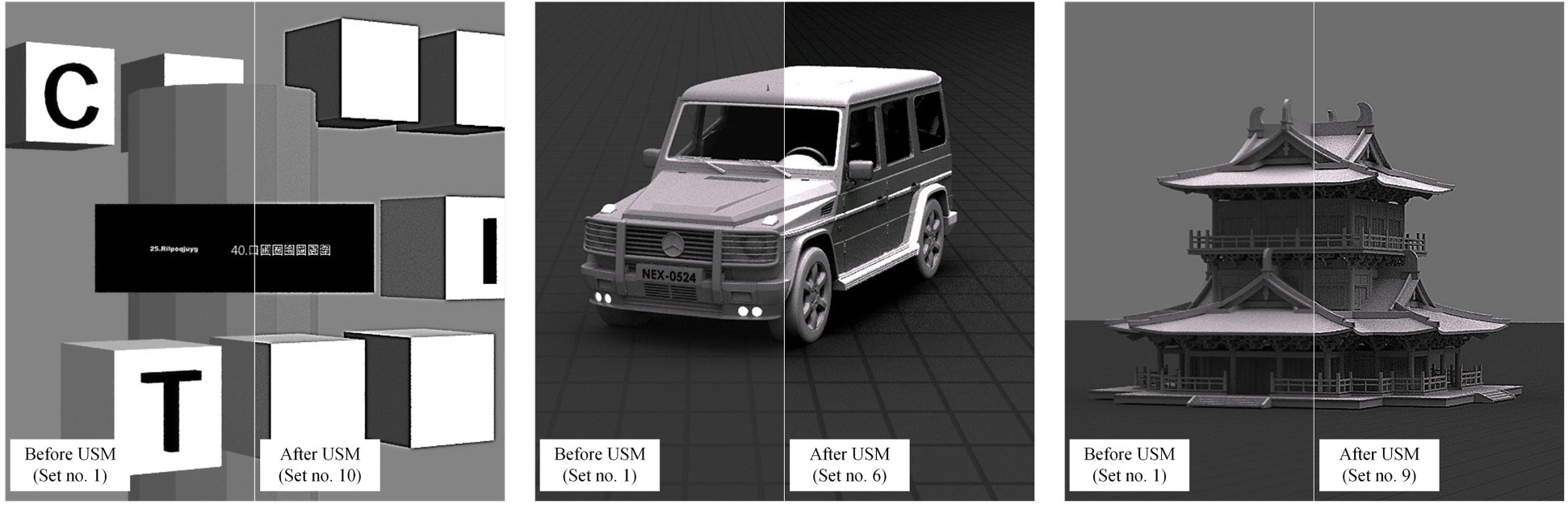


A psychophysical investigation of sharpness and visual perception in stereoscopic virtual reality headsets
With the increasing prevalence of stereoscopic virtual reality (VR) displays, image sharpness has emerged as a critical factor that influences user experience and visual comfort. Although unsharp masking (USM) is widely used for 2D image enhancement, its perceptual effects in stereoscopic VR environments remain underexplored. This study presents a psychophysical investigation, using both objective sharpness metrics and subjective user evaluations, of how different USM parameter settings affect visual perception in VR. A series of side-by-side stereoscopic images were processed using various USM parameters and presented on a VR head-mounted display. Thirty-three participants rated each image using five perceptual attributes: perceived sharpness, clarity, naturalness, preference, and depth perception. Modulation transfer function at 50% (MTF50) measurements were used to quantify image sharpness. The results show that MTF50 is highly correlated with perceived sharpness but negatively correlated with naturalness and preference, suggesting that over-sharpening may degrade image realism. Depth perception was most enhanced in low-frequency scenes, whereas clarity scores exhibited weak or no correlation with MTF50. These findings provide insights into the trade-offs of sharpness tuning in stereoscopic VR imaging and offer guidance for optimizing image-processing pipelines to balance perceived quality and viewer comfort in immersive applications.
T. L. Lu, C. H. Lin, L. C. Ou, and T. H. Lin, “Psychophysical investigation of sharpness and visual perception in stereoscopic virtual reality headsets,” Journal of Electronic Imaging, 34(6), pp. 063035, 2025
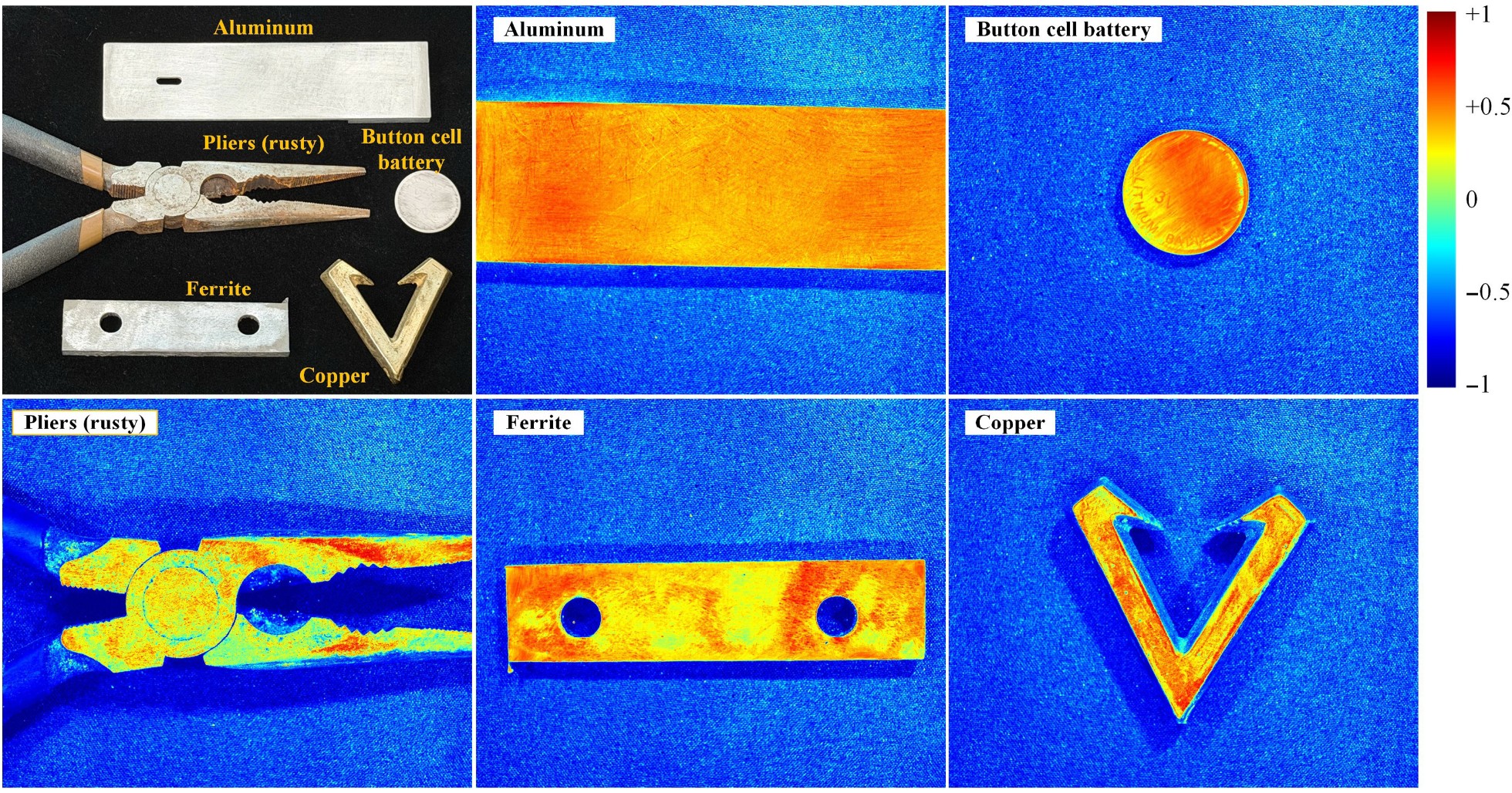

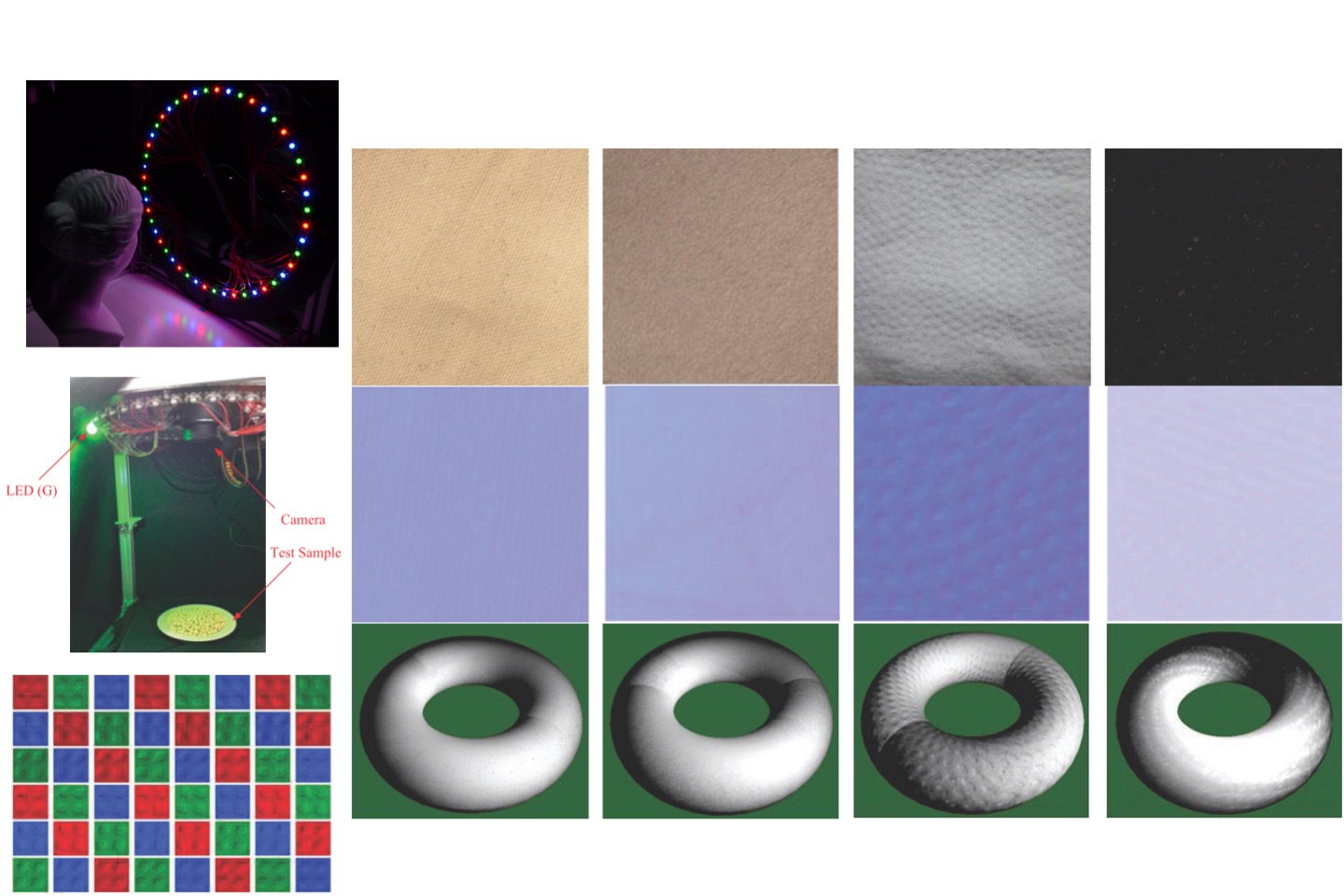
Distinguishing metallic and nonmetallic texturesthrough high-dynamic-range polarization imaging
Distinguishing between metals and nonmetals is critical in many industrial applications. However, distinguishing metallic from nonmetallic textures presents significantchallenges because of the inherent visual ambiguities and technical limitations ofimaging methods. The insufficient dynamic range inherent in imaging sensors limitstheir applicability unless high-dynamic-range (HDR) methodologies are employed.This study introduces an approach that leverages HDR polarization imaging todistinguish between metallic and nonmetallic textures. By employing a four-phasepolarization photography technique, we captured the unique polarization character-istics of light reflected from different material surfaces. Compared with nonmetallicsurfaces, metallic surfaces, dominated by specular reflection, exhibit distinct polari-zation patterns, which primarily demonstrate diffuse reflection. The proposed photography system followed the CIE 45/0 viewing geometry to process the polarizedimages acquired under different exposure values, thereby enabling effective clas-sification and differentiation between the two types of material. After comparing sixdifferent classifiers, this study adopted the cubic polynomial classifier to quantify theextent to which the captured polarization images resemble metallic or nonmetallictextures. Pretrained samples with different colors were effectively categorized intometallic and nonmetallic textures. These findings suggest a significant potential forapplications in industrial quality control and automated inspection systems.
T. H. Lin and S. H. Tsai, “Distinguishing metallic and non-metallic textures through high dynamic range polarization imaging,” Optical Engineering, 64(12), pp. 123102, 2025

Digitisation of impasto and gloss in oil paintings via spatially varying bidirectional reflectance distribution function acquisition
The growth of information technology and the Internet has increased the demand for online art exhibitions. As the digitisation of artworks often requires highly customised equipment and techniques, this study proposes a practical method for obtaining spatially varying bidirectional reflectance distribution function parameters for oil paintings with rich impasto and varying gloss. We combined the photometric stereo algorithm with a deep learning model, which was trained based on real oil painting samples. The proposed method surpasses current inverse rendering and pure deep learning methods that are limited to specific materials or synthetic data. Our system effectively reproduced the nonhomogeneous nature of oil paintings by capturing normal vectors, albedo, roughness, and specular intensity for each pixel. This approach provides a practical solution for digitising oil paintings, enabling the reproduction of impastos and glossy appearances in virtual environments.
C. Yang, and T. H. Lin*, “Digitisation of impasto and gloss in oil paintings via spatially varying bidirectional reflectance distribution function acquisition,” Computer Graphics Forum, 2025
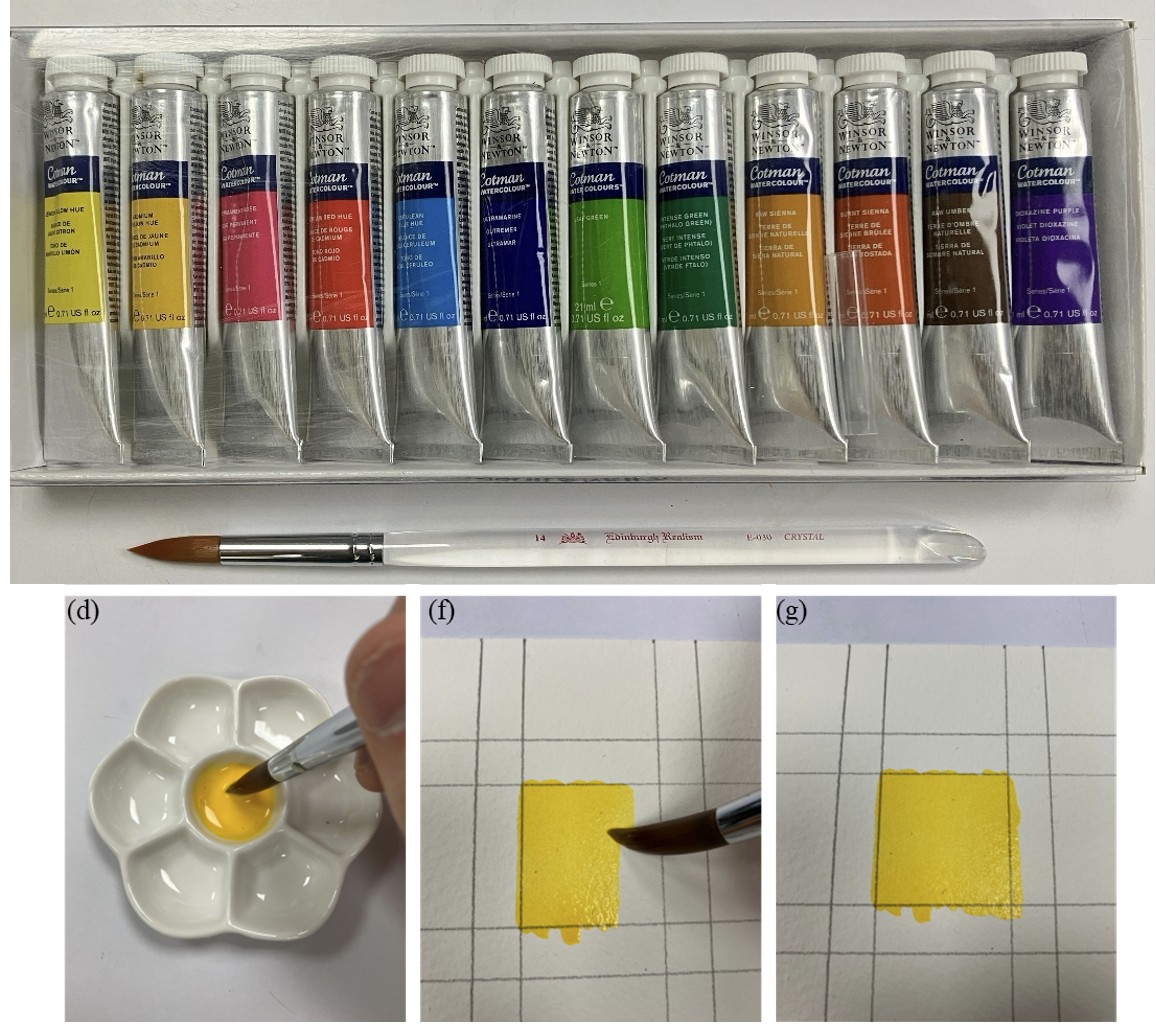

Prediction of watercolor mixing L*a*b* values based on Kolmogorov–Arnold networks
This study developed a watercolor mixing prediction model based on Kolmogorov–Arnold Networks (KANs) to assist beginners in mastering color blending. Using 12 Winsor & Newton Cotman pigments, 594 samples were measured with an EPSON SD-10 under D50/2° conditions, showing Lab* values stabilized two days after drying. Through ratio inversion, the dataset expanded to 1,188 samples. The KANs model (8-10-3) achieved an RMSE of 0.135, comparable to an MLP (0.16) but with a simpler architecture. Results demonstrate that KANs effectively learn nonlinear mixing rules with lower complexity, offering an efficient and educational tool for watercolor practice.
X. E. Sun, C. Y. Yuan, and T. H. Lin, “Prediction model of blended color for watercolor based on Kolmogorov–Arnold networks,” Association Internationale de la Couleur (AIC 2025) Taipei, 2025
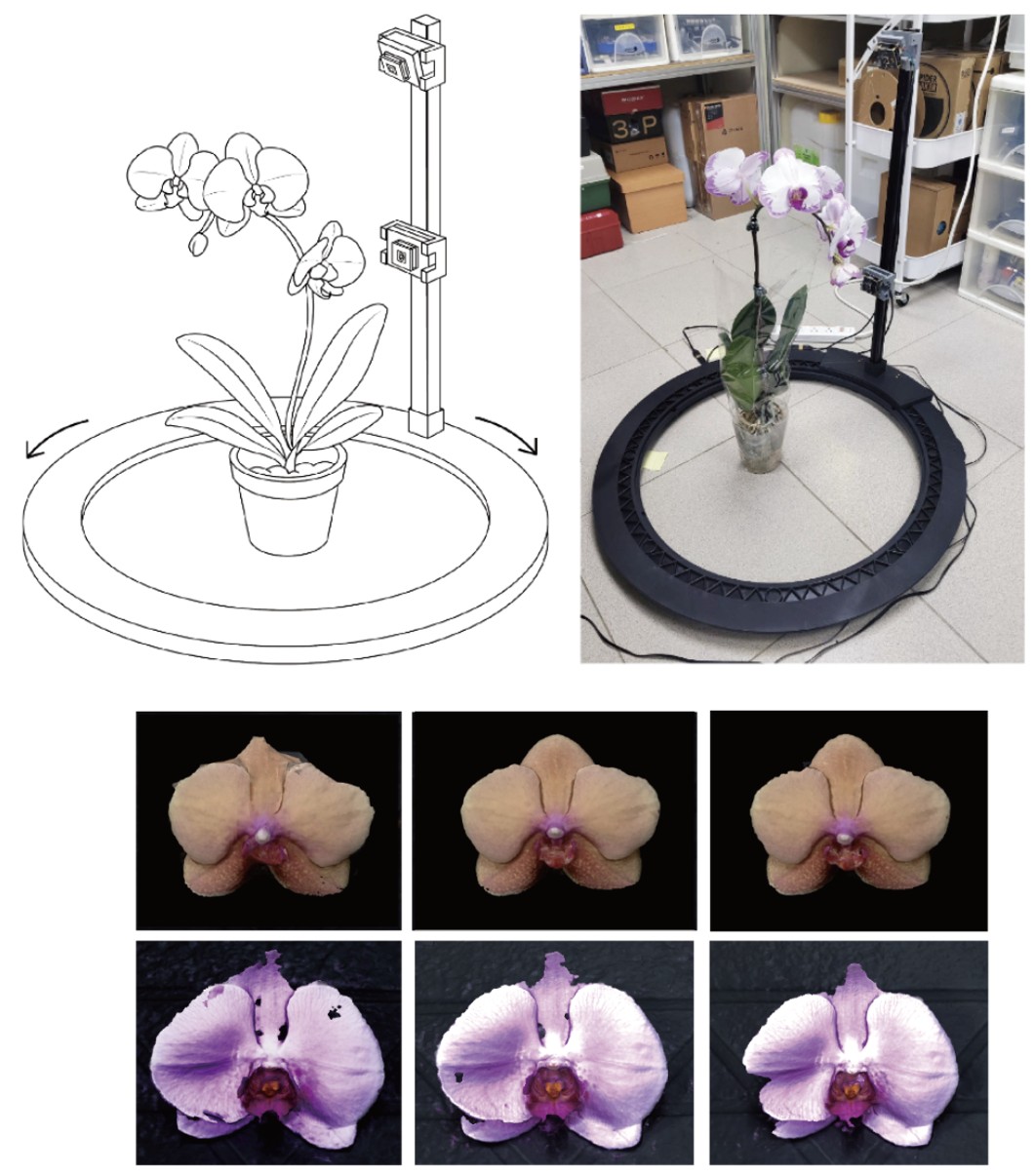

Study on 3D Digital Preservation of Orchids using Photogrammetry method
Taiwan leads globally in orchid cultivation, with phalaenopsis dominating exports. This study introduces a reproducible 360° photogrammetry workflow using an automated dual-camera orbit to capture 4K images of stationary blossoms. The effects of target size, petal texture, and image count on 3D reconstruction were evaluated. Images were acquired via a Python-OpenCV program and processed with Meshroom and Blender. Results show single blossoms yield near-continuous meshes, while whole-plant models are limited by occlusion. Patterned petals reconstruct best, followed by gradient and solid textures. Optimal image counts are about 30 for single flowers and 60 for full plants, as more frames add computation without extra detail. The study defines clear principles for geometry alignment, viewpoint diversity, and background simplicity to support orchid preservation and documentation.
T. H. Liu, C. Y. Yuan, C. P. Tsai, S. C. Chang, and T. H. Lin, “Study on 3D digital preservation of orchids using photogrammetry method,” Association Internationale de la Couleur (AIC 2025) Taipei, 2025
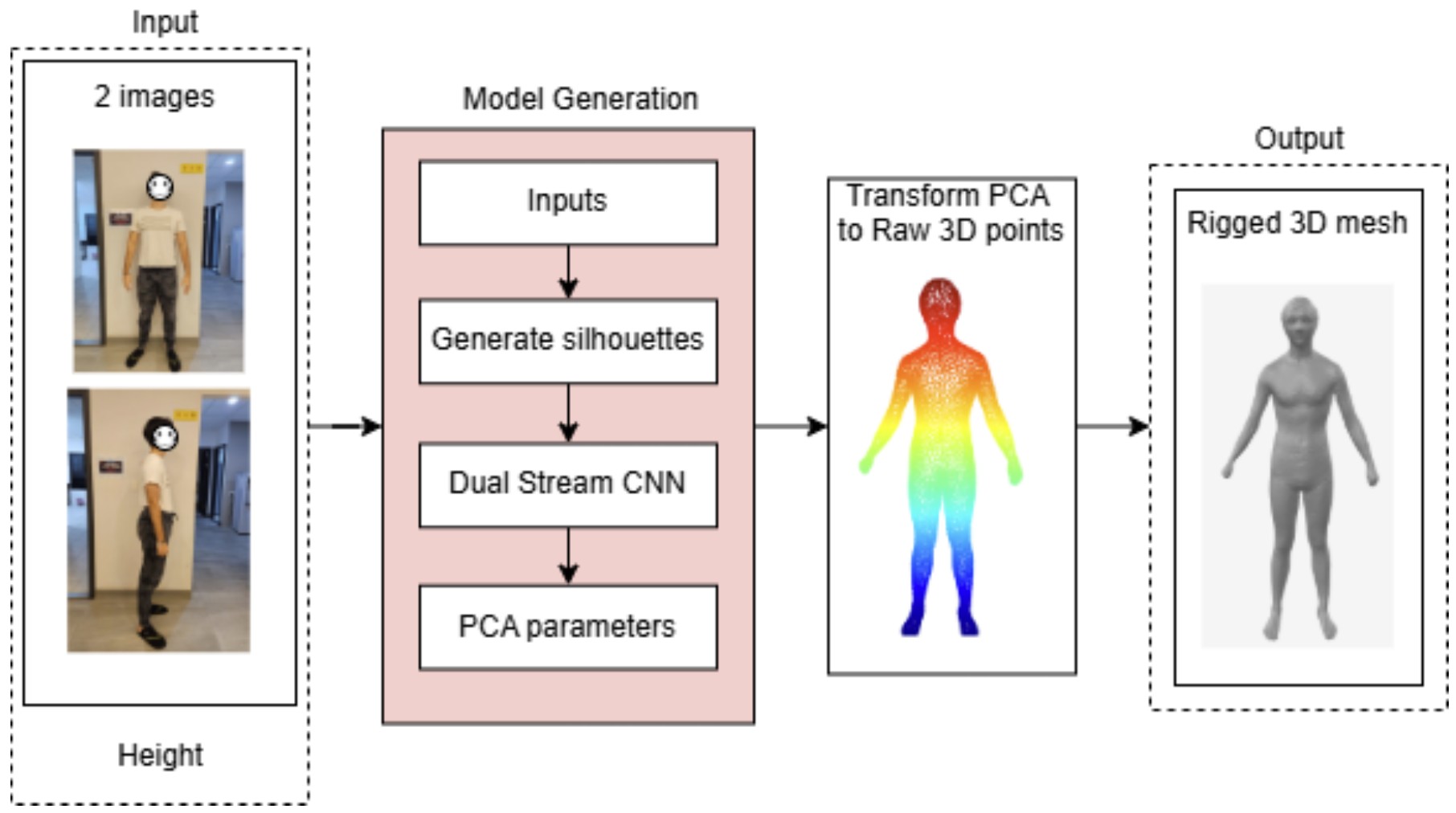

Automated 3D Human Shape Prediction from Two Photographs
This project presents a fully automated system for reconstructing 3D human body models fromtwo 2D photographs. The method extracts bodysilhouettes and predicts 3D shape parameters through aconvolutional regression model trained on PCA-based 3Dshape coefficients. The predicted parameters are used toreconstruct detailed 3D meshes. This approachdemonstrates an efficient and practical solution for2D-to-3D human body modeling with minimal input isachievable.
S. Benitez Leguizamon, G. A. Ayala Blanco, G. D. Benitez Gadea, C. P. Tsai, C. Y. Yuan, and T. H. Lin, “Automated 3D human shape prediction from two photographs,” International Conference on 3D Systems and Applications (3DSA), Taipei, Sept 2025.
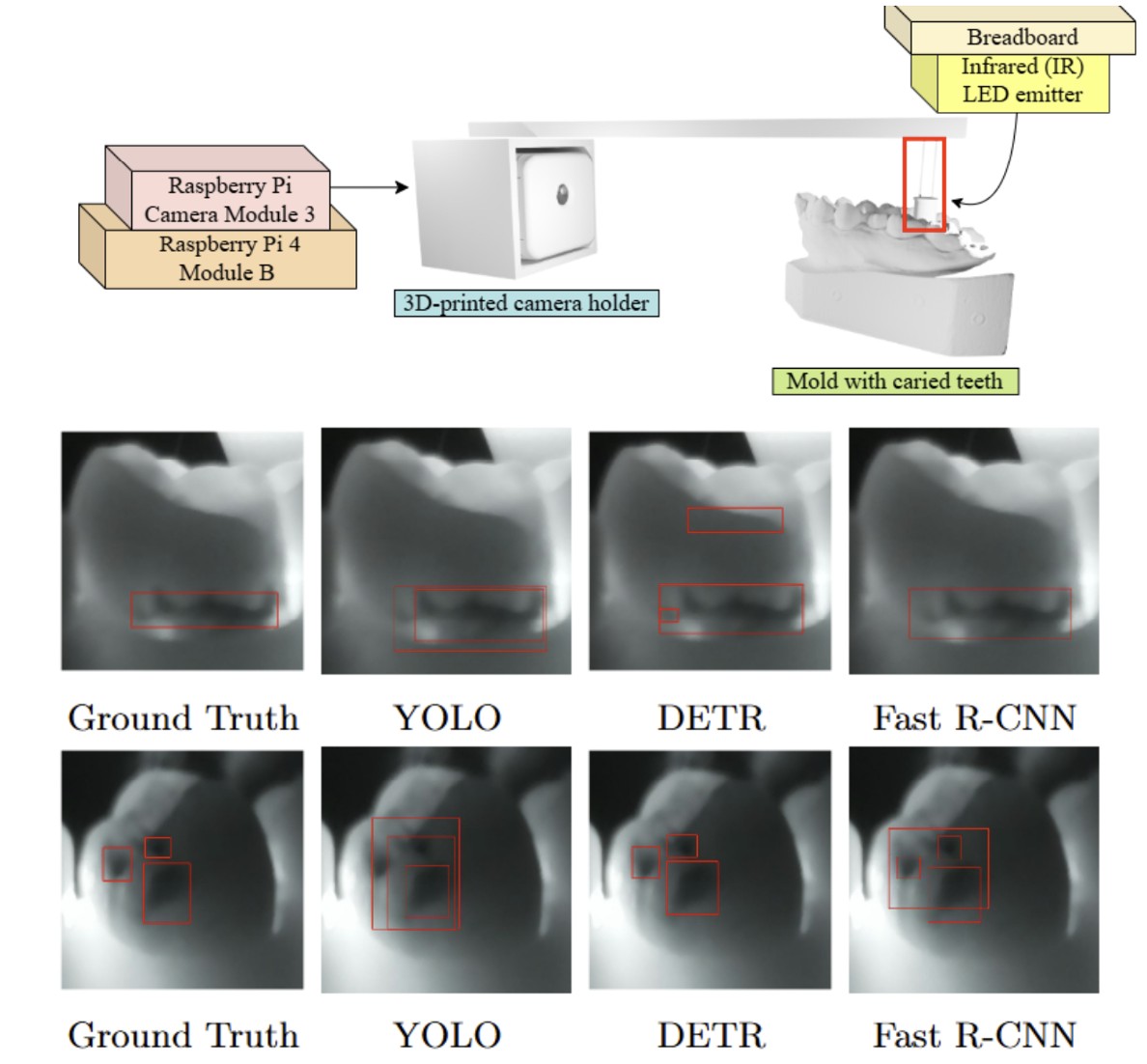

Deep learning based dental cavity detection using near infrared imaging
Dental caries remains one of the most widespreadoral health issues, with early and accurate detection beingcritical to prevent long-term damage. Traditional diagnosticmethods such as X-rays can be invasive, expensive, and limitedin identifying early-stage or subsurface decay. For these reasonscreate a need for non-invasive, efficient, and automateddetection solutions. This paper proposes a fully automatedpipeline for cavity detection using near-infrared (NIR) imagingand state-of-the-art deep learning models. NIR dental imageswere collected and manually annotated to create a task-specificdataset. Three object detection architectures—YOLOv8, DETR,and Faster R-CNN—were trained using transfer learning.Among them, Faster R-CNN achieved the best performance,reaching an mAP@0.5 of 0.742 on our test set. The resultsdemonstrate the potential of NIR imaging combined with deeplearning for dental diagnostics. This work highlights a promisingdirection for AI-driven oral healthcare solutions, especially insettings where access to radiographic equipment is limited.
D. Candia, E. N. Rojas Marcelli, M. Elizeche, M. Zaracho, S. C. Chang and T. H. Lin, “Deep learning based dental cavity detection using near infrared imaging,” International Conference on 3D Systems and Applications (3DSA)
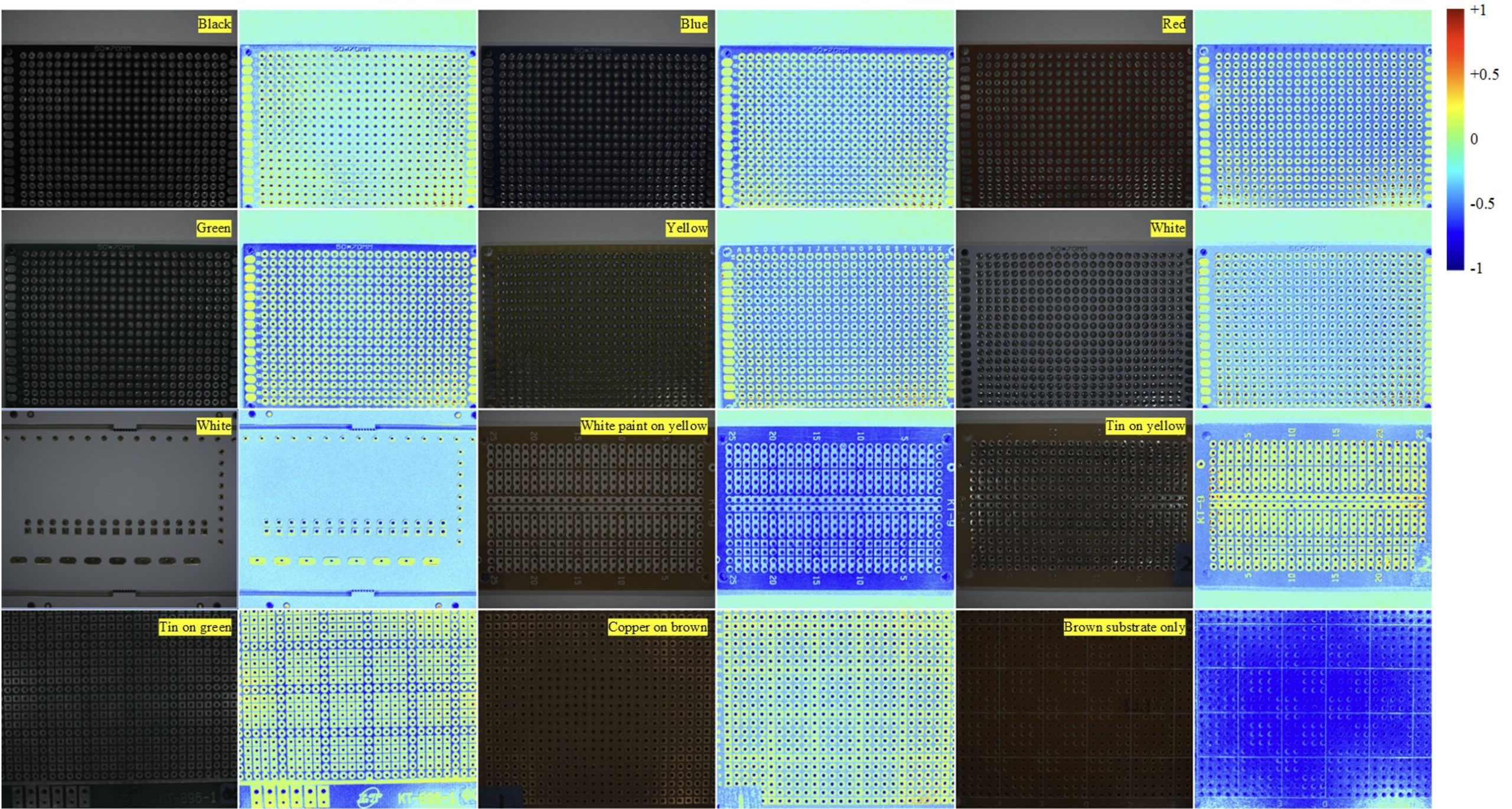

Distinguishing metallic and non-metallic textures through polarization imaging
This research introduces a novel method that leverages polarization imaging to distinguish between metallic and non-metallic textures. By employing a four-phase polarization photography technique, the approach captures the unique polarization characteristics of light reflected from different material surfaces. Metallic surfaces, dominated by specular reflection, exhibit distinct polarization patterns compared to non-metallic surfaces, which primarily exhibit diffuse reflection. The proposed system processes these polarization images to effectively classify and differentiate the two types of materials. Using polynomial classification, pretrained samples with different colors were effectively categorized into metallic and non-metallic textures.
T. H. Lin and S. H. Tsai, “Distinguishing metallic and non-metallic textures through polarization imaging,” SPIE Optics + Photonics 2025, San Diego, CA, Aug. 2025.
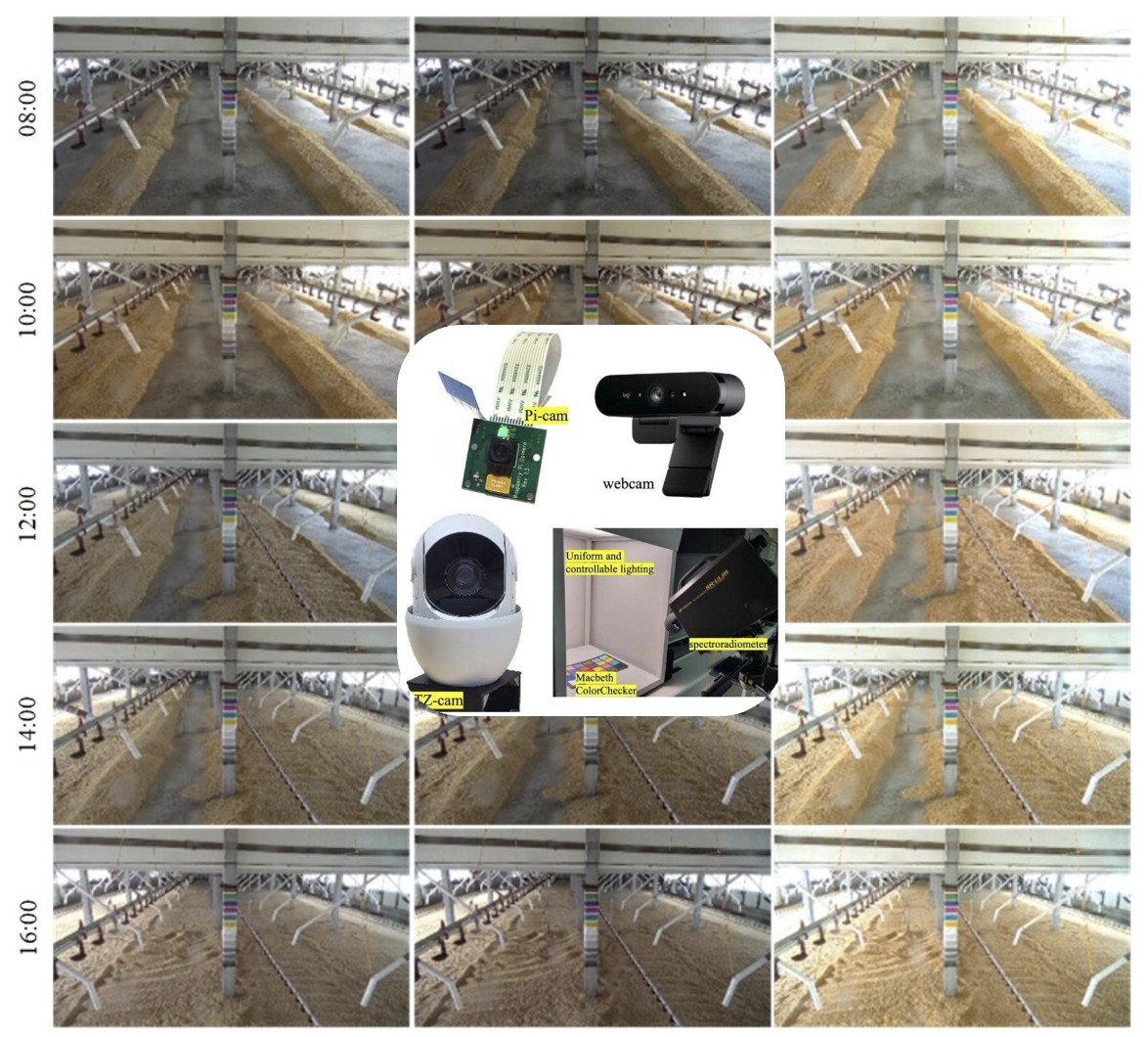


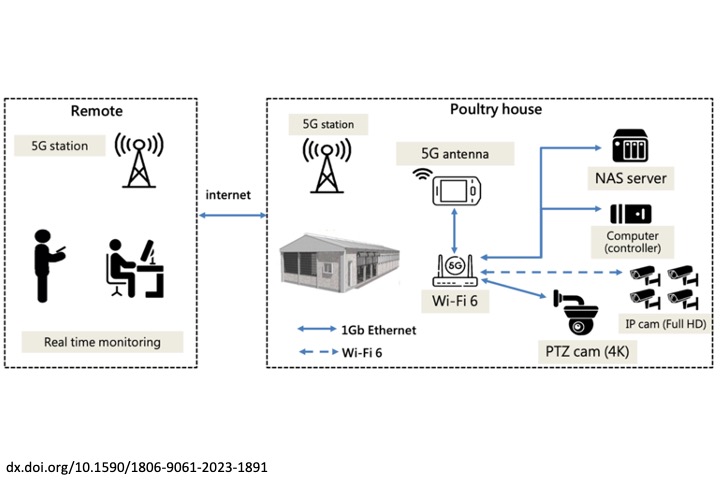
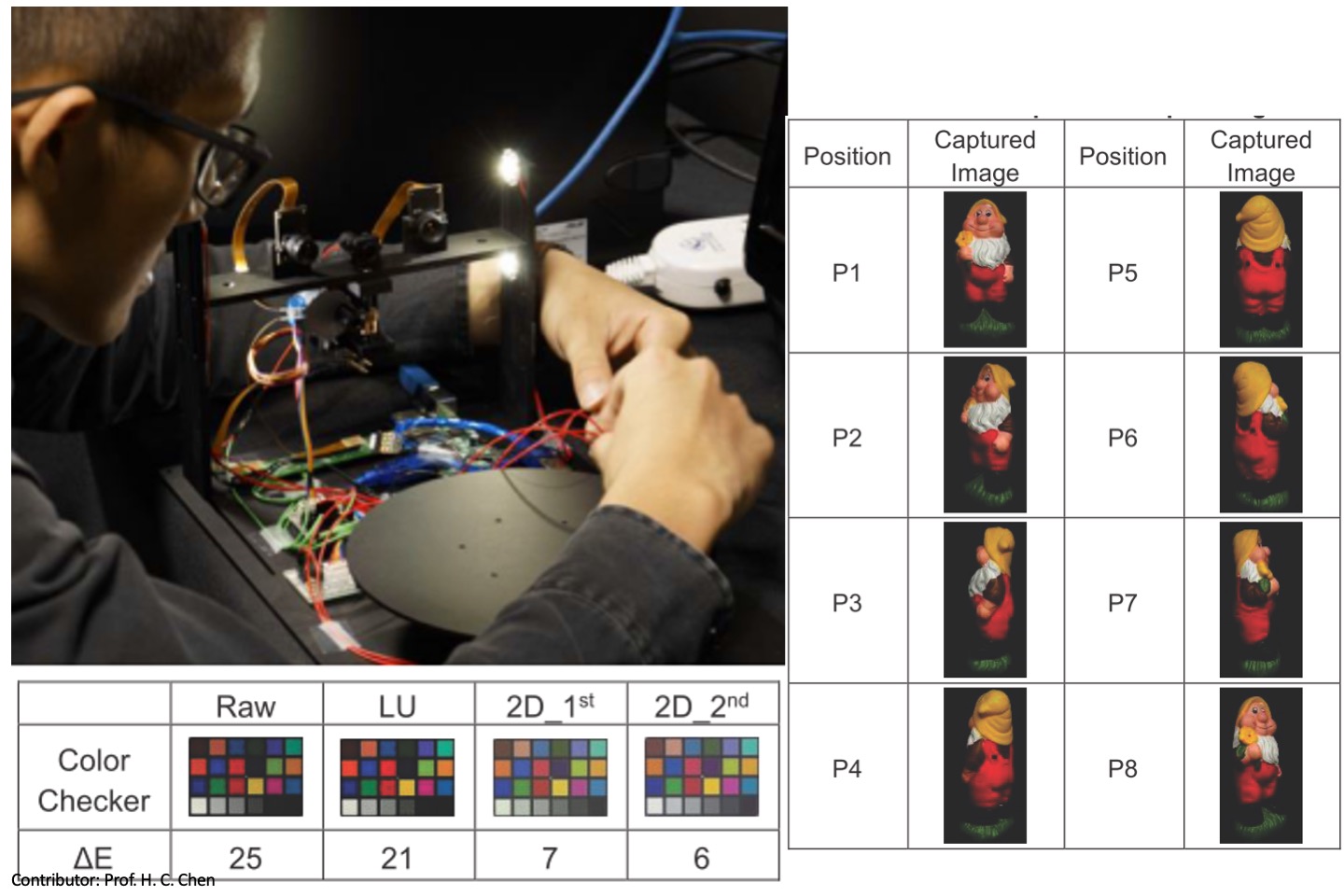
Evaluation of color performance of videoCameras for poultry house monitoring applications
This study examined the critical role of image color accuracy insurveillance systems, particularly in poultry houses, using affordablevideo cameras. Variations in commercial camera color processingcan lead to inconsistent metrics. Therefore, common cameras wereevaluated on the Raspberry Pi platform, aiming to minimize colordifferences through a three-stage correction process. The analysiswithout correction revealed significant color discrepancies, particularlyin the PI cameras using an automatic white balance, with differences ofapproximately 50. Gamma correction was applied to improve accuracy,thereby reducing the color differences to within 20 for most cameras.Polynomial regression further decreased the differences to less than10 across various temperatures, demonstrating superior performance,especially for large initial discrepancies. Field experiments with andwithout color charts confirmed the effectiveness of color restorationusing correction matrices. The study concluded that polynomialregression significantly enhances color accuracy on the Raspberry Piplatform, offering valuable applications across different temperaturesand scenarios, thereby contributing to advancements in related fields.
C. Y. Chou, and T. H. Lin*, “Evaluation of color performance of video cameras for the applications in monitoring poultry house,” Brazilian Journal of Poultry Science, 27(1), pp. 1-13, 2025
2024Y’ achievements


Optimization of 3D Stereoscopic Display Characteristics for Oil Painting Exhibition
This work presents an immersive 3D painting interaction framework that faithfully recreates thecomprehensive appearance of artworks, offering viewersan immersive art appreciation experience. We integratedphysically-based rendering (PBR), 3D display, and humandetection technologies to enable the viewers for exploringthe artwork’s nuances through dynamic rendering andinteractive exploration.
Y. F. Wu, C. Yang, A. J. Caballero, B. D. Bordón and T. H. Lin, “Optimization of 3D stereoscopic display characteristics for oil painting exhibition,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 24’), Dec. 4-6, 2024, Sapporo, Japan.


Composite autostereoscopic images based on multi-view photography system
This study aims at composition of autostereoscopicphoto-frames. The proposed multi-view photographysystem was utilized. The acquired images were rectifiedand superimposed in a virtual background, and thenconverted into the multipixel lenticular format.Subsequently, high-quality 3D photo-frames areproduced using UV curing inkjet printer to have lifelikethree-dimensional effects.
W. L. Chen, and T. H. Lin, “Composite autostereoscopic images based on multi-view photography system,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 24’), Dec. 4-6, 2024,
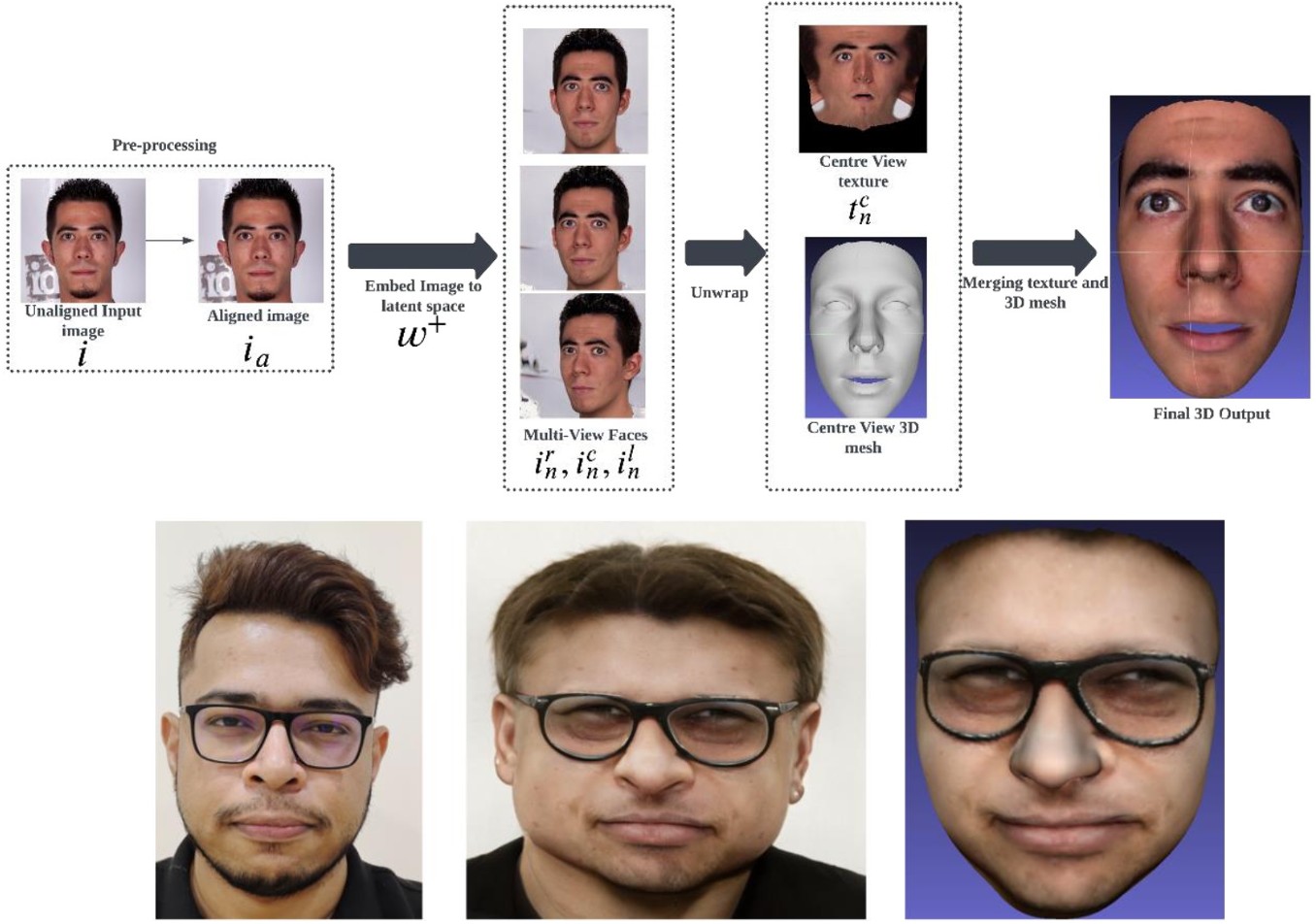

3D-GANTex: 3D face reconstruction with StyleGAN3-based multi-view images and 3DDFA based mesh generation
Geometry and texture estimation from a single face image is an ill-posed problem since there is very little information to work with. The problem further escalates when the face is rotated at a different angle. This paper tries to tackle this problem by introducing a novel method for texture estimation from a single image by first using StyleGAN and 3D Morphable Models. The method begins by generating multi-view faces using the latent space of GAN. Then 3DDFA trained on 3DMM estimates a 3D face mesh as well as a high-resolution texture map that is consistent with the estimated face shape. The result shows that the generated mesh is of high quality with near to accurate texture representation.
R. Das, T. H. Lin and K. C. Wang, “3D-GANTex: 3D Face Reconstruction with StyleGAN3-based Multi-View Images and 3DDFA based Mesh Generation”, arXiv pre-print, Oct. 2024.
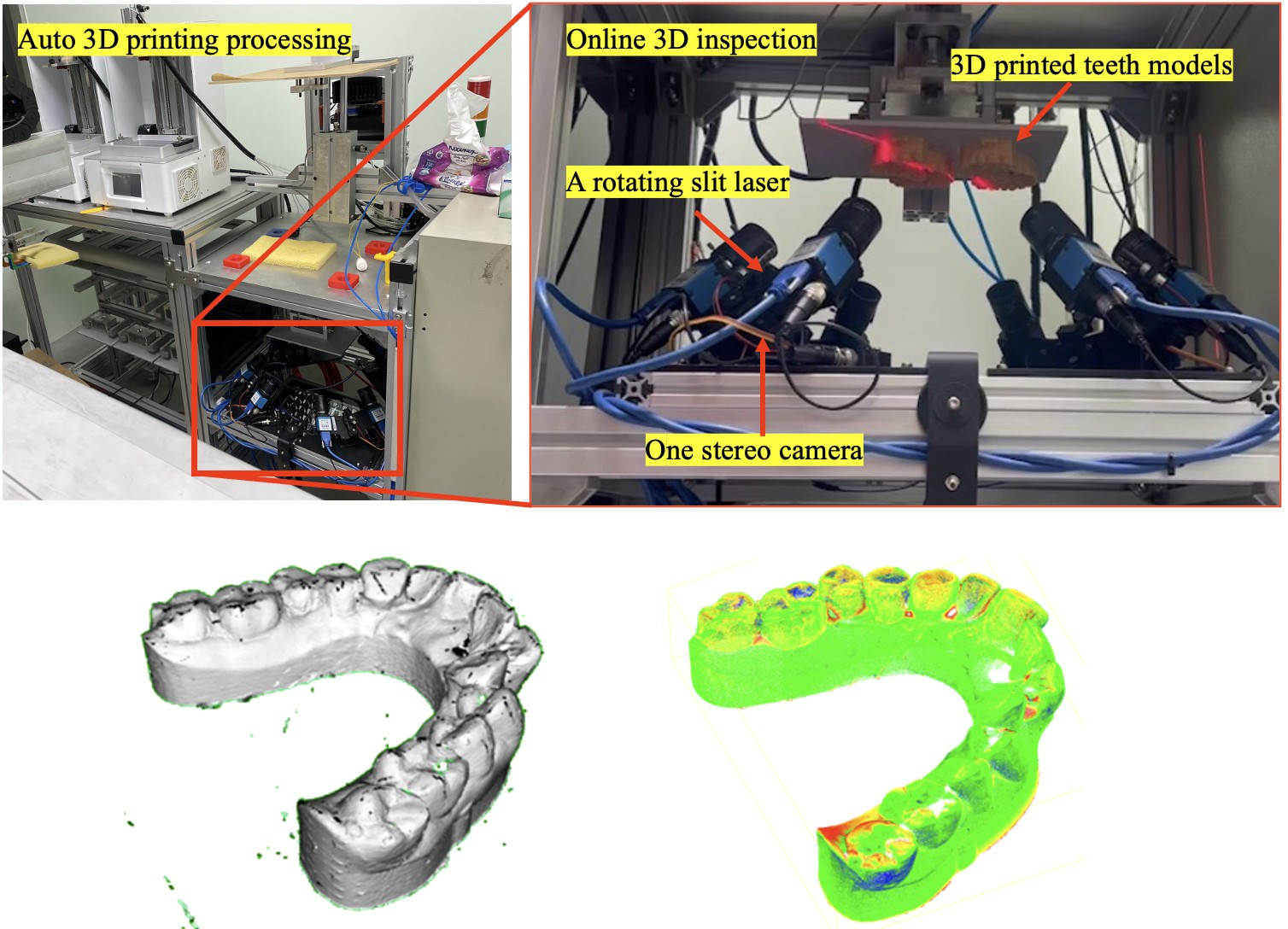

A 3D shape measurement system based on multiple stereo camera arrays
This paper presents an online 3D shape measurement system based on multiple stereo camera arrays which can capture high-quality 3D models. This system is designed by default for online 3D teeth models which are manufactured by photo-curing 3D printing machines. The proposed system integrates eight industrial machine vision cameras whose resolution are1440x1080 pixels. Every two cameras, which are fabricated as a converge type stereo camera, were synchronized to capture the cast stripes on a printed teeth model for immediately verifying the correctness of 3D dimension after the 3D printing process.
T. H. Lin, and S. Y. Lee, “A 3D shape measurement system based on multiple stereo camera arrays,” The 2nd Annual Meeting and conference of Association of Computational Mechanics Taiwan 2024 (ACMT 2024), Oct. 5-6, 2024
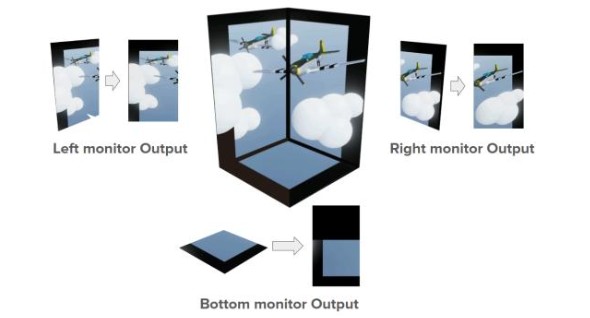

3D immersive display using warped videos
In this paper, we developed a unique 3D display system consisting of three monitors with a resolution of 1920×1080. The screens are supported and connected via an adjustable arm, facilitating optimal positioning tailored to user preferences. The configuration comprises a horizontally oriented base screen, flanked by two vertically aligned screens. This arrangement forms a dynamic stage for rendering 3D contents. The trio of screens is interfaced with a computer equipped with a high-performance graphics card and designed to manage the visual output efficiently across the different screens.
S. R. Mersch Fernandez, K. E. Da Rosa Franco, S. Santacruz Viñales, and T. H. Lin, “3D Immersive Display using warped videos”, International Meeting on Information Display, Aug. 20-23, 2024, Jeju, Korea.
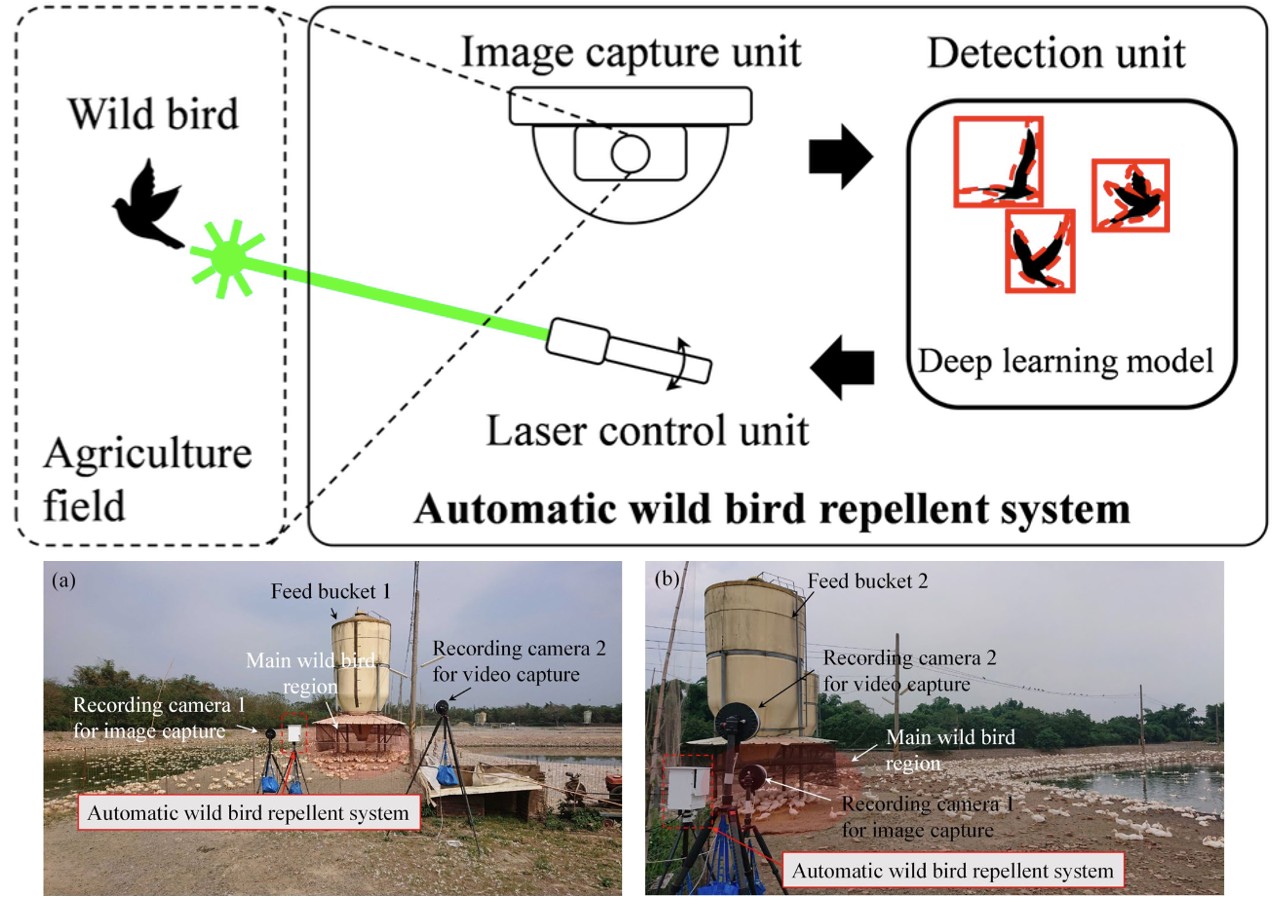

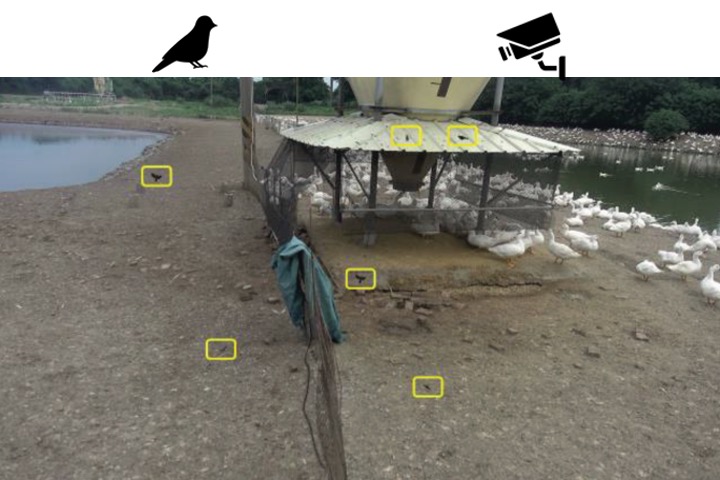
Automatic wild bird repellent system that is based on deep-learning-based wild bird detection and integrated with a laser rotation mechanism
Wild bird repulsion is critical in agriculture because it helps avoid agricultural food losses and mitigates the risk of avian influenza. Wild birds transmit avian influenza in poultry farms and thus cause large economic losses. In this study, we developed an automatic wild bird repellent system that is based on deep-learning-based wild bird detection and integrated with a laser rotation mechanism. When a wild bird appears at a farm, the proposed system detects the bird’s position in an image captured by its detection unit and then uses a laser beam to repel the bird. The wild bird detection model of the proposed system was optimized for detecting small pixel targets, and trained through a deep learning method by using wild bird images captured at different farms. Various wild bird repulsion experiments were conducted using the proposed system at an outdoor duck farm in Yunlin, Taiwan. The statistical test results of our experimental data indicated that the proposed automatic wild bird repellent system effectively reduced the number of wild birds in the farm. The experimental results indicated that the developed system effectively repelled wild birds, with a high repulsion rate of 40.3% each day.
Y. C. Chen, J. F. Chu, K. W. Hsieh, T. H. Lin, P. Z. Chang, and Y. C. Tsai, “Automatic wild bird repellent system that is based on deep-learning-based wild bird detection and integrated with a laser rotation mechanism,” Scientific Reports, 14, 15924, 2024.
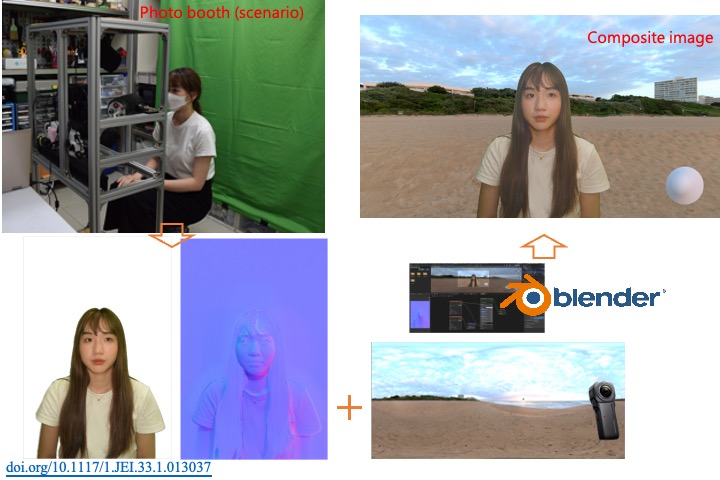


Subjective assessment for inverse rendered composite images in 360-degree images
Due to the rise of social media, synthesized or composited photos are getting increasingly widespread. Among them, image relighting is one of the crucial technologies, which is capable to create convincingly realistic images. This study proposes a framework for relighting a portrait subject when superimposing them onto a 360-degree image. In most image compositions, it is difficult to acquire the 3D shapes of subjects directly to re-render them in a virtual environment. In this study, a well-diffused color portrait image with a corresponding normal map is generated from our photo booth using a photometric method. In addition, a virtual environment based on a principled bidirectional scattering distribution shader and environmental 360-degree texture in the Blender software is utilized to create composite images. After considering different situations, including gender, postures, indoor or outdoor scenes, and color or color-free subjects, each of 128 composite images was played as a 4-second video clip, and various scenarios were conducted for subjective assessment. From the evaluation scores of the 30 participants, the overall satisfaction with the image composition based on the proposed framework was above average (5-point Likert scale > 3 points) and the color-free subject in the 360-degree image was significantly preferred.
Y. J. Chang, and T. H. Lin, “Subjective assessment for inverse rendered composite images in 360-degree images,” Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2024.

Comb Color Analysis of Broilers Through the Video Surveillance System of a Poultry House
Livestock and poultry production are critical agricultural industries. Intelligence in the poultry industry has received increasing attention in recent years. An intelligent monitoring system was implemented to manage the poultry house and improve its feeding conditions. Experts can remotely diagnose the health of chickens using a monitor screen. An intelligent video surveillance system was used in this study to evaluate the physical appearance of broilers in a poultry house. Comb color was studied during the long chicken growth phase, and color changes were statistically analyzed. The video surveillance system includes meticulously color-calibrated cameras with an additional YOLOv4 algorithm for comb detection and color recovery. The image data was stored for up to 90 days and then analyzed to understand comb color behavior during growth. This study develops a technique for automatically extracting comb colors that can assist professionals in making color-related broiler health diagnoses in the future.
T. Y. Wei, and T. H. Lin*, “Comb color analysis of broilers through the video surveillance system in a poultry house,” Brazilian Journal of Poultry Science, 26(1), pp.1-8, 2024.
https://www.scielo.br/j/rbca/a/bPhtvW6c8SLYtNZCXFJRkwH/?format=pdf&lang=en
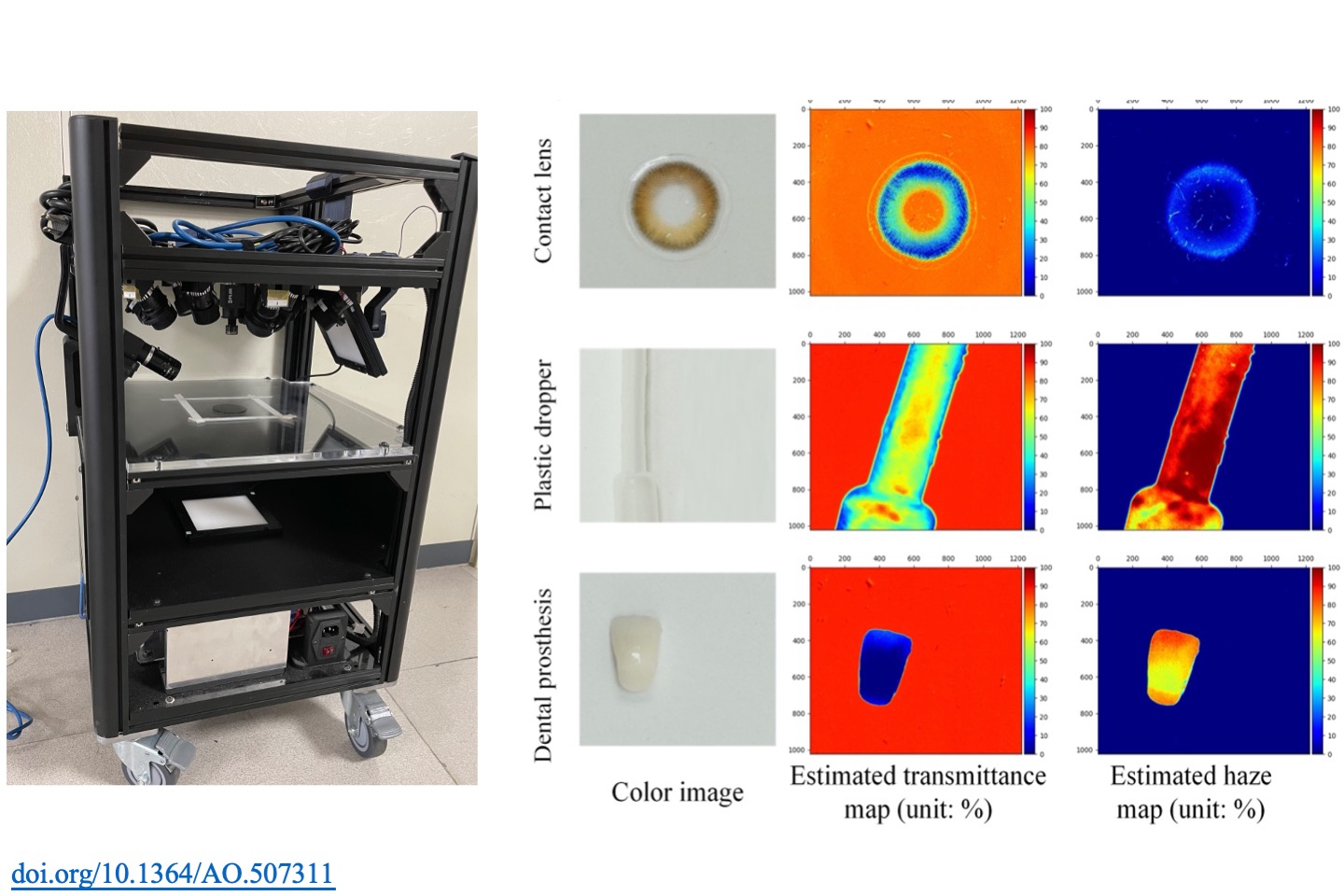

Translucency measurement system based on a polarized camera
This paper proposes a measurement system capable of estimating the transmittance and haze values of a composite object. The system, comprising a polarized camera, a linear polarizer, and backlight, was calibrated to obtain four phase polarization images. Forty-one samples, which covered a wide range of transmittance and haze values, were manufactured to assist in correlating the polarization images and the referenced ground truth from the BKY-Gardner instrument. After the data regression, two linear equations were selected to estimate the transmittance and haze values of transparent objects. The verification experiment for 52 samples demonstrated that the proposed method accurately estimated the transmittance of the samples with a coefficient of determination (R²) as high as 0.96 and an average error of less than 4.1%. The haze estimation had an R² of 0.94 and an average error of 5.08%. Pseudo color maps were used to present the different transmittance and haze values of a single object. The proposed system can perform image-based translucency measurements and obtain individual values of a composite object.
P. Y. Lai, and T. H. Lin*, “Translucency measurement based on image data regression from a polarized camera,” Applied Optics, 63(4), pp. 1170-1181, 2024.
2023Y’ achievements
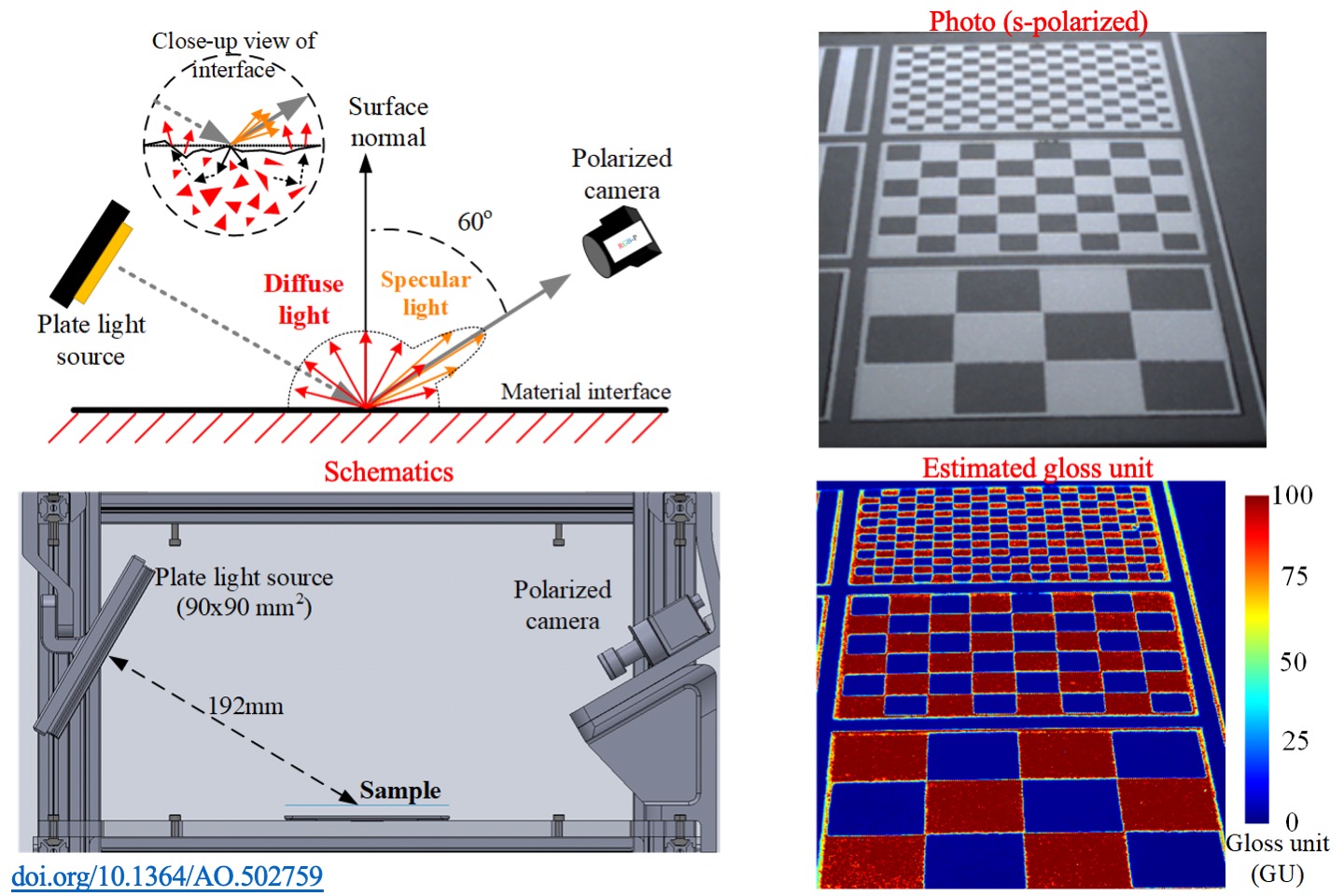

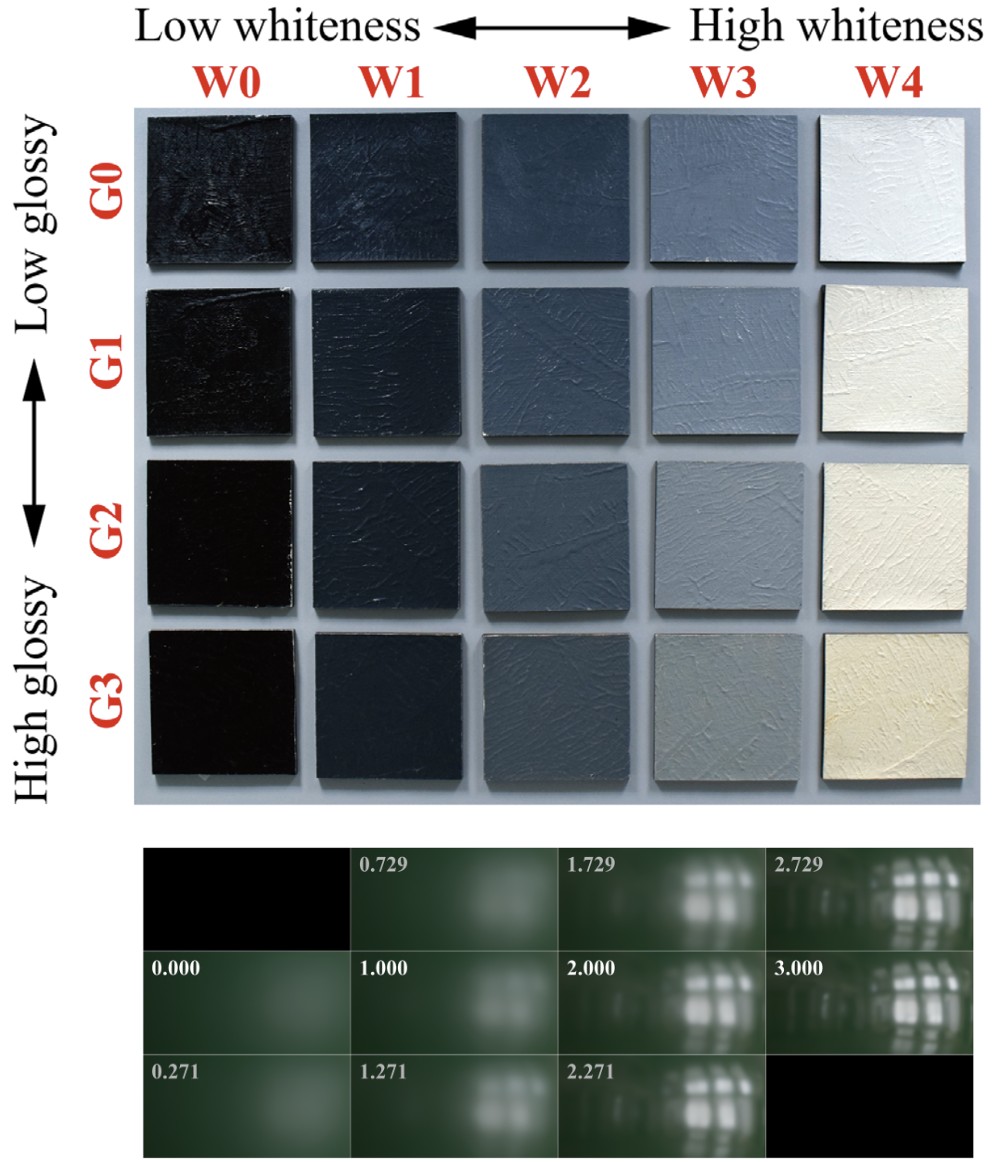
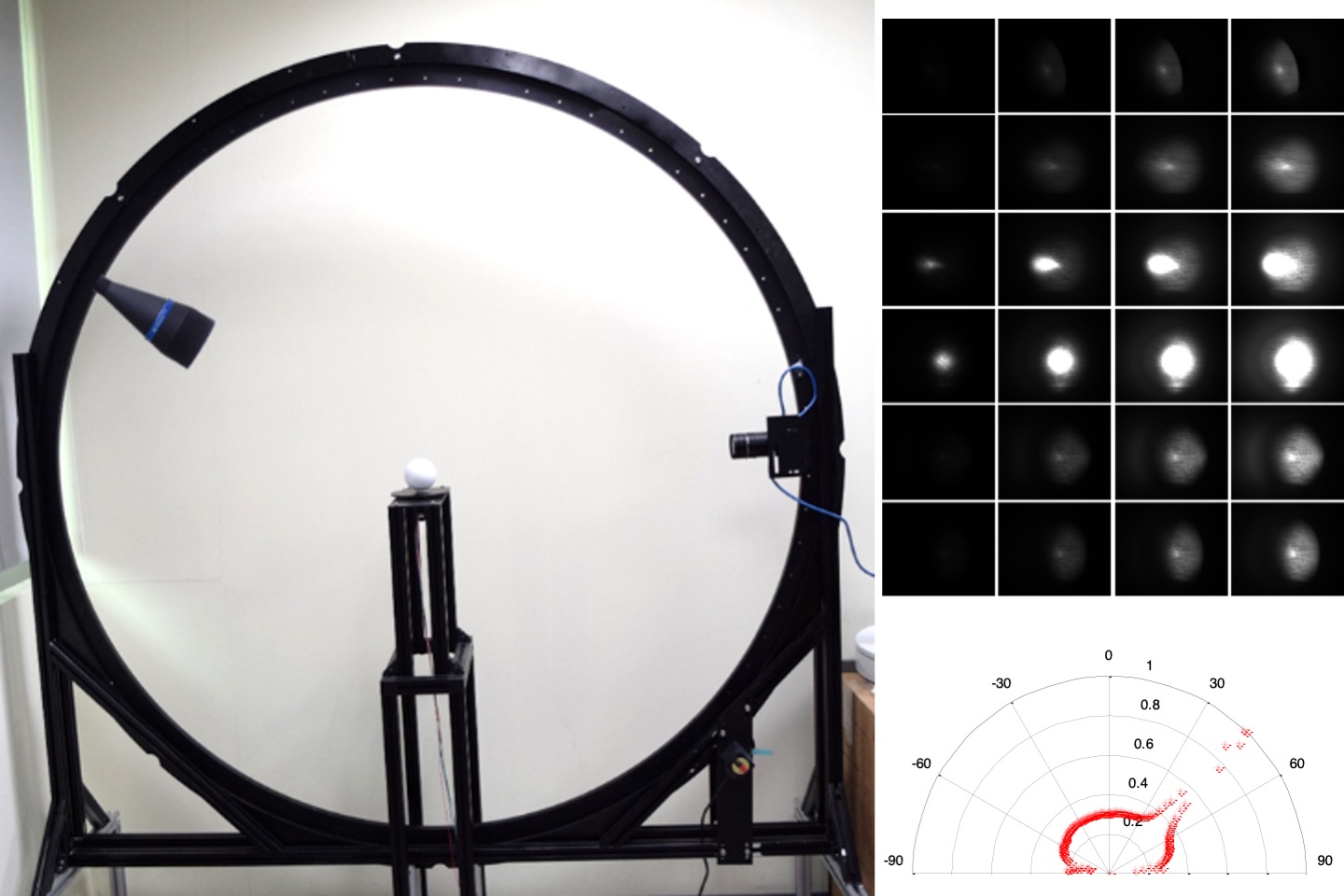
Spatial variant gloss measurement of dielectric material based on a polarized camera
This study proposes an imaging method for gloss measurement solely by a single shot from a polarized camera. The system, comprising a polarized camera and well-diffused LED plate light, inspired by the framework of ASTM D523, and it acquires images at 60° incident direction. The polarization characteristics of dielectric material samples were analyzed. A regression model was developed by using NCS gloss scale and commercial gloss meter. Subsequently, the gloss and spatial resolutions of this method were verified using various types of measurement samples. From experiments regarding different benchmarks, we concluded that the proposed method performs sufficiently for spatial variant gloss measurement.
T. L. Lu, and T. H. Lin*, “Spatial variant gloss measurement of dielectric material based on a polarized camera,” Applied Optics, 62(32), pp. 8686-8695, 2023.
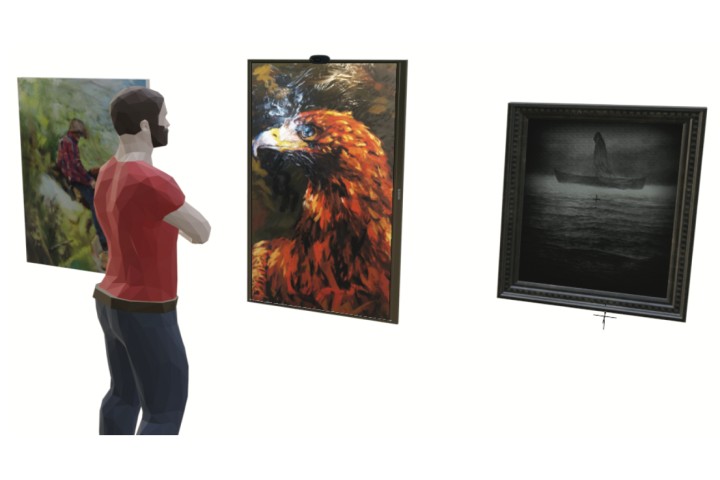


Gesture-Controlled Digital Frame for Art Showcasing with Dynamic Lighting
This paper presents the implementation and evaluation of a 3D representation of digital oil paintings, building upon the foundation of previous work. This digital frame provides an alternative and immersing method for showcasing art and interacting with it. With a camera module in a virtual environment of blender software, it can both capture the viewer’s position relative to the frame to dynamically adjust the painting’s lighting condition and recognize hand gestures to access a different variety of digital paintings.
A. José Caballero, B. D. Bordon Diaz and T. H. Lin, “Gesture-Controlled Digital Frame for Art Showcasing with Dynamic Lighting”, Automation 2023, Dec. 8-10, 2023, Taipei, Taiwan.
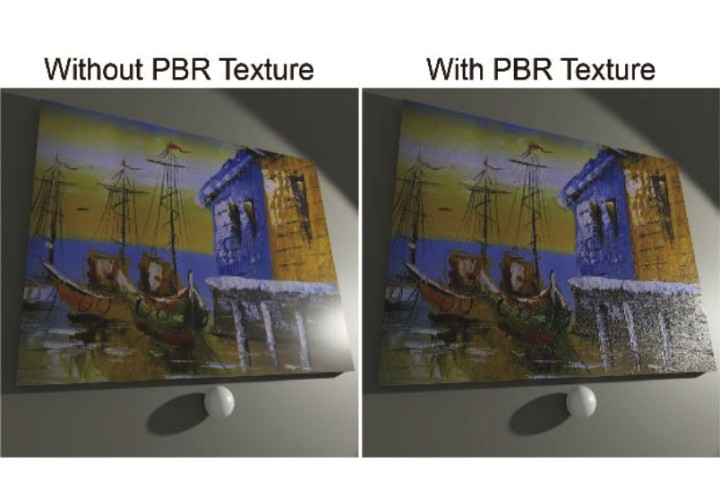


Digitalization of oil paintings: leveraging PBR textures to reproduction of realistic appearance
his research proposes a method to digitize oil painting by capturing PBR textures such as albedo, normal, and height map_x0000_. Unlike traditional methods that focuses on only color and resolution, this study can reproduce the realistic appearance under different viewing angles and lighting conditions in _x0000_ virtual 3D world.
C. Yang, Y. H. Lee, and T. H. Lin, “Digitalization of oil paintings: leveraging PBR textures to reproduction of realistic appearance,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 23’), Dec. 6-8, 2023, Niigata, Japan.
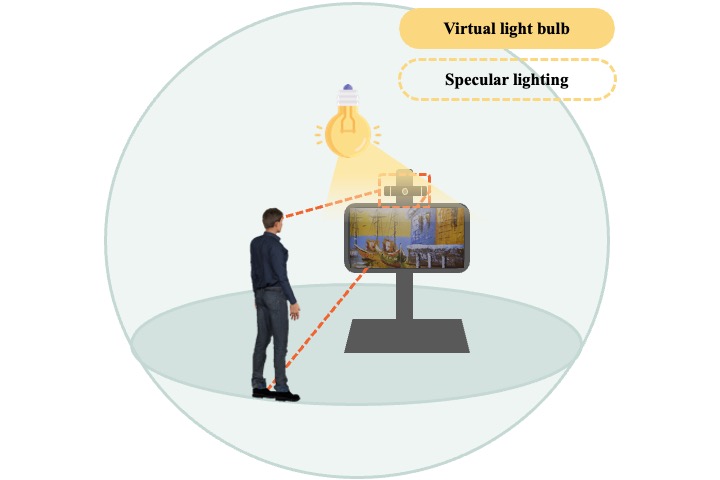

Interactive relit realistic paintings on a digital frame
An innovative 3D interactive digital framework was proposed. We rendered oil-paintings with PBR textures on anti-reflective screens to reproduce realistic lighting effects. After detecting the viewer’s position, the content and re-rendered dynamically to fit the scenario which emphasizes texture details, brushstrokes and colors of artworks due to lighting directions.
Y. H. Lee, C. Yang, and T. H. Lin, “Interactive relit realistic paintings on a digital frame,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 23’), Dec. 6-8, 2023, Niigata, Japan.
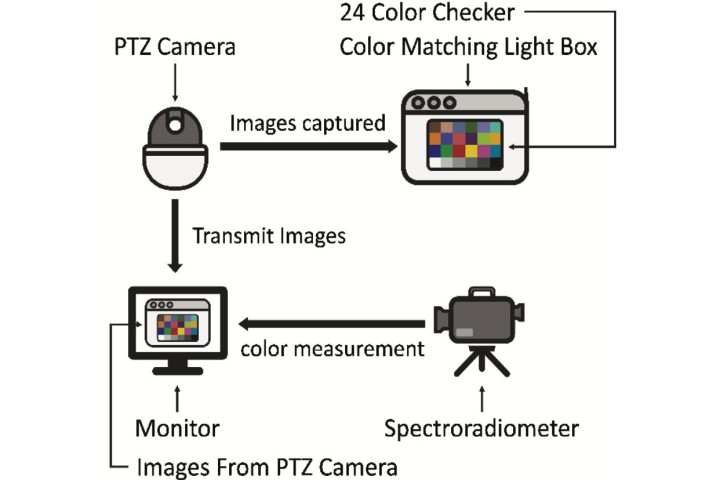

Color difference evaluation for transmitted images of surveillance cameras
Surveillance cameras equipping the pan-tilt-zoom (PTZ) feature are widely utilized in various domains due to their versatile functionalities. However, the measured colors of environment from cameras may differ during transmission. By conducting experiments, this study aims to examine these differences, offering valuable insights into color management within surveillance camera applications.
C. Y. Chou, and T. H. Lin, “Color difference evaluation for transmitted images of surveillance cameras,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 23’), Dec. 6-8, 2023 Niigata, Japan.
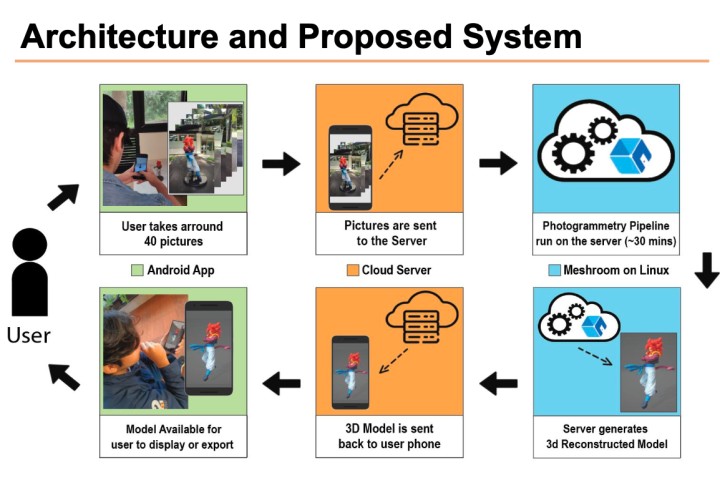

Development of a 3D reconstruction service system by using opensource for smartphone users
This paper aims to create a system with a cloud server that facilitates the generation of 3D objects using smartphone cameras, empowering inexperienced users to create personalized 3D models. The backbone technology is a computer vision technique called “photogrammetry”, which infers geometric characteristics from the collection of photographs or videos.
M. Grijalba Acosta, D. E. M. Krauch Bareiro, J. S. González Arrosse, and T. H. Lin, “Development of a 3D reconstruction service system by using opensource for smartphone users,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 23’), Dec. 6-8, 2023 Niigata, Japan.
2022Y’ achievements
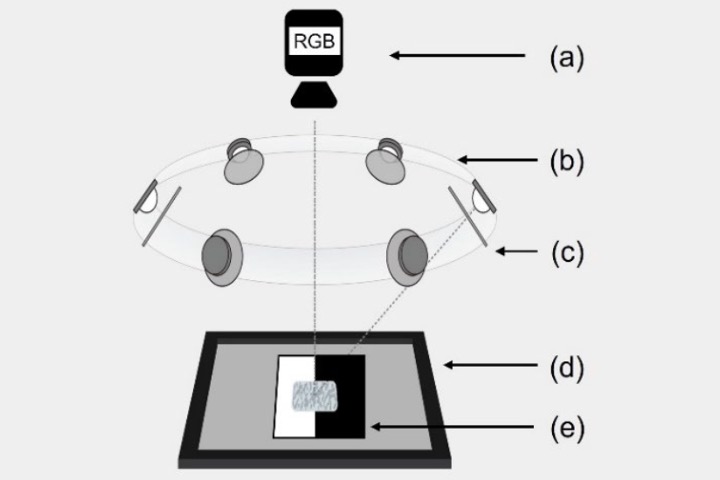

Image Based Objects’ Transparency measurement by a polarization camera
In this paper, we propose an image-based method to quantify the transparency of objects based on a polarization camera. By controlling the status of the backlight, we can obtain the light intensity of penetration in four different phases, and can observe the difference to quantify the haze and transmittance. It is worth mentioning that our method can measure objects’ transparency as small as a pixel, and it benefits to quantify the transparency of compound as well mixed materials.
P. Y. Lai and T. H. Lin “Image Based Objects’ Transparency measurement by a polarization camera,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 22’), Dec. 14-16, 2022 Fukuoka, Japan.
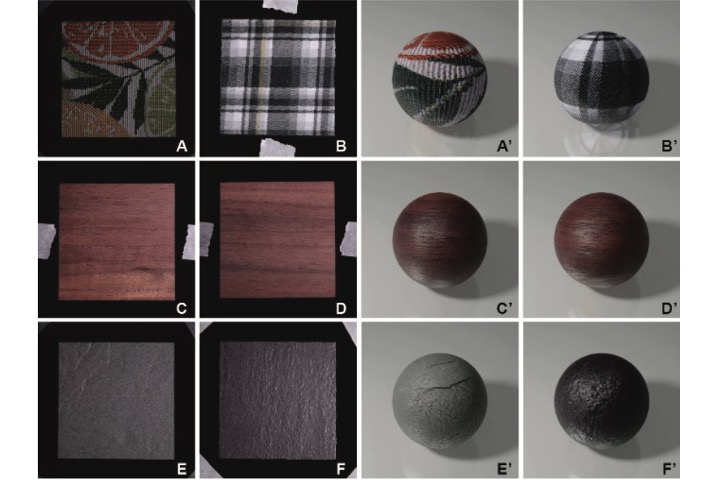


PBR textures capture by CNN trained in virtual 3D scene
This study proposes a PBR (physically based rendering) texture capturing system using CNN (convolutional neural network). To obtain training data, we built a virtual capturing system in computer graphics environment. The final trained CNN was able to generate a set of PBR texture after inputting 4 photos of different lighting conditions.
C. Yang and T. H. Lin “PBR textures capture by CNN trained in virtual 3D scene,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 22’), Dec. 14-16, 2022 Fukuoka, Japan.
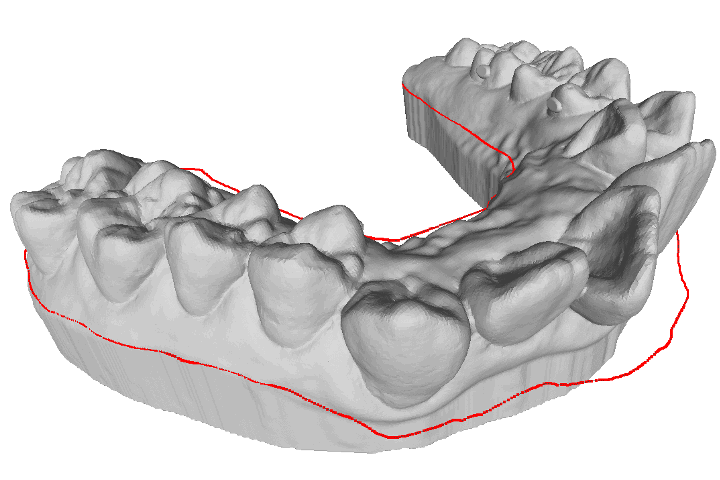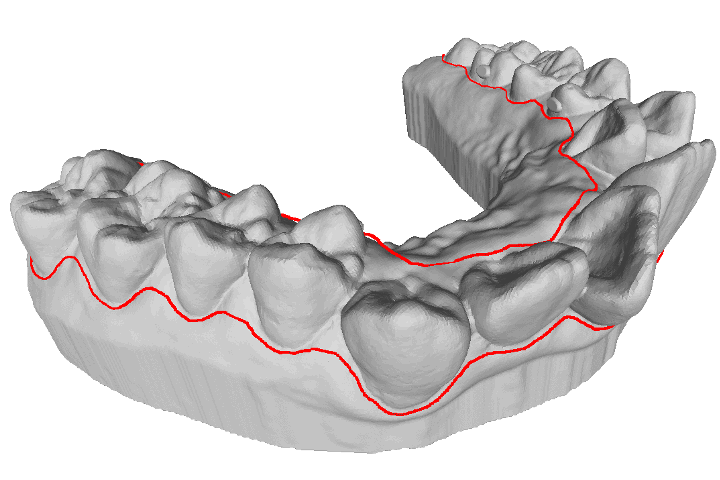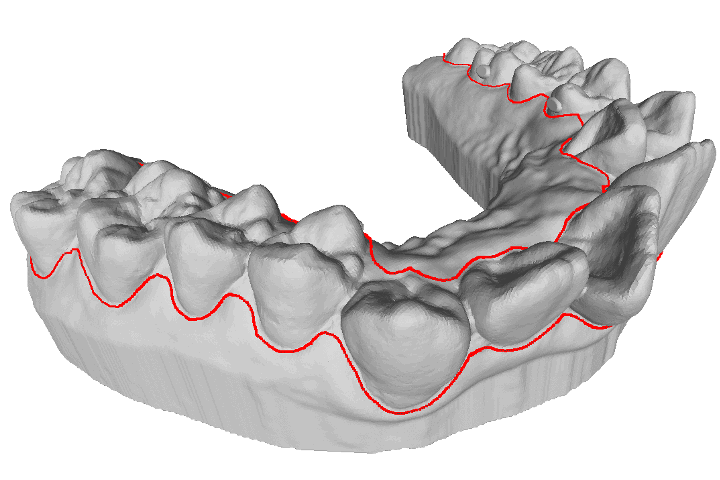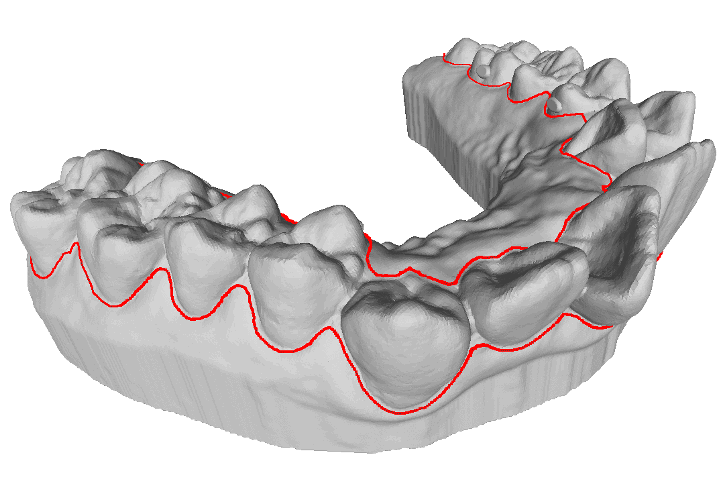

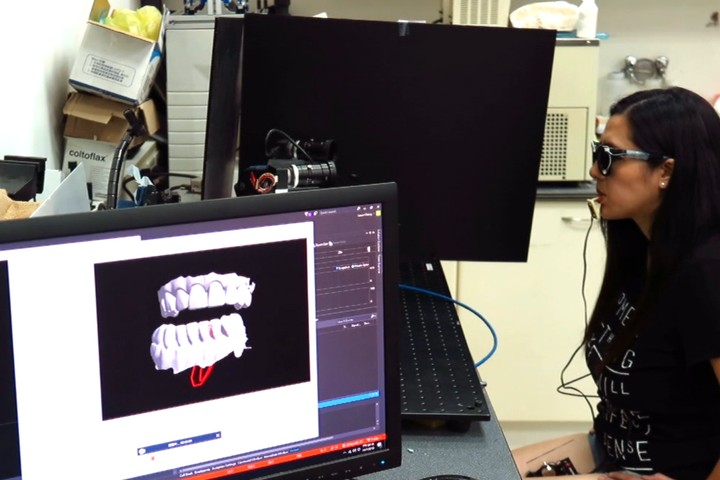
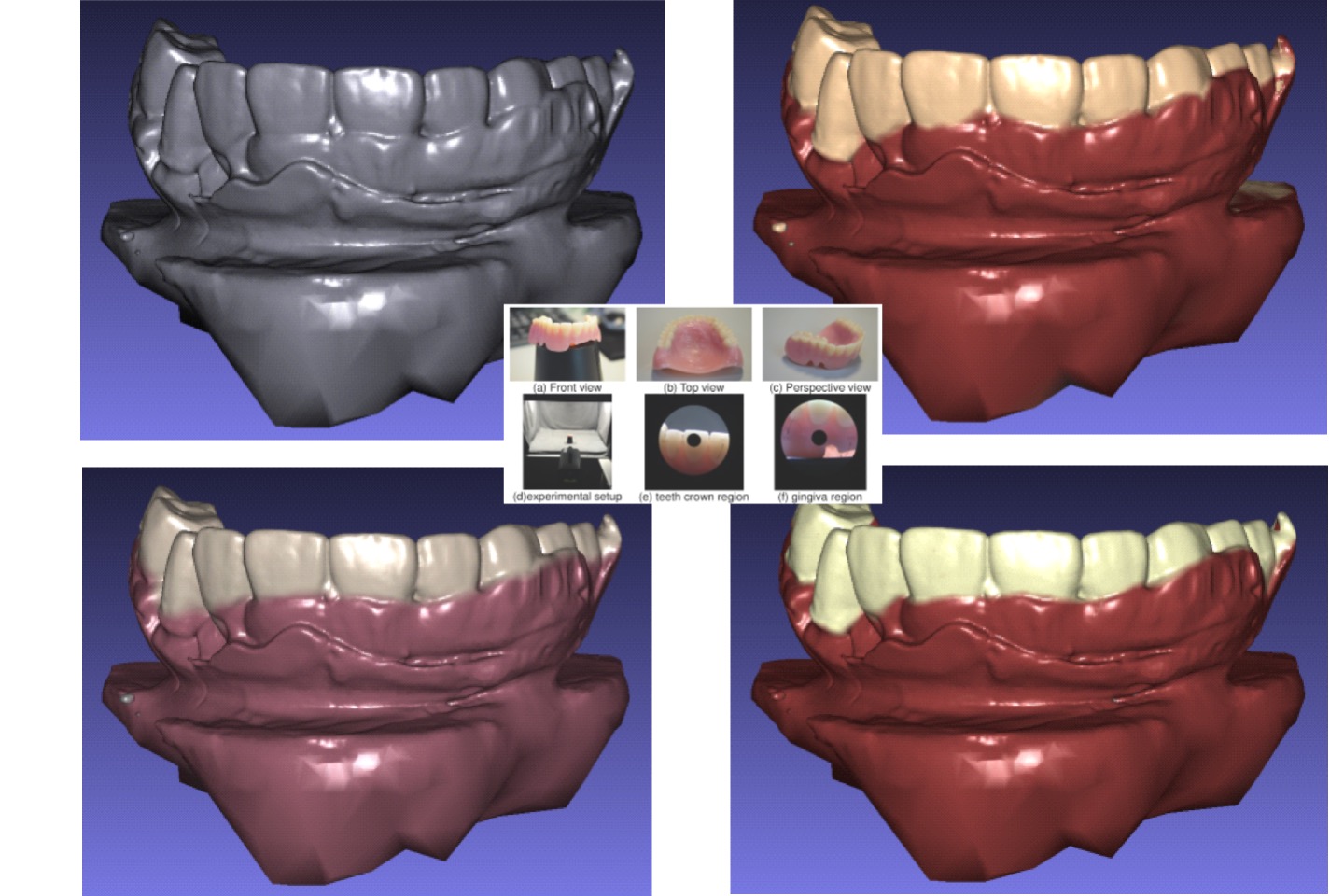
A study for retrieving teeth gingival margin from three-dimensional digital models
Gingival margin (GM) identifies the necessary portion when people manufacture clear aligners. In automatic manufacturing system, it is considered as a three- dimensional (3D) line which needs to be cut and separated. This study proposes a model analysis method which is able to determine the 3D coordinate points of the patient’s gingival margin based on curvature information.
R. B. Chern, and T. H. Lin “A study for retrieving teeth gingival margin from three-dimensional digital models,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 22’), Dec. 14-16, 2022 Fukuoka, Japan.
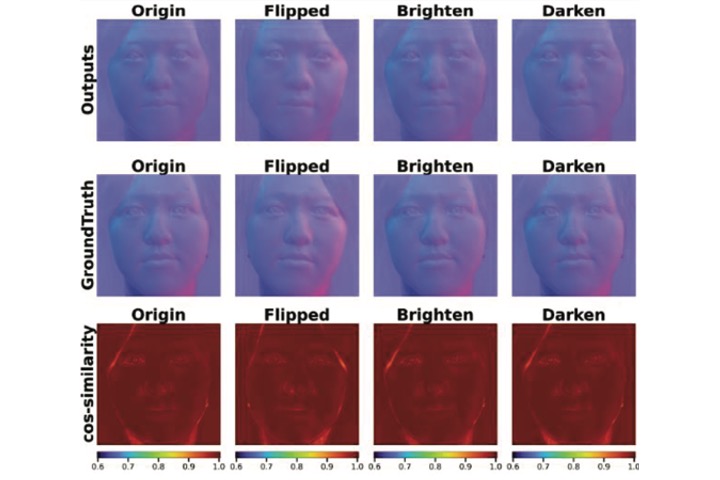

CNN-based normal map generator for creating relightable portrait images
The paper proposes an AI model to generate accurate normal maps for portrait images. We utilized a portrait photo booth system based on photometric methods to generate training data. With these data, users only need to input a portrait image, then it can be converted into normal map image which is further used to relight the color portrait image.
C. Y. Kuo, C. Yang and T. H. Lin “CNN-based normal map generator for creating relightable portrait images,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 22’), Dec. 14-16, 2022 Fukuoka, Japan.
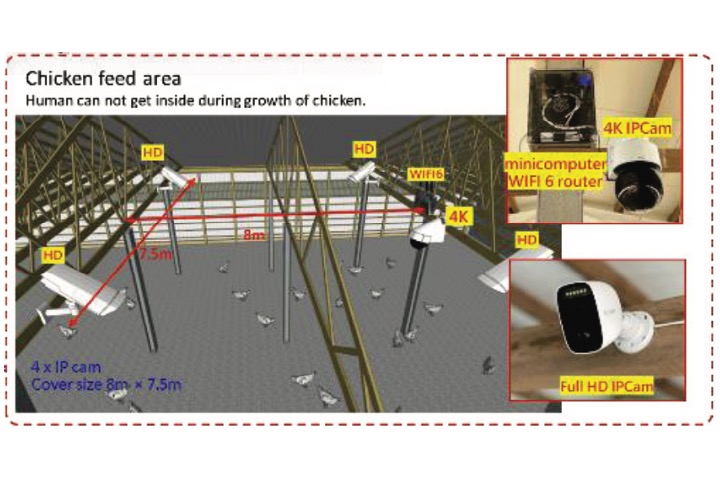

Long term chicken cockscomb color detection of the video surveillance in a poultry house
This paper aims to observe the color chicken cockscomb in a long term during growing. To achieve that, the color correction algorithm was applied to surveillance system in the poultry house to suppress the affection due to the changing daylight. Based on the color-corrected video, the YOLOv4 AI model is used to detect the chicken cockscomb automatically and collect the color for analysis of the growth state of a group of chickens.
T. Y. Wei, T. L. Lu, T. H. Lin, and Y. C. Tsai “Long term chicken cockscomb color detection of the video surveillance in a poultry house,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 22’), Dec. 14-16, 2022 Fukuoka, Japan.
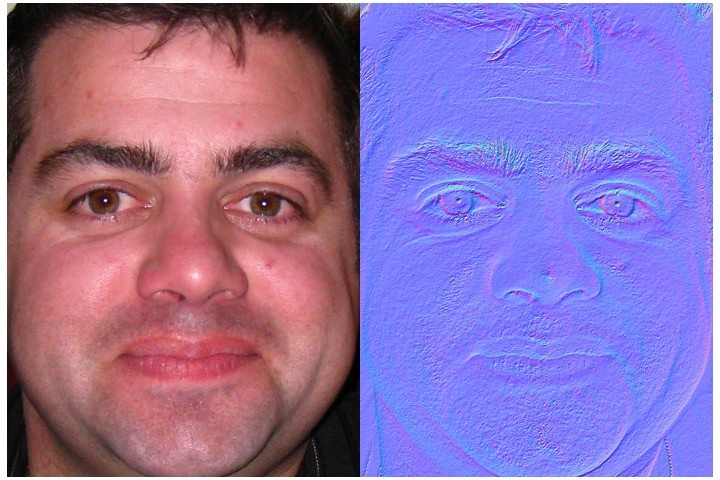


A survey of the normal map generator of gimp from single shot human face image
This study proposes the idea of generating near to accurate normal map from a single image of human face. We used 70,000 human face images from Flickr-Faces-High-Quality Dataset and used various software to automatically generate individual normal map which is a critical layer in various applications. From experiments regarding different scenarios, we concluded that the proposed system performs acceptably for generating normal image for human face.
R. Das, T. H. Lin and K. T. Wang, “A survey of the normal map generator of gimp from single shot human face image”, International Conference on 3D Systems and Applications (3DSA2022), Nov. 24-25, 2022, Taipei, Taiwan


Material classification of printed circuit board by polarization photography
We have developed related image processing methods for polarized photography.
H. H. Tsai, T. L. Lu and T. H. Lin “Material classification of printed circuit board by polarization photography,” Imaging and Applied Optics Congress 2022 (OPTICA), July 11-15, 2022. Vancouver, Canada
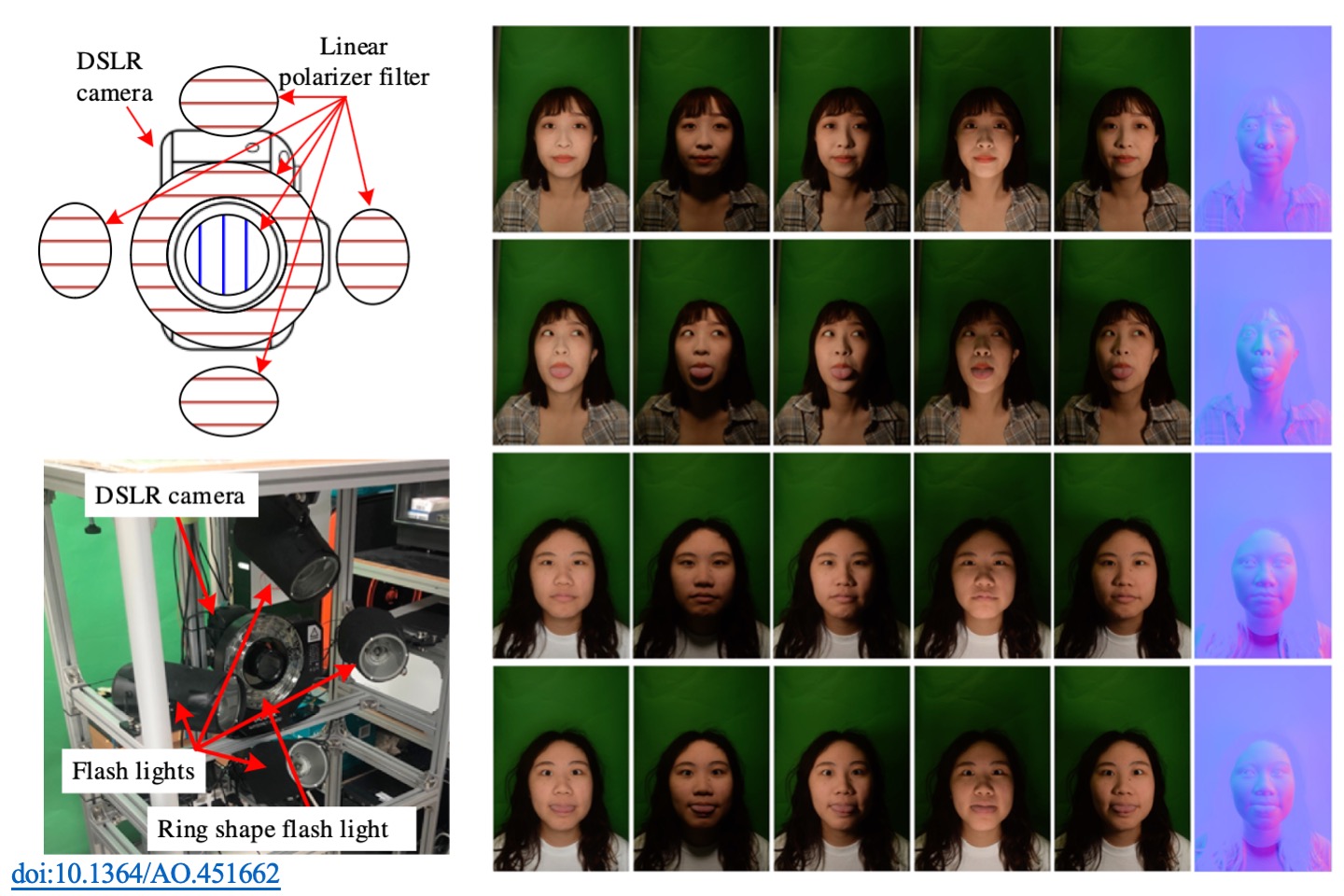

A portrait imaging relighting system based on a simplified photometric stereo method
This study proposes a portrait image relighting system based on a simplified photometric stereo method. The system, comprising a controllable DSLR camera and five polarized flashlights, can obtain a color shade-less image and synthesize a normal map from shaded images. When calibrating the photometric stereo, the normal map is taken as a linear combination of shaded images and clamped with respect to specific normal directions on a white-coated sphere. The relit images were generated through inverse rendering in a predefined virtual environment. To evaluate personal preference, 24 adult subjects were recruited to conduct subjective assessments comparing the deep portrait relighting (DPR) method results. From experiments regarding different scenarios, we concluded that the proposed system based on a simplified photometric stereo performs acceptably for relighting portrait images.
H. Y. Chang, and T. H. Lin*, “Portrait imaging relighting system based on a simplified photometric stereo method,” Applied Optics, 61(15), pp. 4379-4386, 2022.
2021Y’ achievements
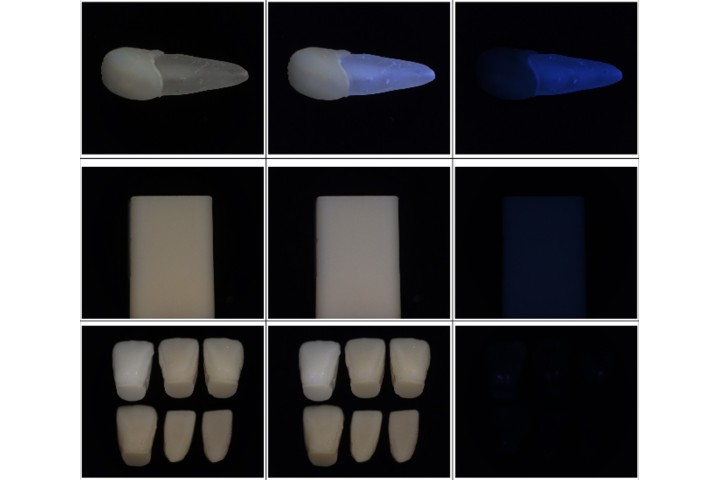

Teeth color and shade matching
Teeth shade matching and reproduction technology can help the dentist to produce a denture appearance more suitable and make customers feel confident and beautiful. Developing our technology can avoid the technology of advanced countries. Taiwan will be a super-aging society in the next decade and the requirement for dentures is above one hundred thousand. The digitalization of dental appearance is helpful for data collecting and reproduction of clinical cases. Moreover, big dental data also help the development of material and set standards. In addition, polarimetric photography is a new technology for computer vision. In this project, polarized illumination, and polarized camera are applicated to capture the different components of dental visual appearance. In the project, we focus on the design of the experiment device, experiment calibration, and the analysis of both polarized color and fluorescent color. And the pilot experiment about glossy, translucency, and texture for next year.
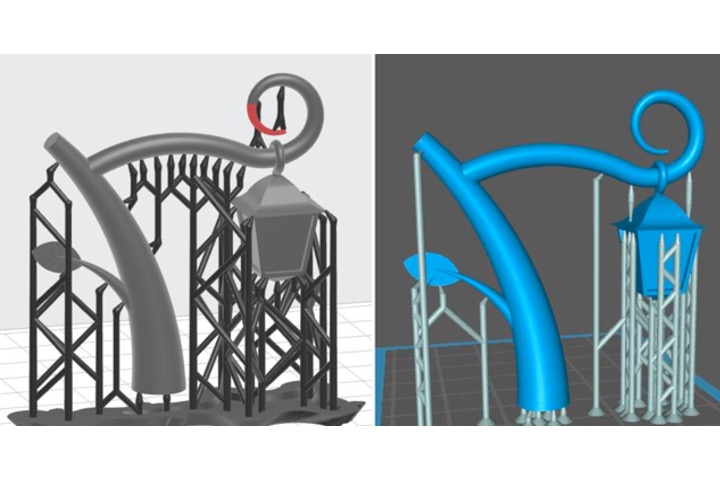

Supporter generating algorithm for the slicing of 3D printing
This project developed a 3D slicing algorithm, which is focusing particularly on the support material algorithm for photo-curing 3D printer. This includes the optimal generation strategy incorporating small-scale projection interference and strategic tree-like structures.
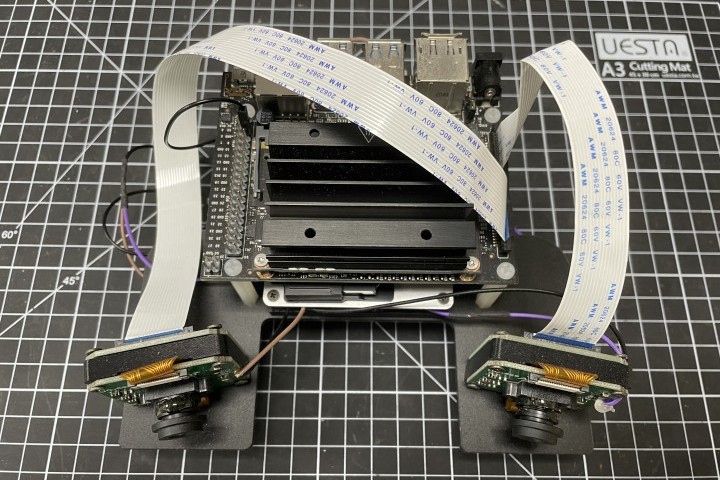

DIY Structure light 3D scanner
We use the Jetson nano as the primary procesing platform for our 3D scanner, paired with a pico projector and an automatic motor (by trigger) to become a 3D scanner. This scanner supports one-click scanning and is a standalone, DIY, cost-effective structured light 3D scanner.


Color calibration applicated at the poultry house video surveillance
The digitalization of the livestock industry is developing during this decade. During the Covid-19 pandemic, remote management and monitor for poultry houses have become a new demand of the livestock industry. There are many types of researches that focus on using the computer vision system (CVS) to identify the situation of poultry and livestock. However, there are few kinds of research focusing on analyzing the color information of living poultry. In this research, we are dedicated on monitoring the situation of the poultry house by remote cameras. The lumination of poultry houses change frequently since they usually have an opening or semi-opening structure. Therefore, the color is too unstable to be controlled for identifying correct information including the health of the chicken. A higher order polynomial equation, which is one of popular method, is a fast and efficient solution to calibrate the color of images.
T. L. Lu, T. Y. Wei, P. Y. Lai, R. B. Chern, T. H. Lin and Y. C. Tsai, “Color calibration applicated at the poultry house video surveillance,” Asia Color Association Conference 2021, Nov. 2-3, 2021, Indonesia.
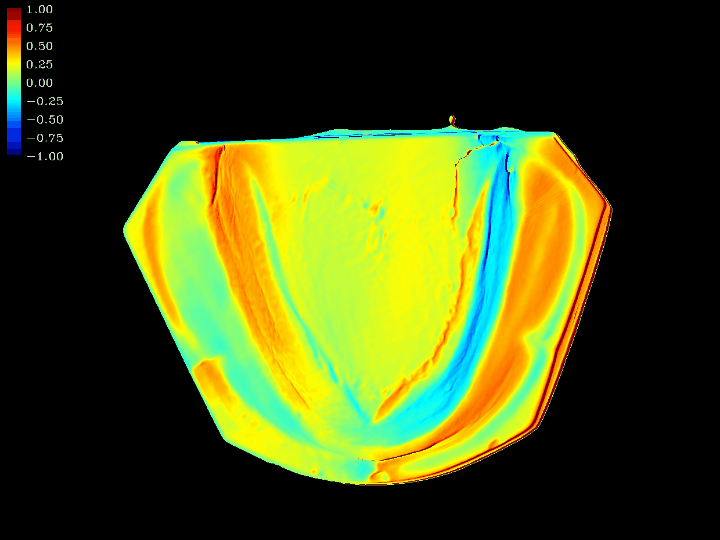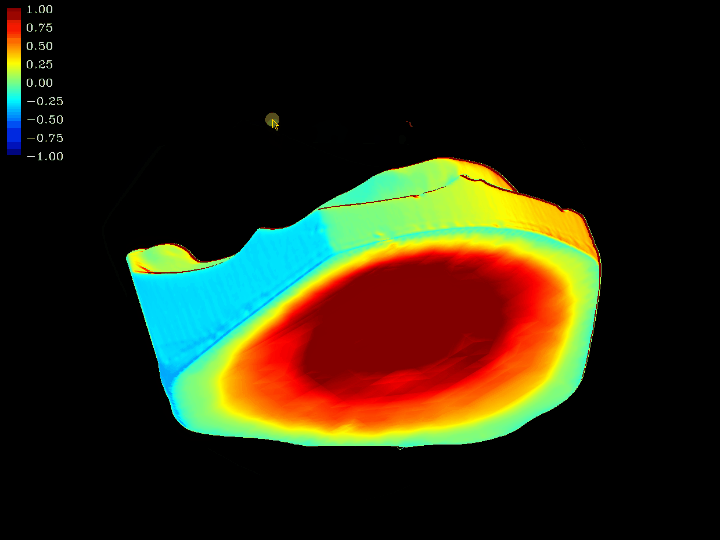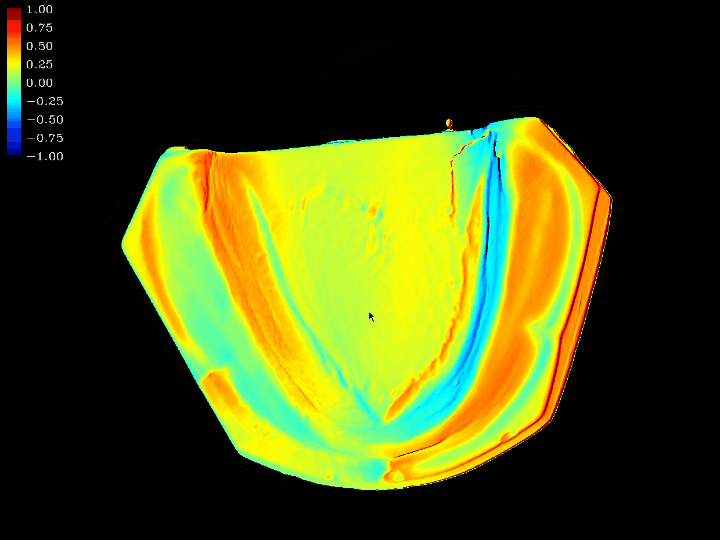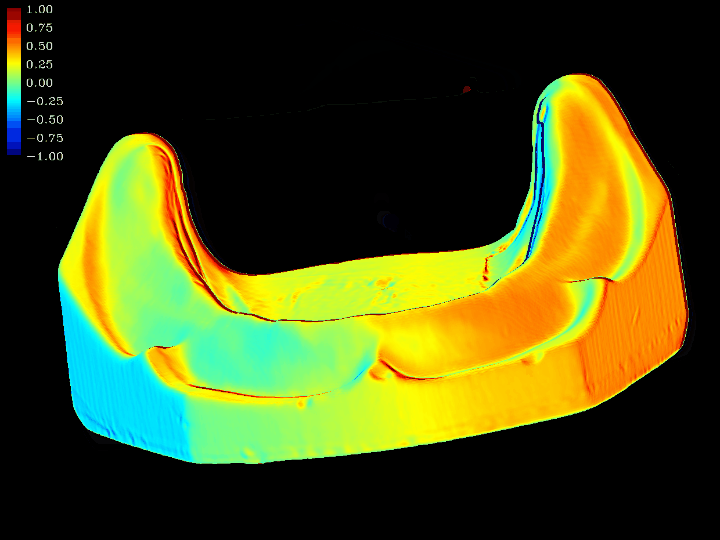

3D Model difference and error comparison
This work involves 3D model difference and error comparison. Using computer graphics algorithms, we compare the errors between two 3D models that have been positioned through the ICP algorithm. This comparison technique enables real-time computation of the differences between the two 3D models.


Optimized slicing and queue for massive 3D printing
Photo-curing 3D printing often need to consider the amount of time, for waiting for the material to solidify and the mechanism to operate. Especially in situations where a large amount of printing is required, this technology takes into account factors such as the minimum stacking height and the maximum stacking area, and optimally arranges the section layers that require a large number of batches of printing through various permutations and combinations, so that the printing efficiency can be effectively promote.
2020Y’ achievements

Microscopic image and optical inspection
This project serves the needs of a specific enterprise to develop microscopic imaging equipment and exclusive qualification product management software. This technology used backlight and specific lighting conditions to highlight the outline appearance of the inspection object. We further developed the hardware system and control inspection software. Measurement levels is up to 0.2micron.


Multiview camera system and computational photography
This technology uses 17 cameras to shoot multiview stereoscopic images, to produce wonderful instant multi-angle stereoscopic photos (Bullet time effect). We have developed the robust calibration camera system, and considered the precise arrangement of the printed autostereoscopic image under the best viewing parallax. At the same time, it also allows the user to quickly preview the 3D image on the stereoscopic display.
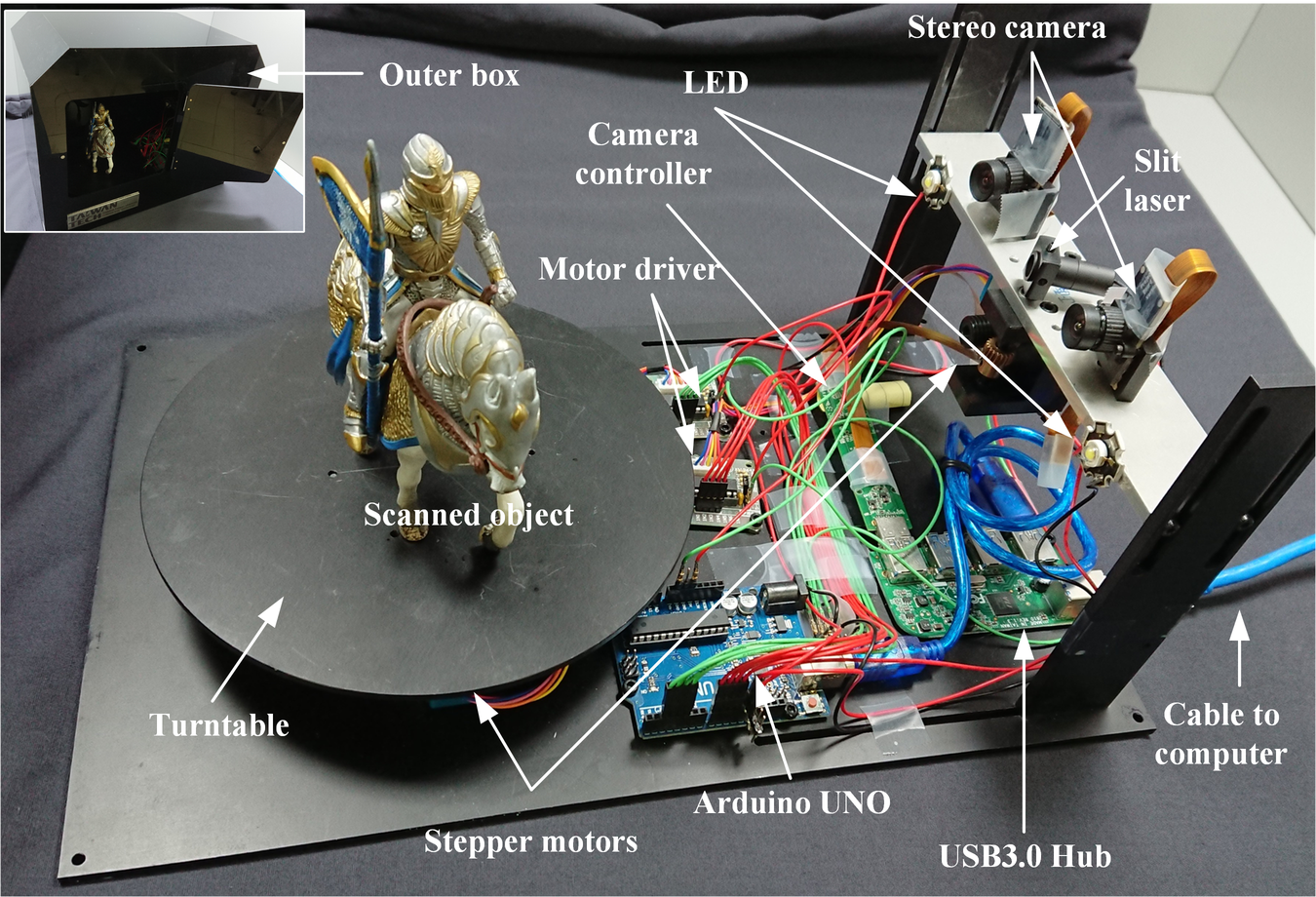

Automatic 3D color shape measurement system based on stereo camera
This study proposes an automatic three-dimensional (3D) color shape measurement system based on images recorded by a stereo camera. The system, comprising several off-the-shelf components, is cost-effective yet capable of obtaining quality color 3D objects. In the proposed system, a turntable carrying a checkerboard is used to assist the simultaneous calibration of the stereo camera and the turntable. A slit laser is driven to swing forward and backward for generating stripes on test objects. The stereo images are collected and analyzed for obtaining matching pixels, and consequently, the 3D point coordinates based on epipolar geometry are obtained. Screened Poisson reconstruction is utilized to integrate and smooth the scanned surfaces. With additional color images from the same camera, several multi-view texturing methods are benchmarked. We concluded that our proposed system can successfully and automatically reconstruct quality 3D color shapes of various objects.
T. H. Lin*, “Automatic 3D color shape measurement system based on stereo camera,” Applied Optics, 59(7), pp. 2086-2096, 2020.
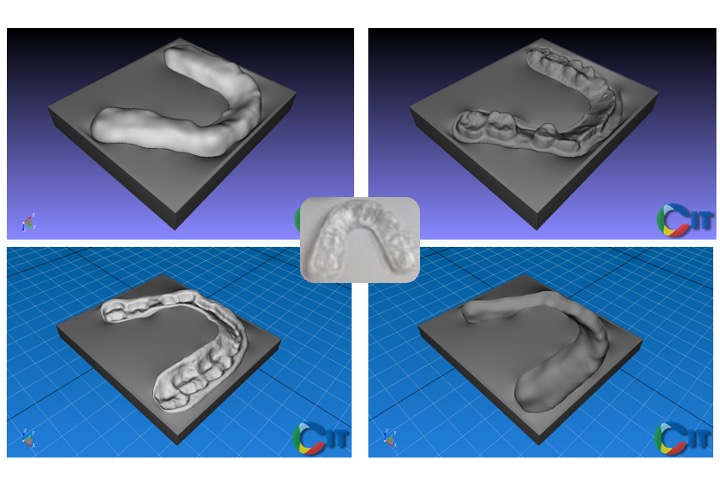

3D parting mold algorithm for few-undercut 3D models
This work is to automatically detect the self-interference area of a 3D model, and through 3D posture adjustment, the model’s parting mold interference can be as few as possible. After the adjustment is completed, our algorithm further demostrated the algorithm to automatically find the continuous parting line that can be parted and generate 3D models of the upper and lower molds.


A camera array system based on DSLR cameras for autostereoscopic prints
This study used 7 Nikon DSLR cameras and Arduino for external synchronization trigger. As a result, bullet-time photography effect was carried out. In addition, we have also invented an one-click calibrication technology that can simultaneously correct the 3D coordinates and colors for multi-camera systems. Moreover, we synthesize slanted-lenticular naked-eye multi-view frames through high-resolution sub-pixel photos.
T. H. Lin, Y. L. Lau, C. C. Lee and H. C. Huang, “A camera array system based on DSLR cameras for autostereoscopic prints,” Electronic Imaging 2020, Jan. 26-30, 2020, San Francisco, USA.
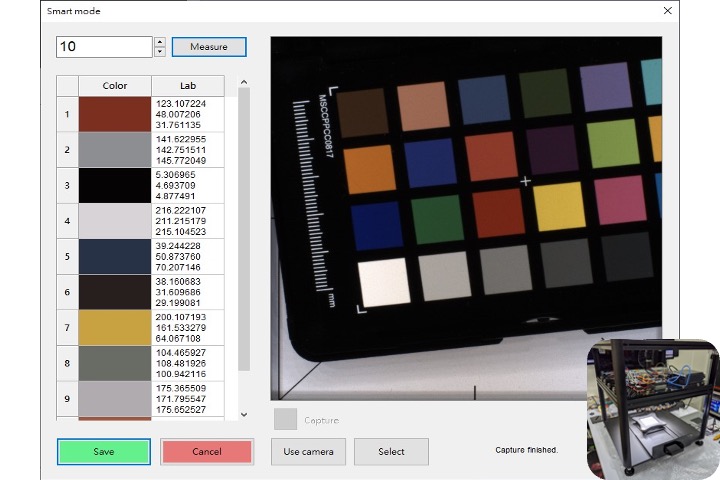

Image based material inspection and color differenc analysis software development
This development introduces Visual Appearance, simplifies it and converts it into practical products according to CIE standards. Image calculation can achieve extremely small area color measurement, such as rapid quality control of multi-color products. This color difference calculation meets current CIE specifications, ISO standards, etc., and this technology has been converted into commercial products
2019Y’ achievements
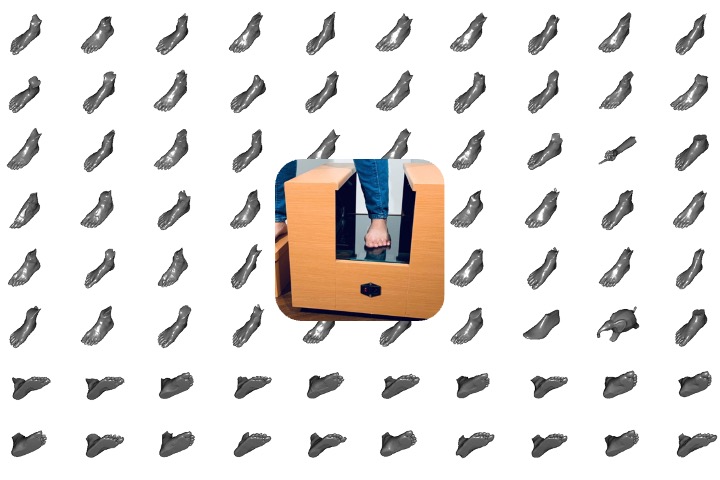


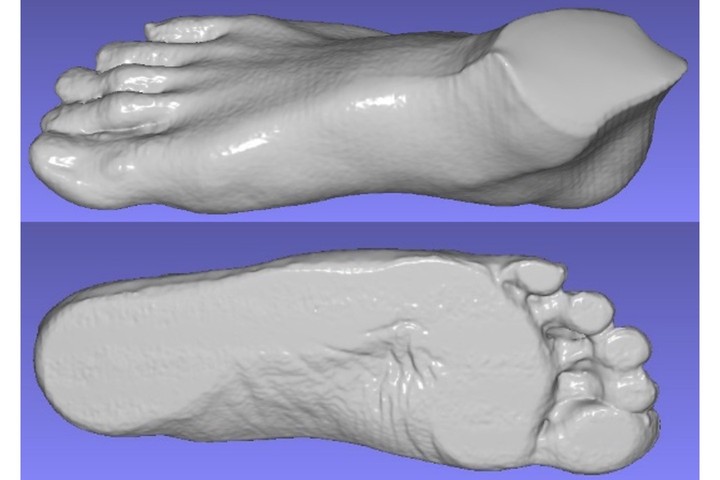
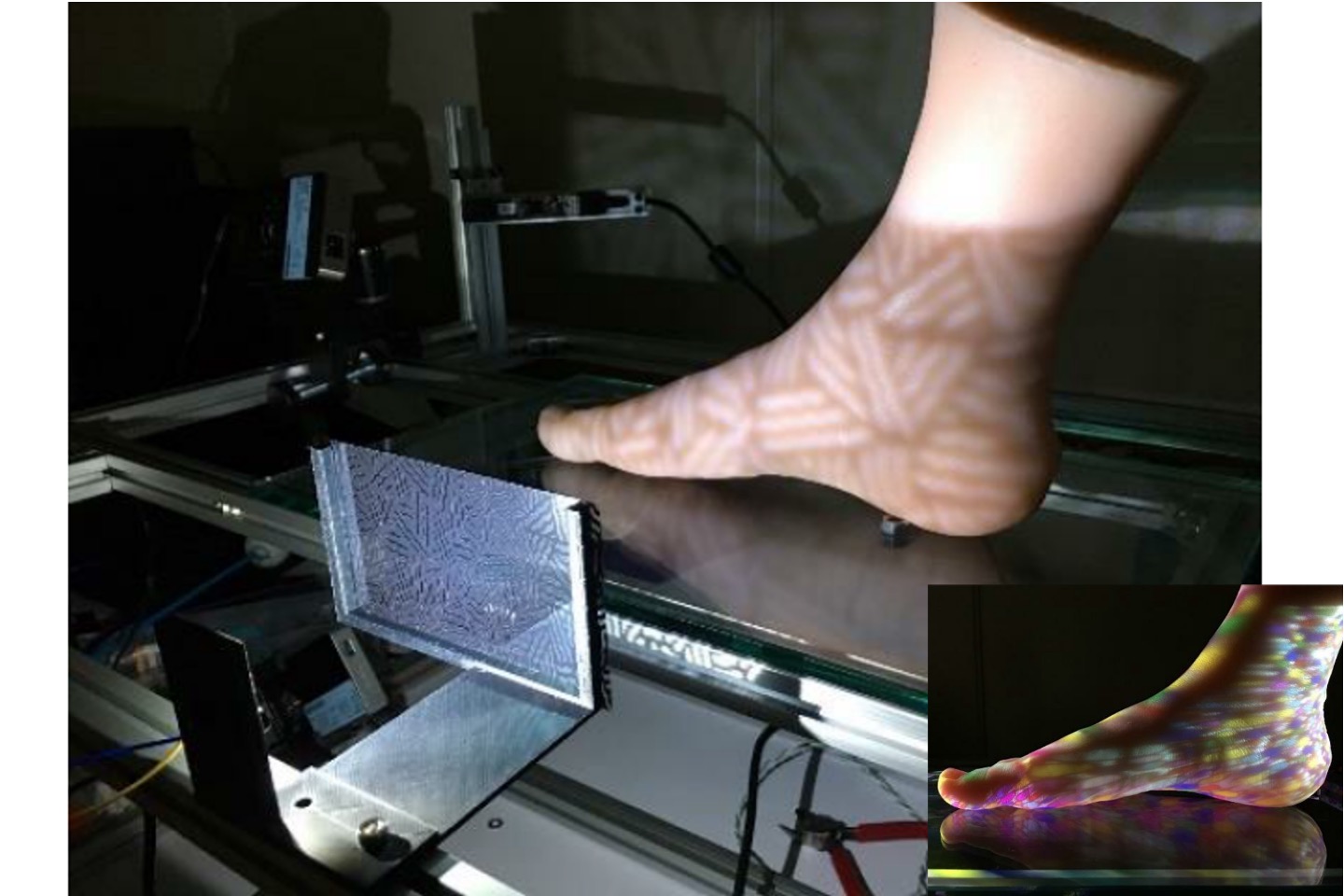
Automatic 3D foot scanner
We have developed a unique 3D calibration technology that is able complete the coordinate 3D calibration of four laser systems and the linear motor with one click. This technology uses a line laser and 4 VGA-60fsp level cameras, with the scanning accuracy of up to 0.3mm, and can complete a 3D scan of the entire foot, including the footprint, in about 3 seconds. After performance testing, it can complete 3D scanning and data collection of about 500 feet in 8 hours a day.

Outdoor Wild Bird Detection based on YOLO algorithm
This study focuses on outdoor bird detection in video surveillance to reduce the risk of avian influenza (AI) in poultry farms. Once a bird is detected, our system will trigger another action to drive away the bird. We utilized YOLO algorithm for object detection, and add diversity samples to the dataset to train the model, then recognition accuracy is improved.
B. C. Zhu, T. H. Lin, Y. C. Tsai, K. W. Hsieh, F. M. Fan and P. K Lei, “Outdoor Wild Bird Detection based on YOLO algorithm,” (Oral) Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 19’), Nov. 27-29, 2019 Sapporo, Japan.

Accuracy Verification of Visual Appearance Acquisition Device of Non-Metallic Material Based on Sparse SVBRDF
In this paper, we proposed a visual appearance acquisition device comparing with commercial product. Our device is capable of restoring the visual appearance for non-metallic materials based on spatially varying bidirectional reflectance distribution function (SVBRDF). A benchmark comparing to commercial product Radiant Vision is carried out to verify the reliability of the proposed device.
T. L. Lu, Y. L. Liu, Y. C. Hsieh, T. H. Lin, “Accuracy Verification of Visual Appearance Acquisition Device of Non-Metallic Material Based on Sparse SVBRDF,” (Oral) Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 19’), Nov. 27-29, 2019 Sapporo, Japan.
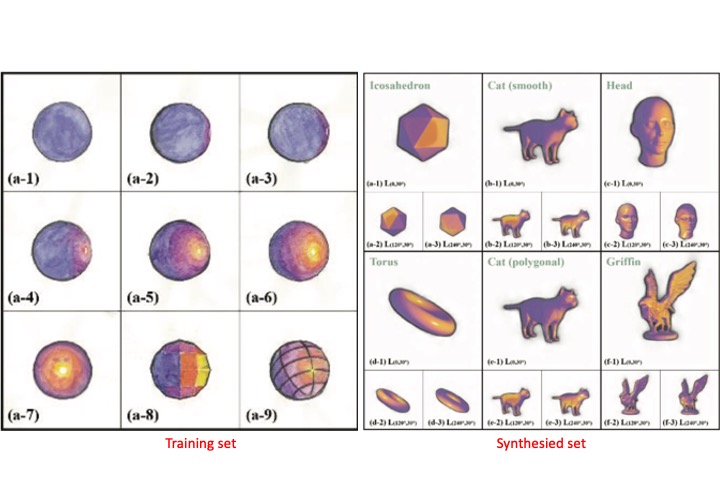

Deep Convolution Neural Networks for Painting-like 3D Rendering,
A 3D rendering model which uses deep convolutional neural networks to imitate 2D painting style is proposed. User can feed the networks with simple paintings of specific objects to render images of 3D objects with any orientations in accordance with the painting style.
Z. Yang, P. L. Sun, and T. H. Lin, “Deep Convolution Neural Networks for Painting-like 3D Rendering,” (Oral) Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 19’), Nov. 27-29, 2019 Sapporo, Japan.
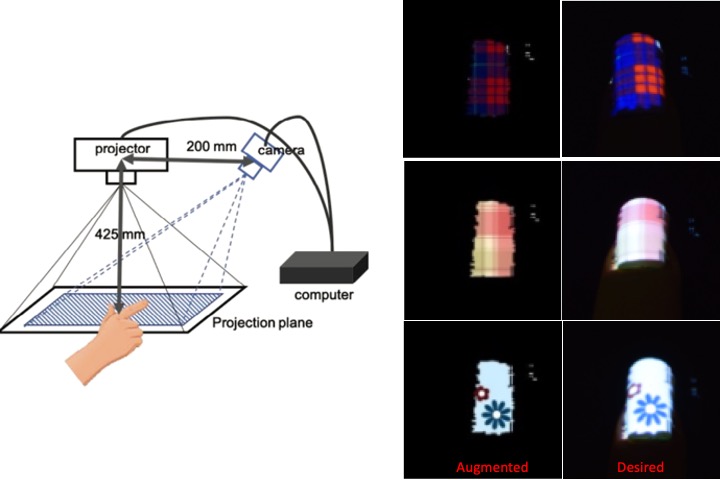

Developing an Augmented Reality System of Nail Make-up
We developed system for AR application. In practice, we utilized color to extract nail area. Additional color projector, which is well calibrated, will cast desired patterns on nails. As a result, augmented and vivid patterns on nail are carried out by our formulated algorithm. It’s useful for customers and nail-salon.
Y. R. Chou, and T. H. Lin, “Developing an Augmented Reality System of Nail Make-up,” (Poster) Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 19’), Nov. 27-29, 2019 Sapporo, Japan.
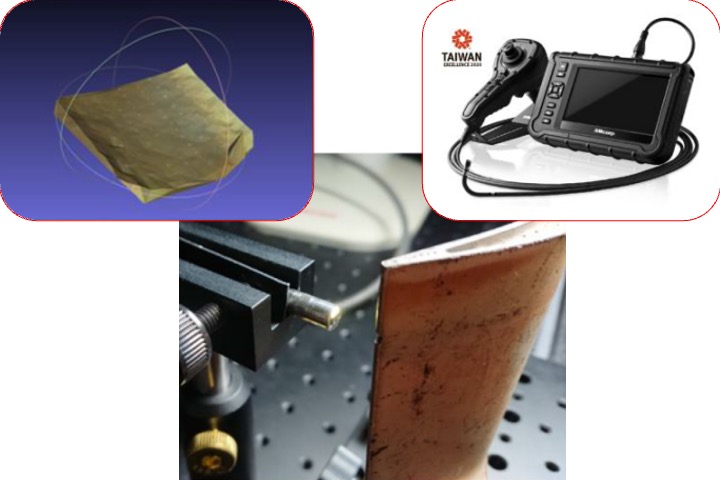


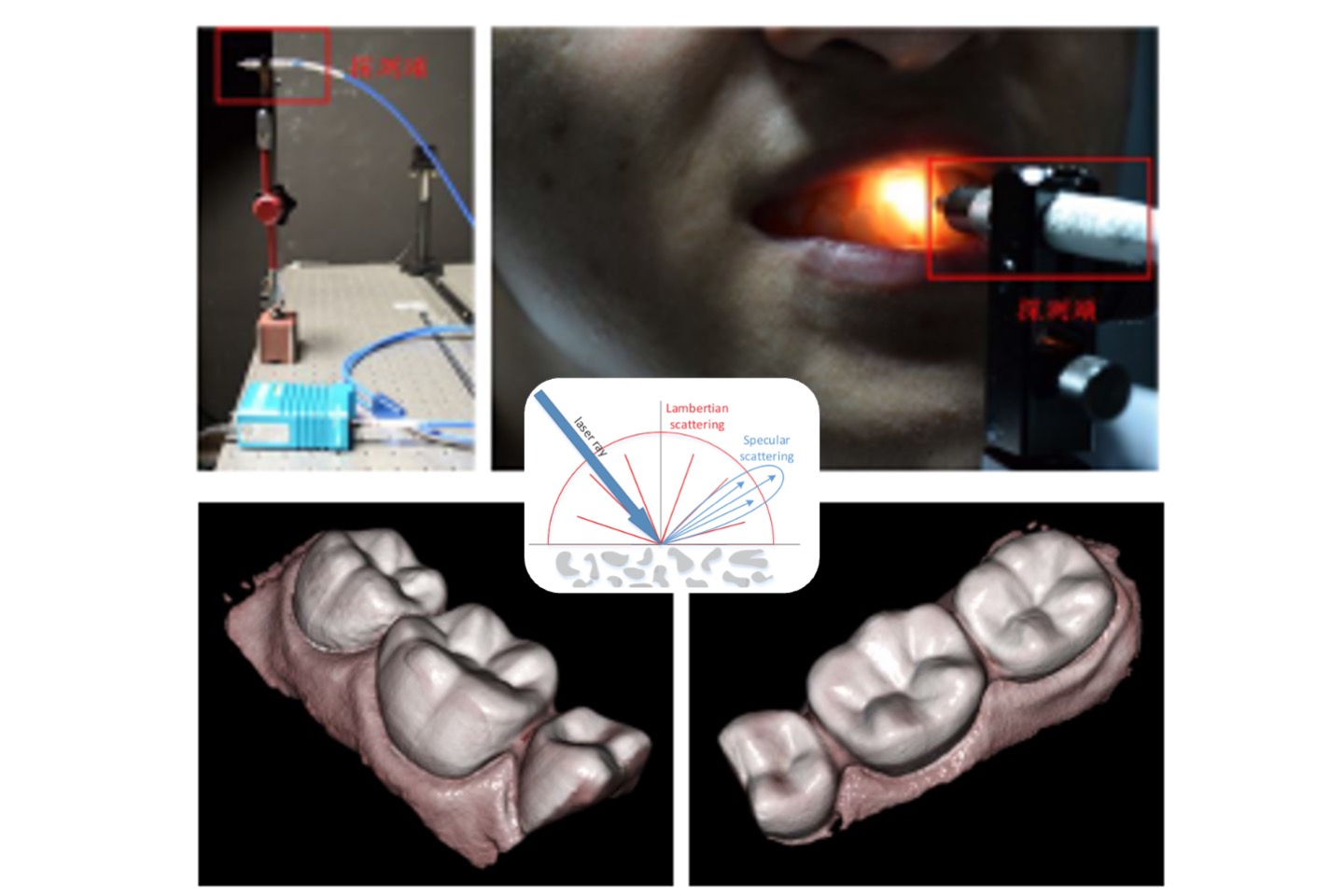
Industrial endoscope 3D measurement software
We assist a company in accelerating the development of 3D measurement technology for endoscopes, especially for precise 3D measurement of small sizes.
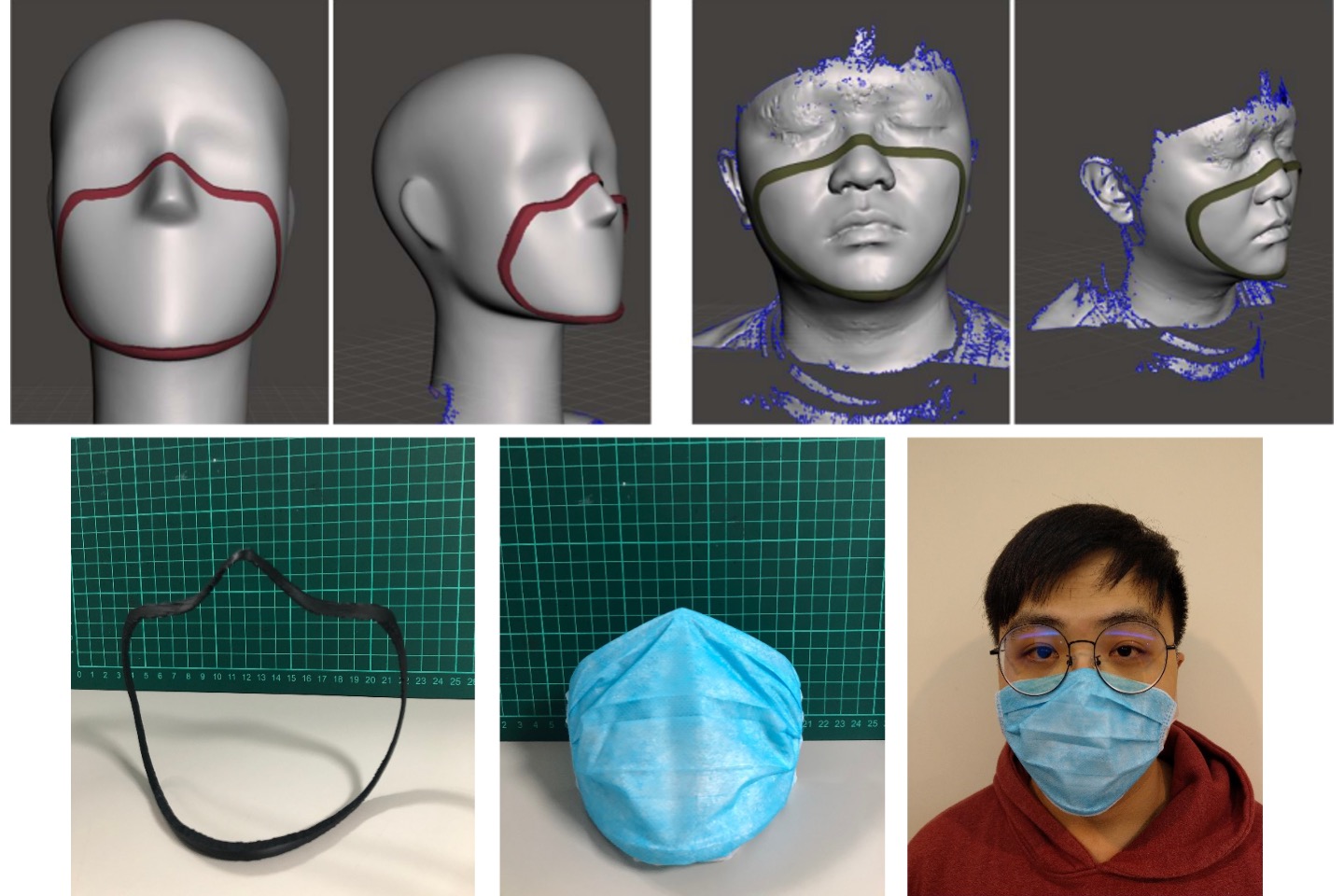

Customized mask-design
In this study, we have developed a rapid method for designing mask frames. By utilizing a 3D scanner to capture the 3D shape of the face and the area around the mouth, and using software to sketch that region, a customized 3D mask frame can be created. Subsequently, this personalized frame can be printed using 3D printing equipments. Based on several dust experiments, the results have demonstrated that this design effectively prevents external dust from infiltrating the nose and mouth.
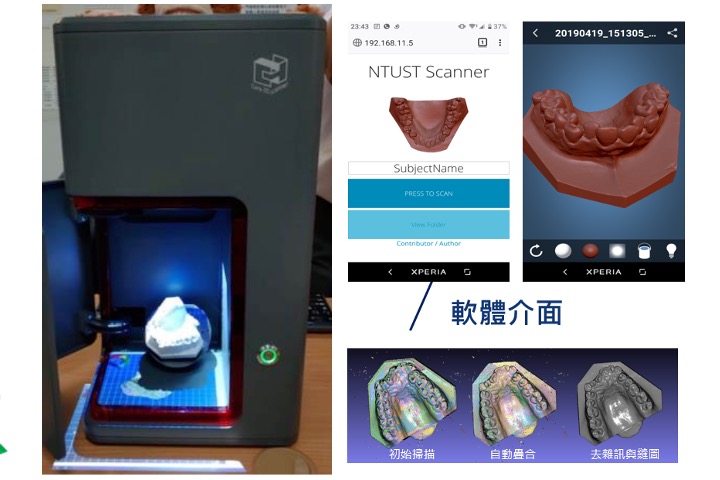

Affordable strcuture light 3D scanner
Product development: we develop low-cost structured light 3D scanners, using DLP and industrial cameras, with single-axis stepper motors. For tooth mold applications, the accuracy can reach 20micron.
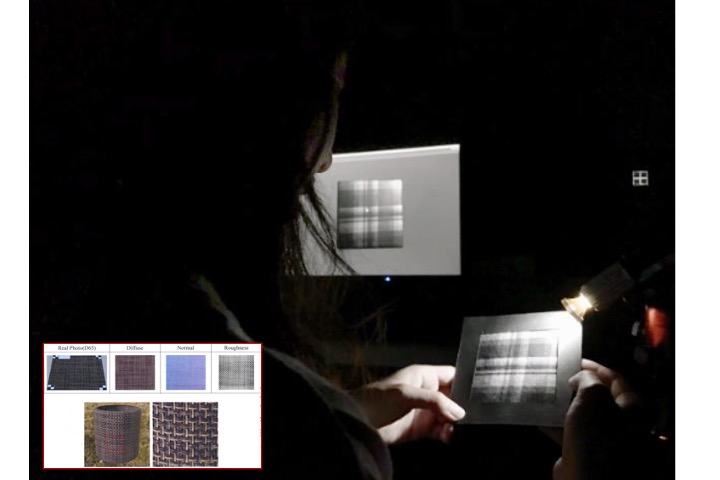

Visual appearance matching for SVBRDF type – PBR texture
In this study, we conducted a large number of human factors experiments to verify the data obtained from the self-made PBR material acquisition device. And we evaluated the visual appearance of digitally simulated textures and actual objects.
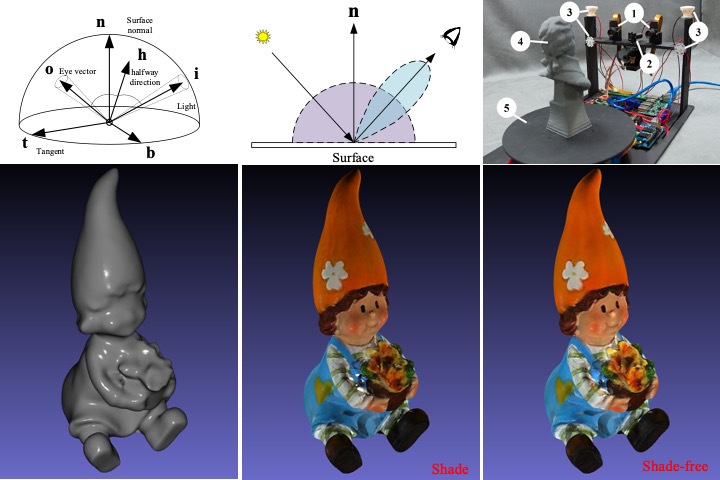

Shade-free texture acquisition for 3d scanning system
3D scanning technology is mature to obtain quality 3D shapes of real objects. However, to obtain a uniform and shade-free texture is still a challenging task, particularly for commercial products. We propose a practical solution in our 3D scanner to capture 3D object with highly uniform shade. This scanner utilizes a swinging laser in front of the cameras to scan 3D shape, and then captures additional colour images for texture. Those images are again adjusted according to the scanned 3D shape. Based on this design, the colour uniformity of scanned 3D object is significantly improved.
T. H Lin, K. L. Chan, H. S. Chen, “Shade-free texture acquisition for 3d scanning system,” CIE 2019, Jun. 16-19, 2019 DC. USA.
2018Y’ achievements
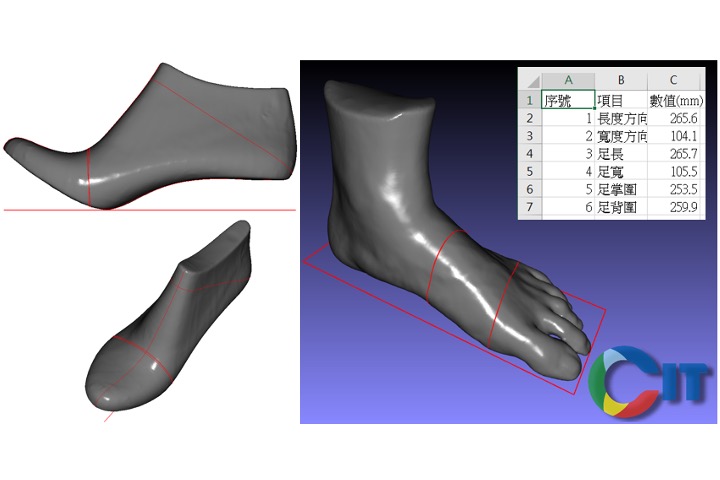

3D Foot feature analysis and automatic shoe recommation algorithm
For the 3D foot shape, we have developed a one-click algorithm that can quickly calculate common 3D features of the foot, such as length, circumference, angle, etc. Similarily, this technology is also applicable to shoe last analysis. After quickly collecting features, it can be compared with the data on cloud database and appropriate shoe suggestions can be given.
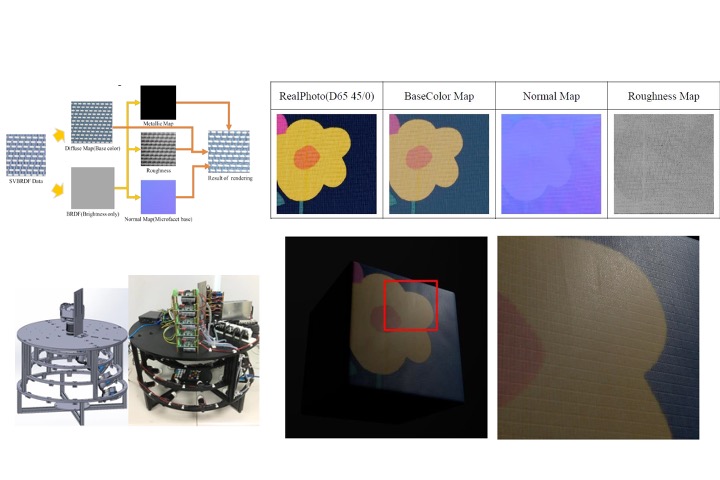

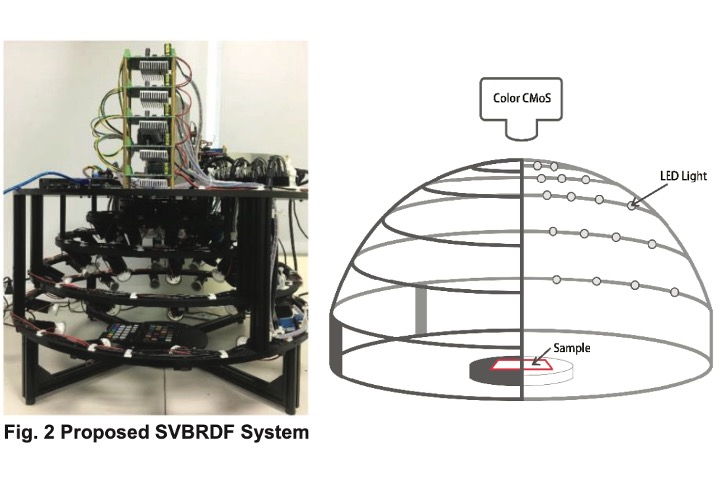
SVBRDF-Texture acquisition system
In this study, we developed a SVBRDF measurement device for non-metallic materials. The equipment contains 4-5 digital color cameras and 54 spherically distributed LED bulbs. At the same time, we have also developed related software algorithm such as color correction and uniformity correction. Through photogrametry technology, the PBR material properties of a 10x10cm size block can be estimated, including roughness, normal vector and diffuse color.
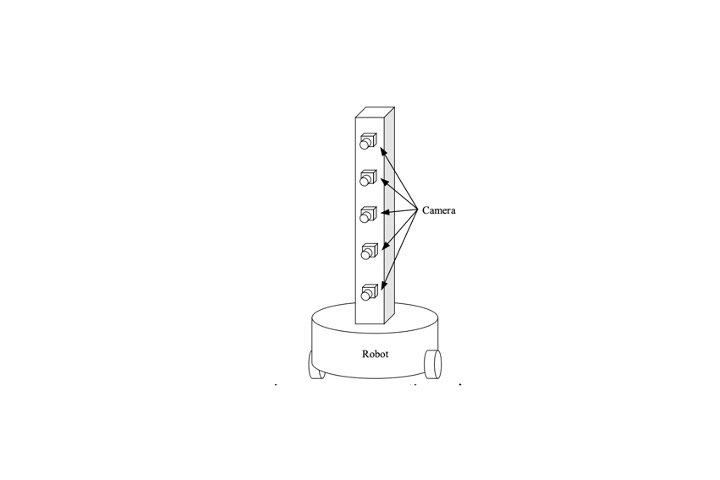

Imaging system based on multi-camera on unman robotic vehicles
Unmanned robots or vechicals are regarded as new tools that can replace a large amount of labor. In this project, we extensively evaluated the suitability of all camera and sensing systems for robots.

Jaw motion tracking system
We use specific markers as features and stereoscopic videos to track the jaw, which can effectively assist the teeth in correct bite.
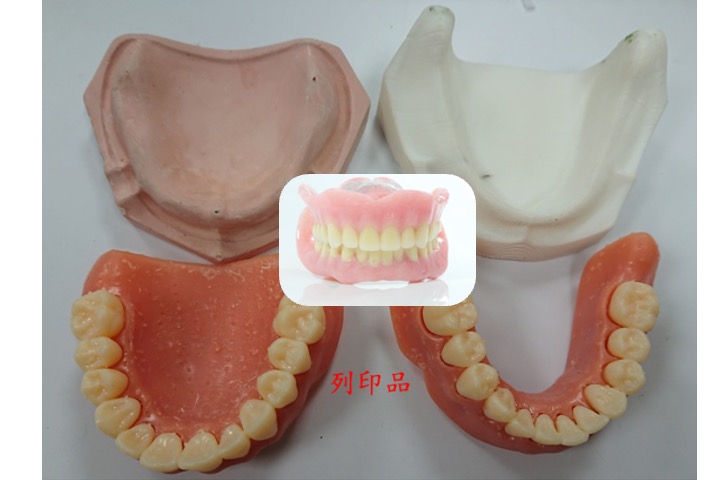

Dual materials 3D printing
The multi-material 3D printing technology we have developed can simultaneously mix two materials plus a support material for printing in the same process. We used dentures as an example to verify the feasibility of our proposed method.


Feature enhancement for the defocusing structured-light 3D scanning system
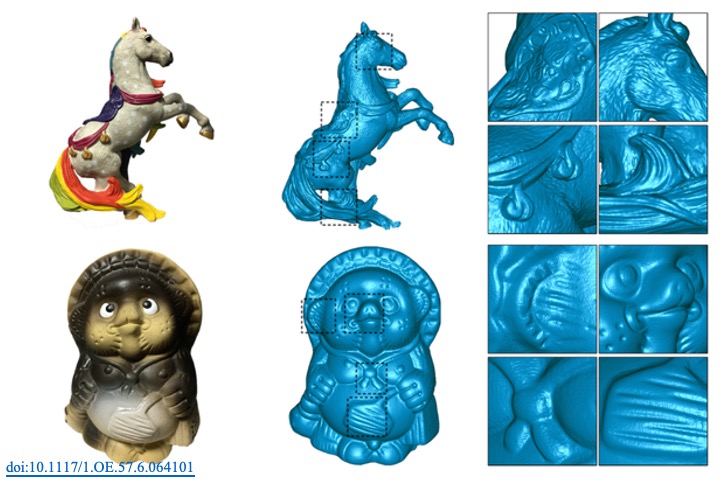
Structured-light systems consisting of a camera and projector are powerful and cost-effective tools for three-dimensional (3-D) shape measurements. However, most commercial projectors are unable to generate distinct patterns due to defocusing and shallow focusing issues. We propose a hybrid method for enhancing the calibration and scanning features of the defocusing structured-light 3-D scanning system. Instead of using conventional sequential binary patterns, we replace the highest-level binary pattern by a high-order sinusoidal pattern. In our proposed system, a pan-tilt stage carrying a checkerboard is used to assist the simultaneous calibration of the camera and projector. Initially, the camera is calibrated to obtain the extrinsic positions of the stage. In addition, we utilize the multiplication of vertical and horizontal stripe patterns to enhance the corresponding features between the camera and projector. The projector is then calibrated using the extrinsic features determined from the calibrated camera. The experimental results show that the use of the high-order sinusoidal pattern significantly improves reprojection error. Our proposed method can easily be incorporated in the defocusing projector for scanning various types of objects.
Y. L. Liu+, and T. H. Lin*, “Feature enhancement for the defocusing structured-light 3D scanning system,” Optical Engineering, 57(6), pp. 064101, 2018.
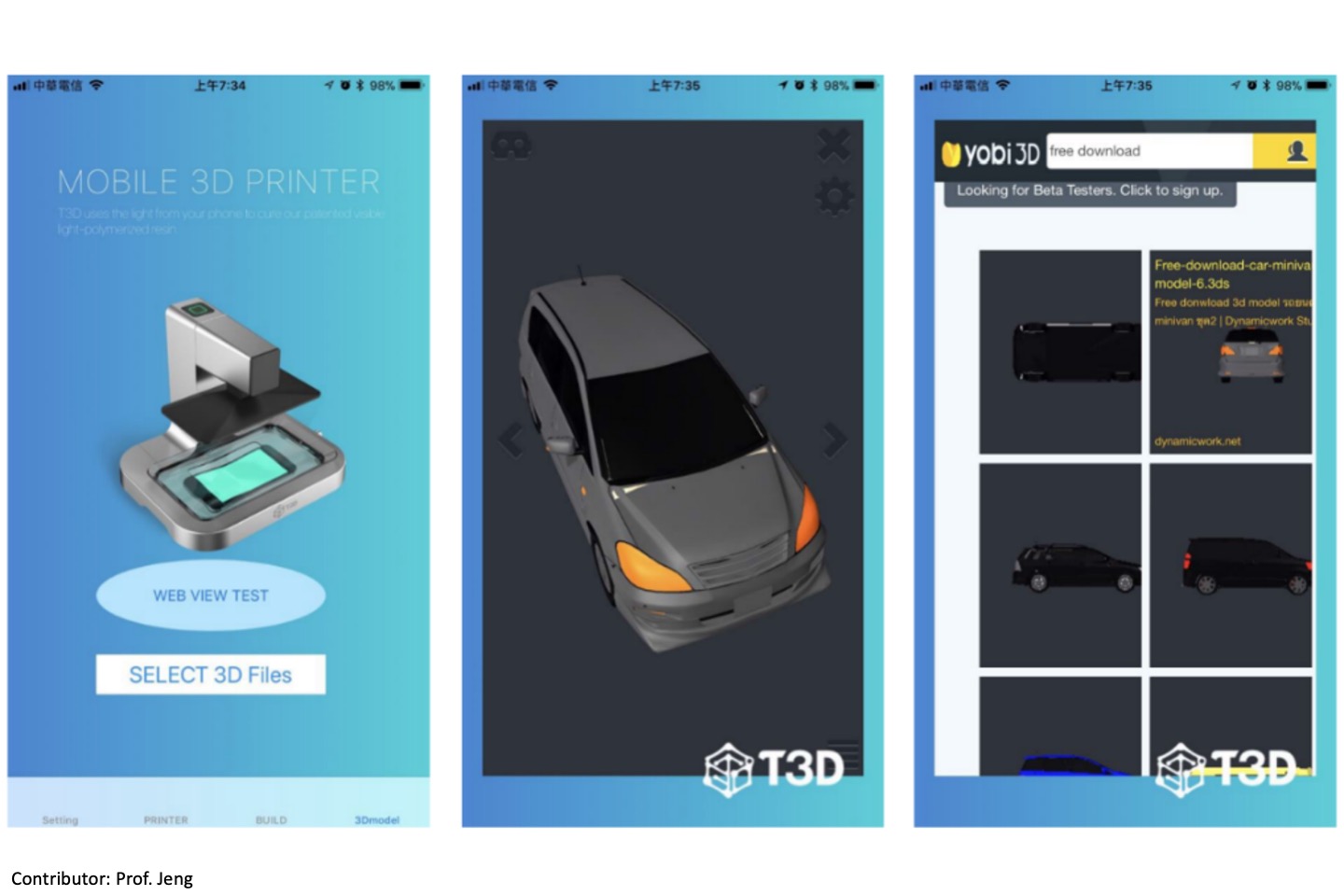

Developing Cloud Service of 3D Models for 3D Printing
Mobile phone 3D printing uses the mobile phone as a light-energy source to further cure the material. The mobile 3D printing relies on the cellphone itself to perform the operation and control. However, the difference among the cell phones is not easy to simply unify the APP function for the advanced operations, including the slicing and model repair. This technology conducts online software deployment and establishment of slicing software, the construction of repair software is compiled. The data file management services, protection, and load balance are established as well.
Y. C. Peng, and T. H. Lin, “Developing Cloud Service of 3D Models for 3D Printing,” 3D Systems and Applications (3DSA 18), Aug. 29-30, 2018 Taipei, Taiwan.
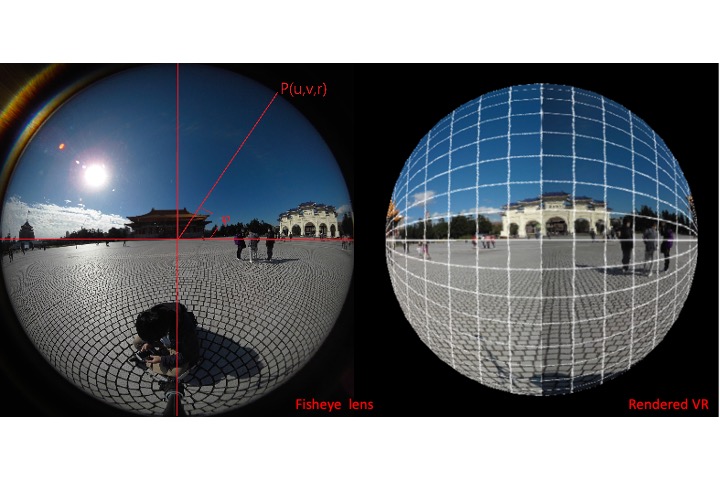

Study on Rendering 360 degree photograph from two fish-eye cameras
We utilized the openGL (computer graphics) tool to efficiently render VR360 images.
Y. C. Hsieh, Y. L. Lau, T. H. Lin, “Study on Rendering 360 degree photograph from two fish-eye cameras,” 3D Systems and Applications (3DSA 18), Aug. 29-30, 2018 Taipei, Taiwan.
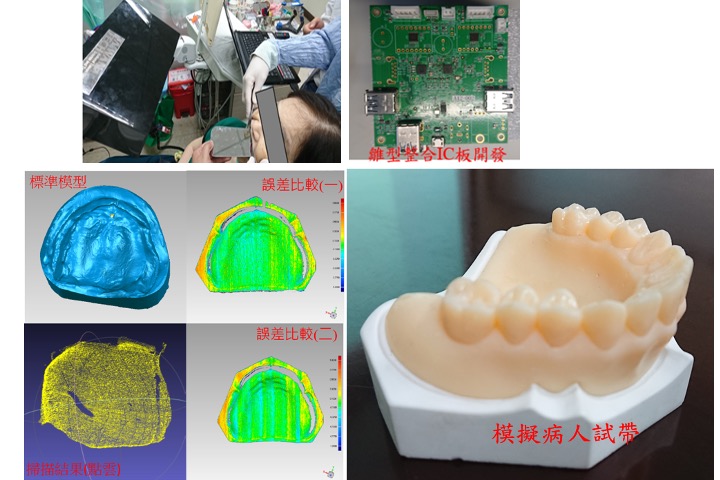

Intra oral 3D scanner
We integrated the previously developed 3D scanner (stereo-type) into an intraoral 3D scanner for clinical use, and produced full dentures through case verification.
2017Y’ achievements
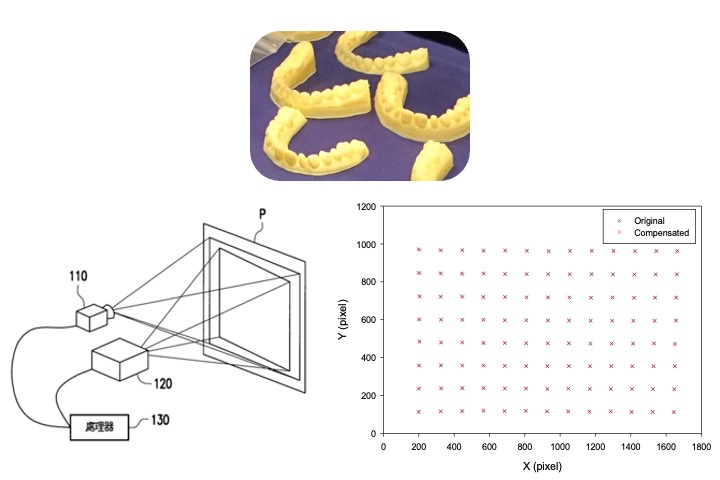

Single-pass automatic projecotor distortion method
Projectors involves complex optical lens designs. Due to physical limitations and cost considerations, the projected image is usually non-linearly distorted and cannot achieve correct image projection. We have developed an automatic correction method that our software-compensation in a single-pass process to automatically correct projector distortion and assign accurate dimensions such as DPI. This technology is used in photo-curing 3D printing to achieve excellent printing improvement.
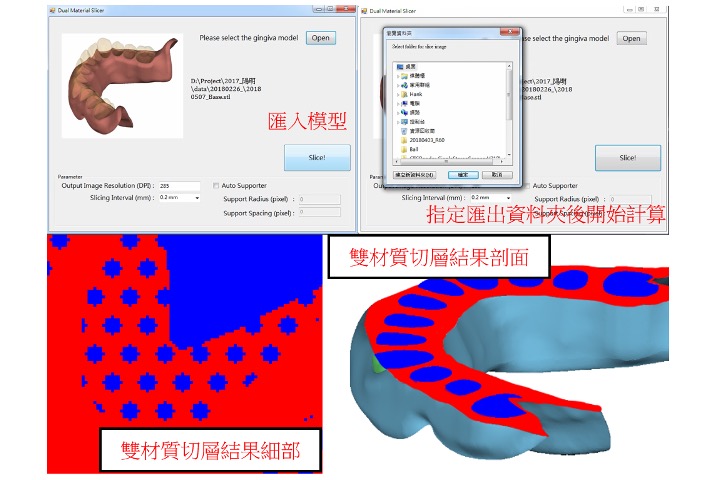

photo-curing multi-material 3D slicing software development
We develop multi-material 3D splicing software specifically for photo-curing type printers to introduce new applications suitable for dual materials. For example, the teeth and gums of a complete denture should be adapted to different strengths and biosafety properties. The algorithm also includes a third material to print simultaneously with the support.
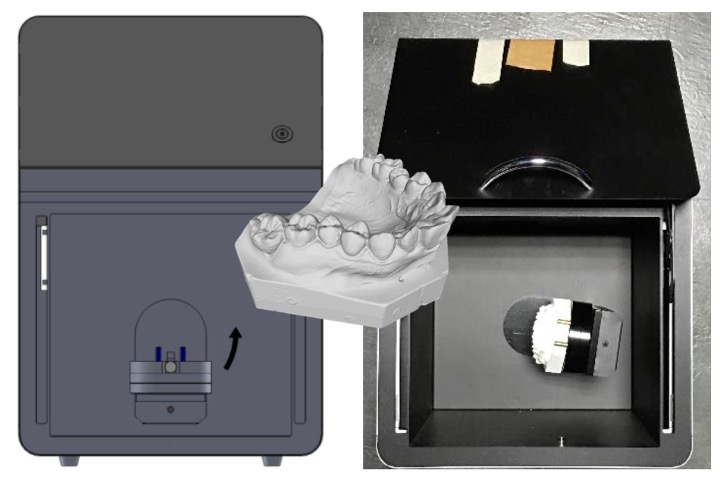


3D teeth mold scanner (two-axises)
This project converts structured light 3D scanning technology into a 3D scanner product specifically for tooth mold scanning. The equipment is equipped with a dual-axis (pan-tilt) motor, a high-speed synchronizable projector and our owned software.
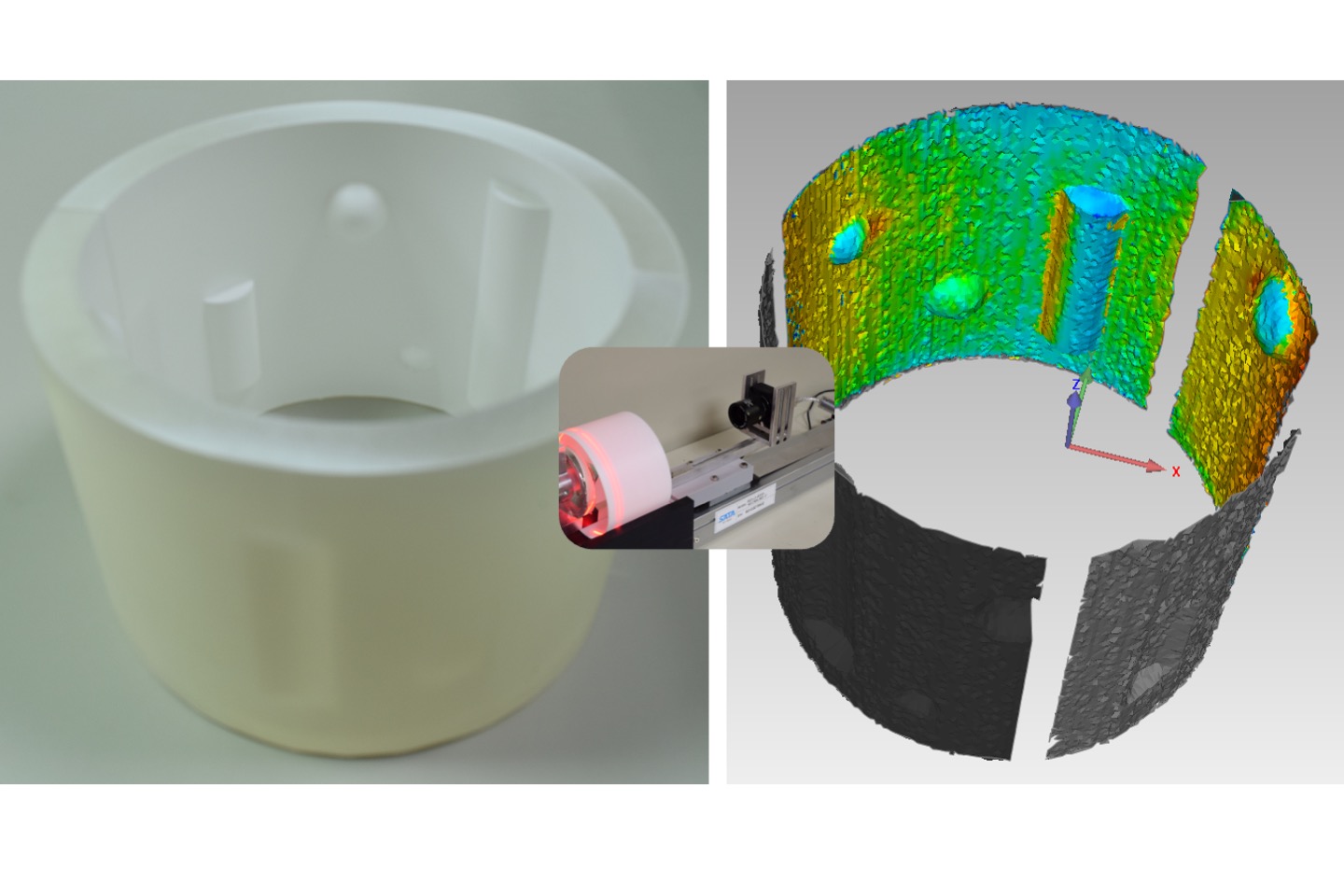

Inner profile reconstruction pipes using dual omni-directional mirror and laser
This research develops an internal contour 3D scanner, which is equipped with an omnidirectional reflector, annular laser, camera and linear motor to achieve the purpose of 3D reconstruction for tube/pipe inner surface.
C. M. Kuo, T. H. Lin, C. Y. Chen, “Inner profile reconstruction pipes using dual omni-directional mirror and laser,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 17’), Dec. 6-8, 2017 Sendai, Japan.

Fast System Calibration of Multi-Camera for Foot Scanner
This paper presents a fast system calibration of multi-camera that allows you to quickly calibrate multiple cameras at the same time. Once the camera is used in the system, it is necessary to be calibrated, whether it is used for image recognition or scan reconstruction. We utilize known-size block for calibration.
D. Y. Lai, W. Huang, Y. L. Liu, and T. H. Lin, “Fast System Calibration of Multi-Camera for Foot Scanner,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 17’), Dec. 6-8, 2017 Sendai, Japan

Development of image-based BRDF measurement system for 3D model rendering
Rendering photorealistic scenes have already become the main issue in academic research. Since the popularity of VR and AR products are recently growing up, improving immersive user experience is getting important. To achieve the realistic visual effect for virtual 3D objects, people have to precisely record the light-field’s data between the illumination and the surface structure of objects. Therefore, most researchers currently dedicate on Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Functions (BRDF) to estimate the physical surface appearances of 3D objects. In this paper, we develop an image-based BRDF measurement system which integrates the functions of 3D geometry and surface reflection. With the 3D geometry reconstruction and fully recorded physical light reflection information, people would utilize these data to render physical based and photo-realistic 3D objects.
Y. L. Liu, C. C. Lee, and T. H. Lin, “Development of image-based BRDF measurement system for 3D model rendering,” IPPR Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, August 21-23, 2017, Nantou, Taiwan
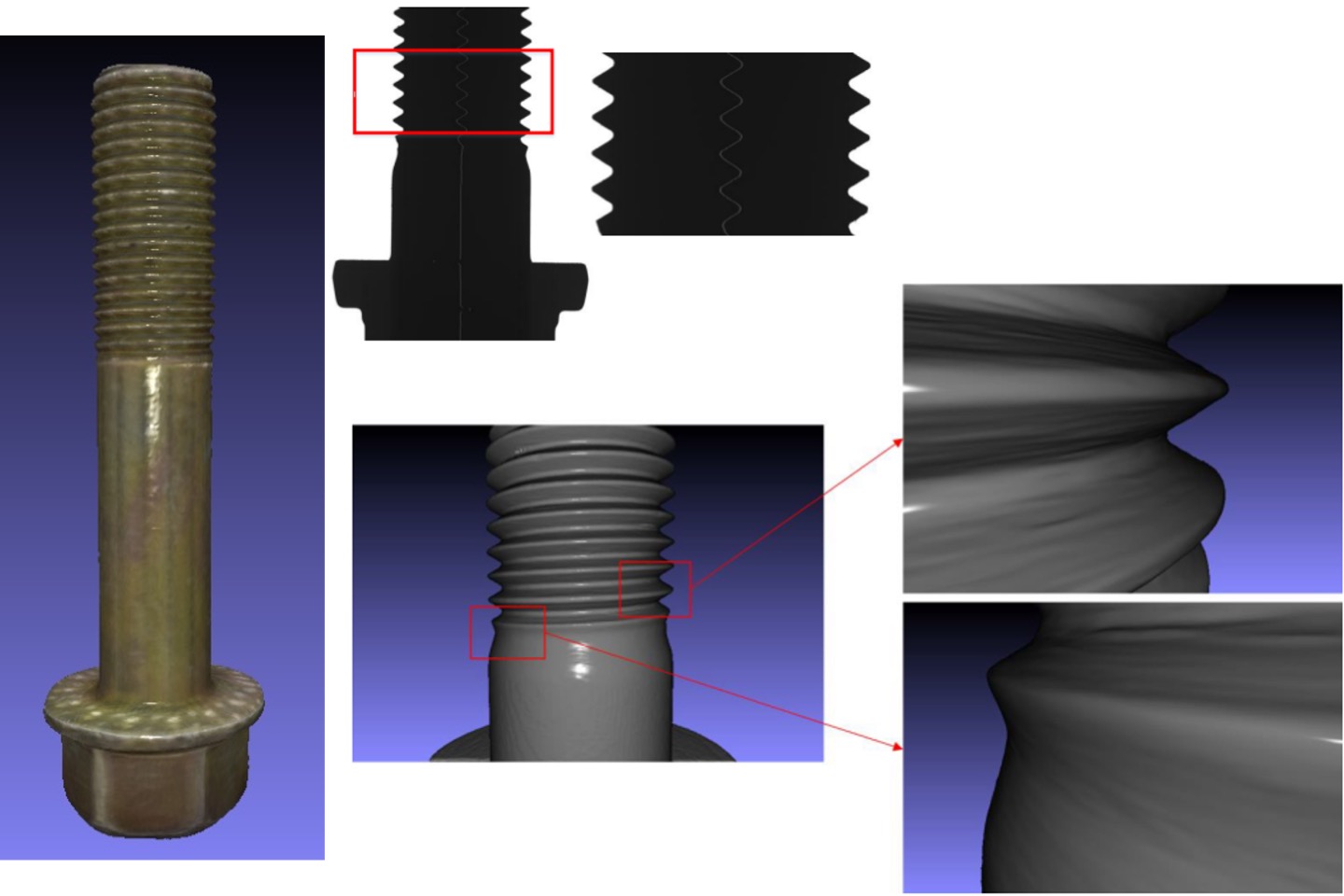

High accuracy 2D/3D screw measurement and reconstruction
Automatic Optic Inspection (AIO) often requires quantitative inspection and objective automatic calculations to ensure their accuracy and reproducibility. This development used 2D image data as the main input, and calculate the contour image obtained from the optical inspection system for mechanical components (such as screws) to estimate the screw pitch size. In terms of 2D measurement, we use a special lens to take the contour image. We assumed that its conditions were approximately flat, and then use sub-pixel technology was to increase the measurement accuracy as small as 0.2 micron, and to reconstruct for 3D structure.
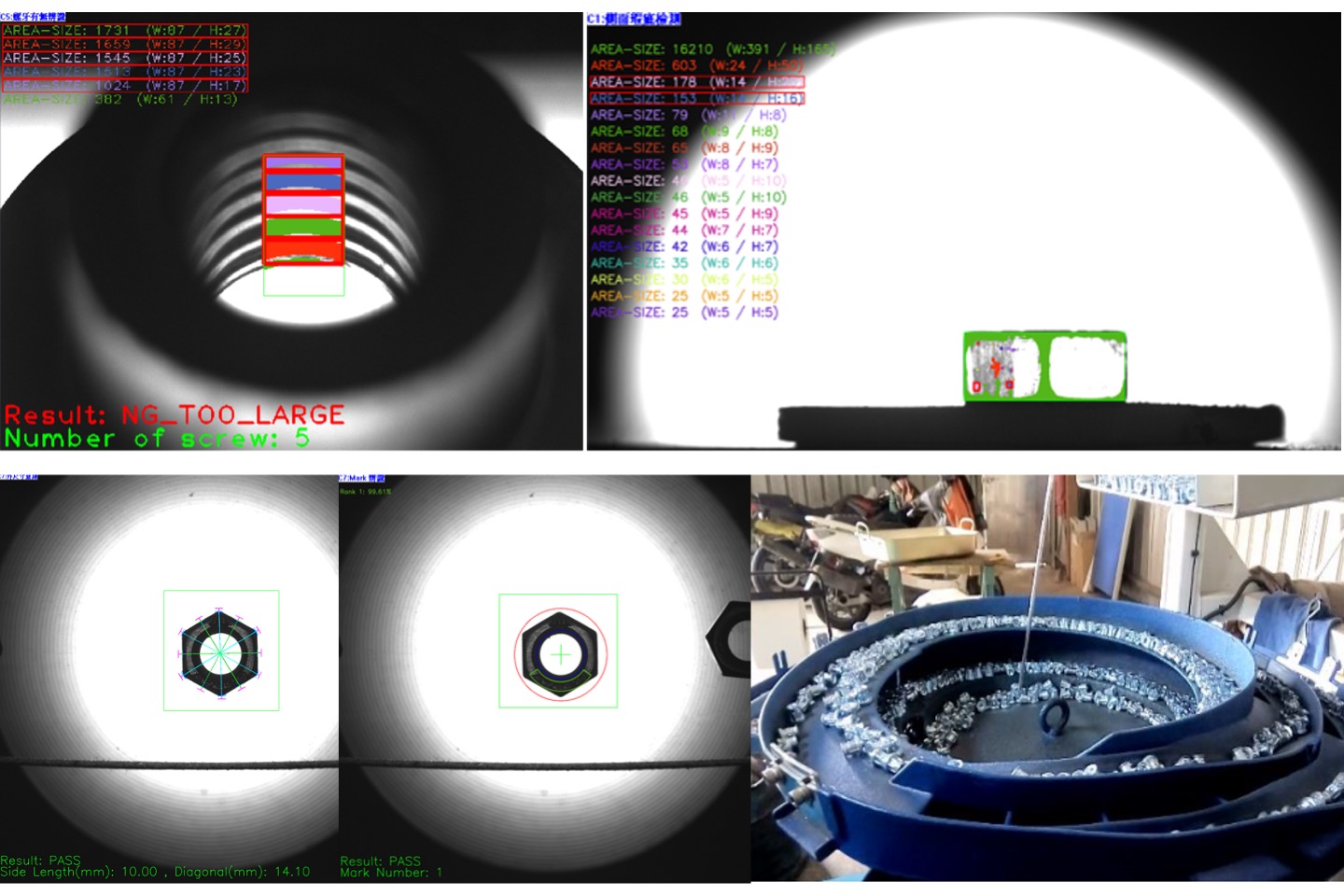

High-speed image-based inspection for nuts
Automatic optical inspection (AOI) system used in this study is a high-speed turntable with more than 600 inspections per minute. The basic principle includes back-projection parallel light illuminating the object to be measured and receiving it with a digital camera on the other side, and automatically transporting single-size nuts through mechanical operation such as vibrating plates, turntables, conveyor belts and other mechanisms. During the sorting process, the same nuts will be automatically sent to a specific inspection location. It needs to pass through approximately 3 to 6 inspection stations according to the inspection requirements in order to meet the inspection standards. Software development concept: with adjustable judgment logic, 3 to 6 inspection stations, and up to 13 types of defect detection (such as size, symmetry, uniformity) and defect classification, high-speed screening of nuts is carried out to facilitate classifying nuts into good quality and various defective grades.
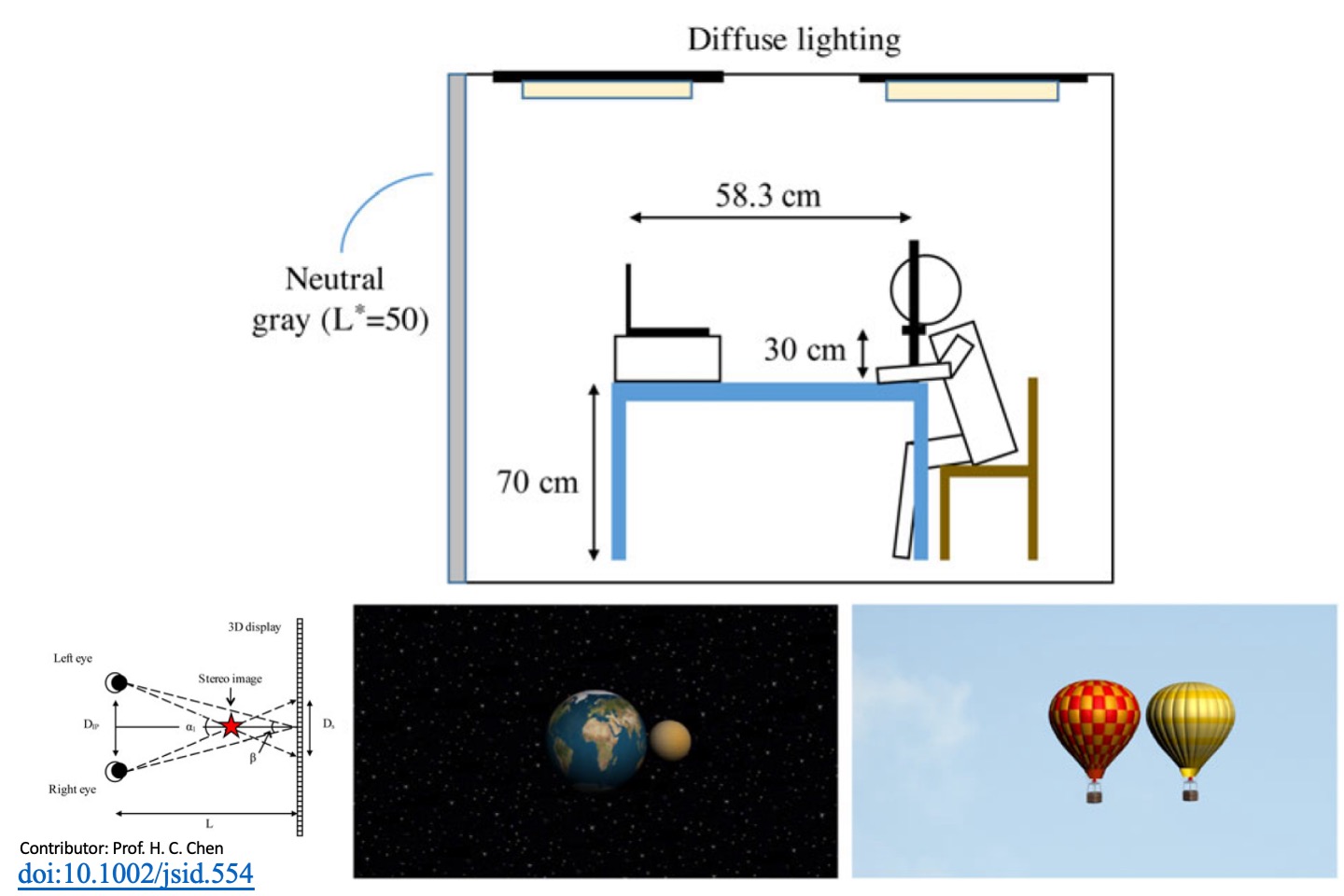

Visual comfort in autostereoscopic display
Autostereoscopic displays are likely to become widely used products in the future. However, certain physiological factors, especially visual comfort, limit their development. In this study, four observational parameters – ambient illuminance, image content, scaling ratio, and horizontal distance between major and minor objects – were evaluated to determine the degree of visual comfort offered by 3D computer-generated images on an autostereoscopic display. Visual comfort score with the range of 0–1 is designed to represent the degree of visual comfort for the 3D images with different manipulations of ambient illuminance, image content, scaling ratio, and horizontal distance between major and minor objects in this study. Subjects were asked to indicate images that produced discomfort. The proportion of images for each condition where participants indicated that viewing the image was comfortable was computed. Images receiving a proportion of 0.5 or greater were classified as acceptable. The disparity ranges over which acceptable images were attained for each participant and for each condition were analyzed with analysis of variance. The analytical results indicate that ambient illuminance and image content have a significant effect on the acceptable disparity range, while scaling ratio and horizontal distance between major and minor objects did not.
H. S. Chen+*, H. F. Wang, C. J. Chou, and T. H. Lin, “Visual comfort in autostereoscopic display,” Journal of the Society for Information Display, 25(5), 2017.
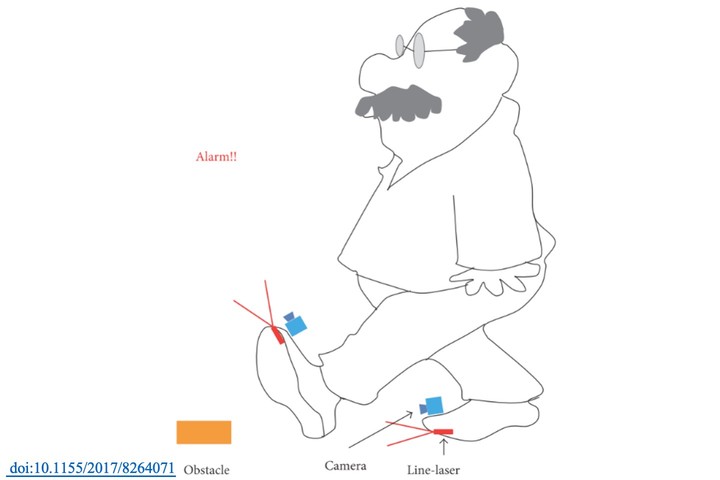

Fall Prevention Shoes Using Camera-Based Line-Laser Obstacle Detection System
Fall prevention is an important issue particularly for the elderly. This paper proposes a camera-based line-laser obstacle detection system to prevent falls in the indoor environment. When obstacles are detected, the system will emit alarm messages to catch the attention of the user. Because the elderly spend a lot of their time at home, the proposed line-laser obstacle detection system is designed mainly for indoor applications. Our obstacle detection system casts a laser line, which passes through a horizontal plane and has a specific height to the ground. A camera, whose optical axis has a specific inclined angle to the plane, will observe the laser pattern to obtain the potential obstacles. Based on this configuration, the distance between obstacles and the system can be further determined by a perspective transformation called homography. After conducting the experiments, critical parameters of the algorithms can be determined, and detected obstacles can be classified into different levels of danger for causing the system to send different alarm messages.
T. H. Lin+*, C. Y. Yang and W. P. Shih “Fall Prevention Shoes Using Camera-Based Line-Laser Obstacle Detection System,” Journal of Healthcare Engineering, vol. 2017, Article ID 8264071, 11 pages, 2017.
2016Y’ achievements

A comparison of watermarking for 3D models under different lighting conditions
Nowadays, digital 3D models become more and more popular, therefore the counterfeiting issue is important. The watermarking is one of the technique to deal with the information of copyright. This paper proposes a method by adjusting the original texture color of a virtual 3D model to generate an invisible color difference as watermarking, and the color adjustment method will generate a just noticeable difference (JND). After the watermark is added, we can apply a specific virtual illuminant to render the virtual 3D model, the color difference between the watermark and the original texture will be enlarged to be noticed. This study focused on the analysis of the color difference quantity under various illuminants.
H. L. Liu, Y. L. Liu, and T. H. Lin, “A comparison of watermarking for 3D models under different lighting conditions,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.

Study on Rendering Ultra High-Resolution Image for 3D Models
Nowadays, it has become much easy to browse the masterpieces of culture art by the virtual museum. With the innovation of emerging technologies, museums now can hold a media art exhibition by using 3D motion sensors, high-resolution displays and virtual reality to reinterpret the artifacts for people. To efficiently render high-resolution images is therefore important. In this paper, we propose a practical solution to render an ultra-high resolution image, which has almost no limitation in image size, for 3D digital heritage model based on OpenGL.
C. C. Lee, Y. L. Liu, and T. H. Lin, “Study on rendering ultra high-resolution image for 3D models,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.
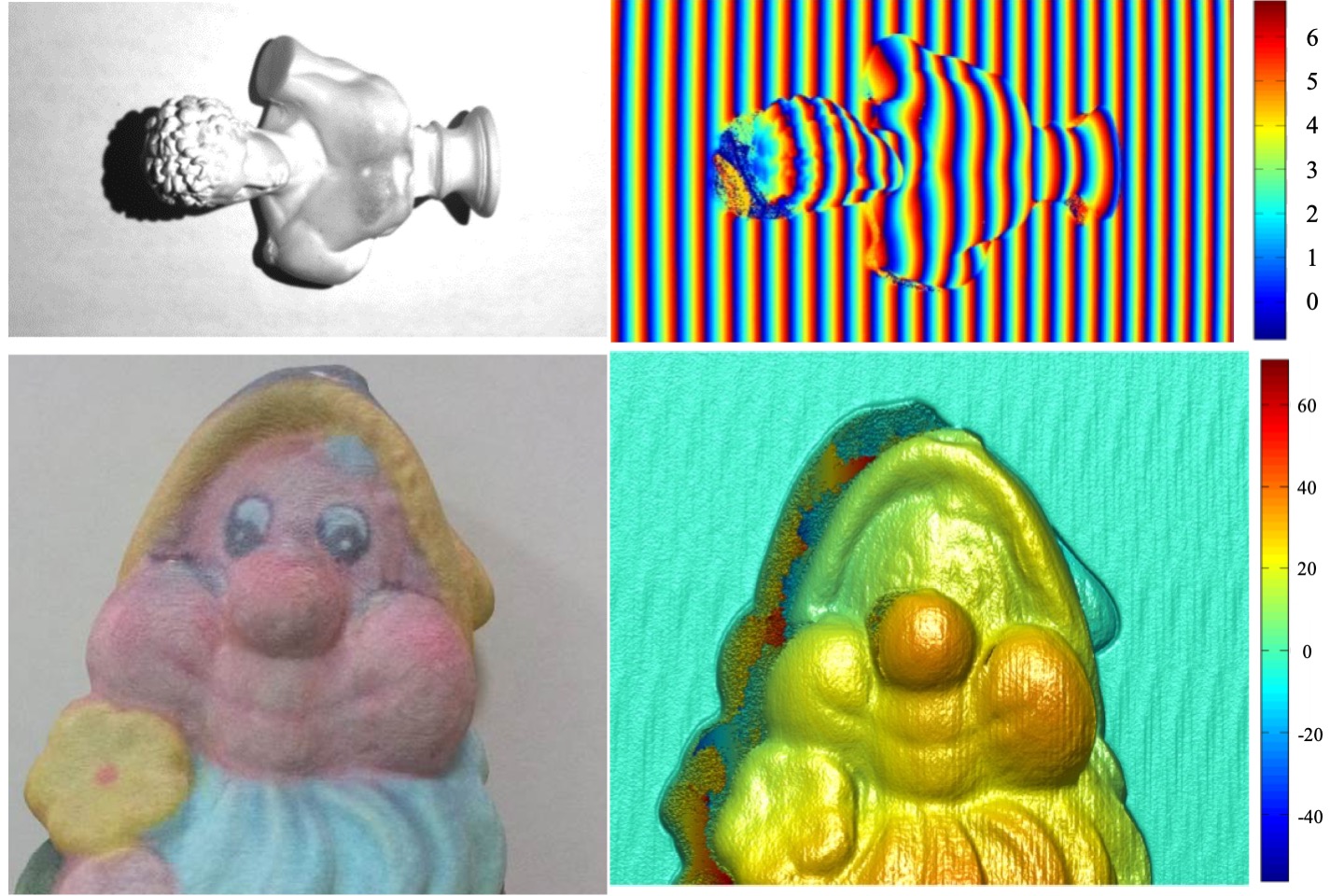


Surface Inspection of Micromechanical Parts Based on the Phase-Shifting Method
Phase-shifting method, which is an optical measurement method and able to detect the surface profiles of the object, has many capabilities including high speed, high resolution and real-time. So, it is one of the most useful solutions for the 3D shape measurement. In this paper, we propose a practical method which is based on phase-shifting method to inspecting the surface quality of micromechanical parts. In optical inspection, the surface material roughness and surface reflection, i.e. color appearance, are always important. Since the material’s reflectivity and absorptivity may affect the 3D measurement, particularly in accuracy. Different surface micromechanical parts are used to compare and verify the measurement result.
T. Y. Hsiao, Y. L. Liu, and T. H. Lin, “Surface quality inspection of micromechanical parts based on phase-shifting methods,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.
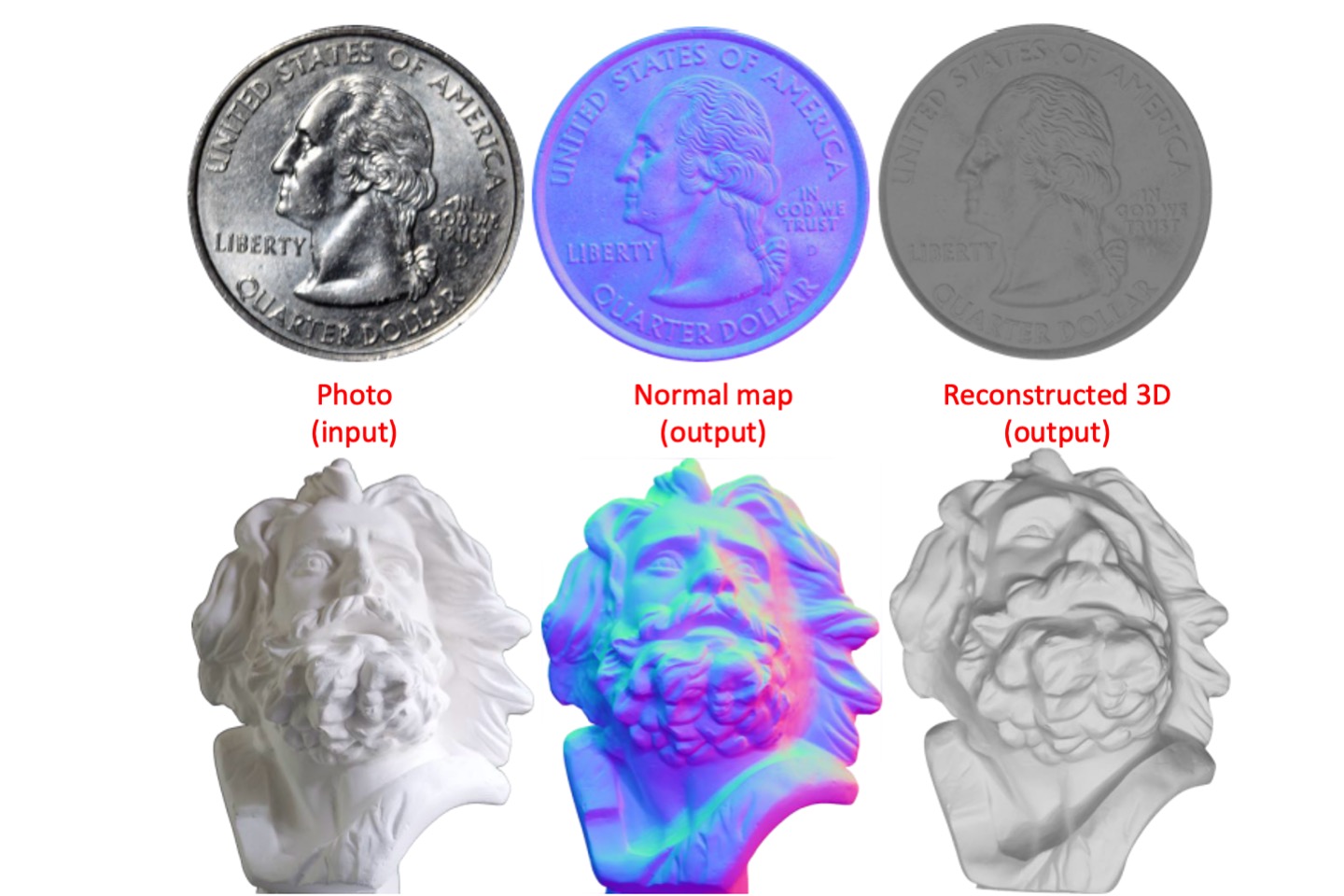

Developing a Photometric Device for generating quality texture and normal maps
Normal map is a well-known texture technology for enhancing the surface detail in shading 3D models, as well as assisting 3D reconstruction. In this paper, we plan to develop a device which is able to generate normal map and recover 2.5D shapes of lambertian objects under a fixed viewpoint and specific lighting conditions. Our method is based on photometric stereo and spherical harmonics algorithms. Photometric stereo is the first approach to obtain rough surface normals. Moreover, current researches have already proofed that spherical harmonics can recover lambertian lighting conditions in low-dimension and linear subspace. Thus, the quality improvement in our result is therefore verified.
Y. C. Chen, and T. H. Lin, “Developing a photometric device for generating quality texture and normal map,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.
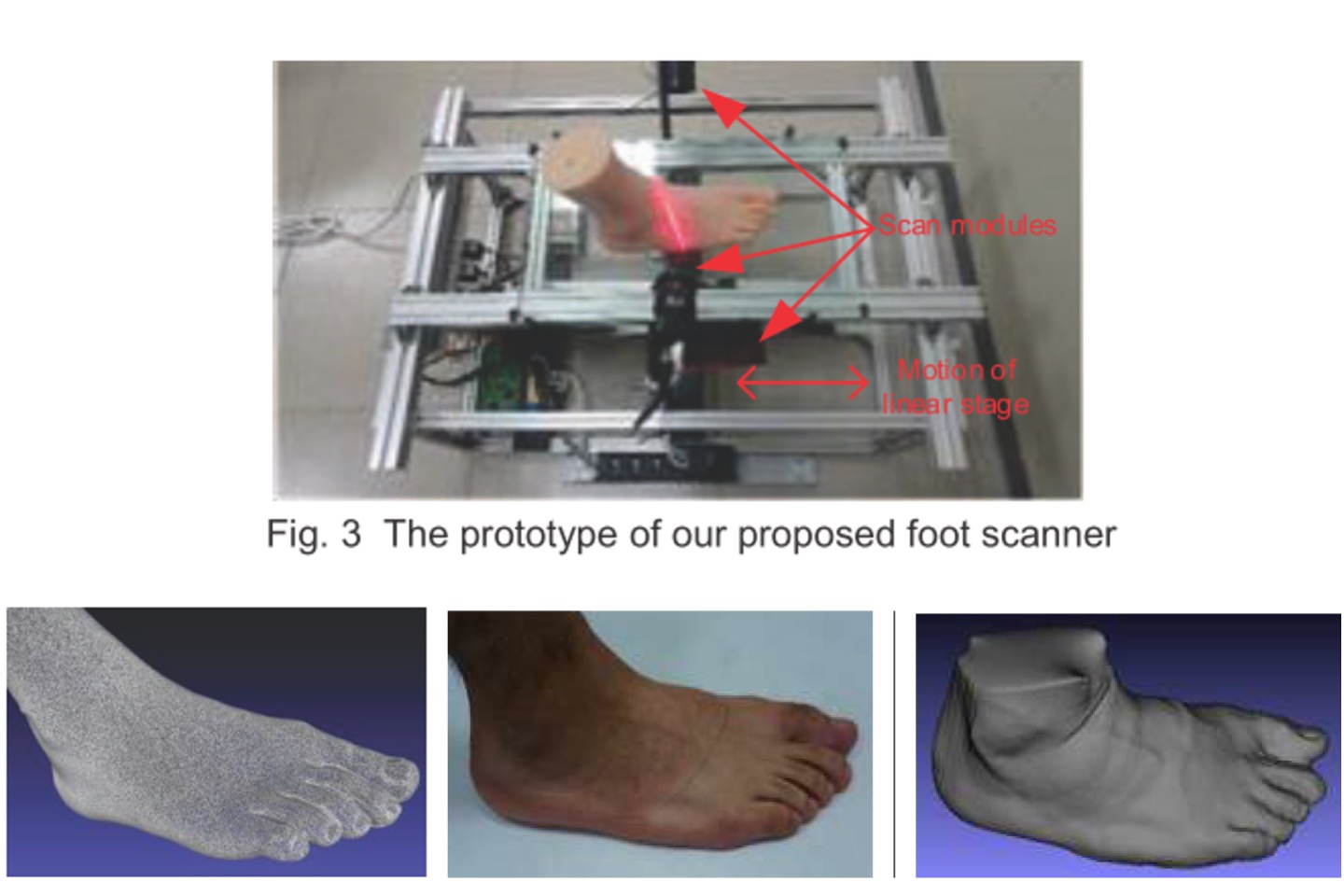

Developing a Foot Scanner Based on Multiple Laser Triangulation Scanners and One Linear Stage
This study presents a self-developed foot scanner by using three scanner modules, a linear stage, and a software algorithm to obtain 3D foot models. The scanner uses a common reference checkerboard that acts as the coordinate system of the object. Thus, different scanner heads reconstructed models are in the same coordinate system, and therefore automatically together, no need to locate them.
W. Huang, and T. H. Lin, “Developing a foot scanner based on multiple laser triangulation scanners and one linear stage,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.
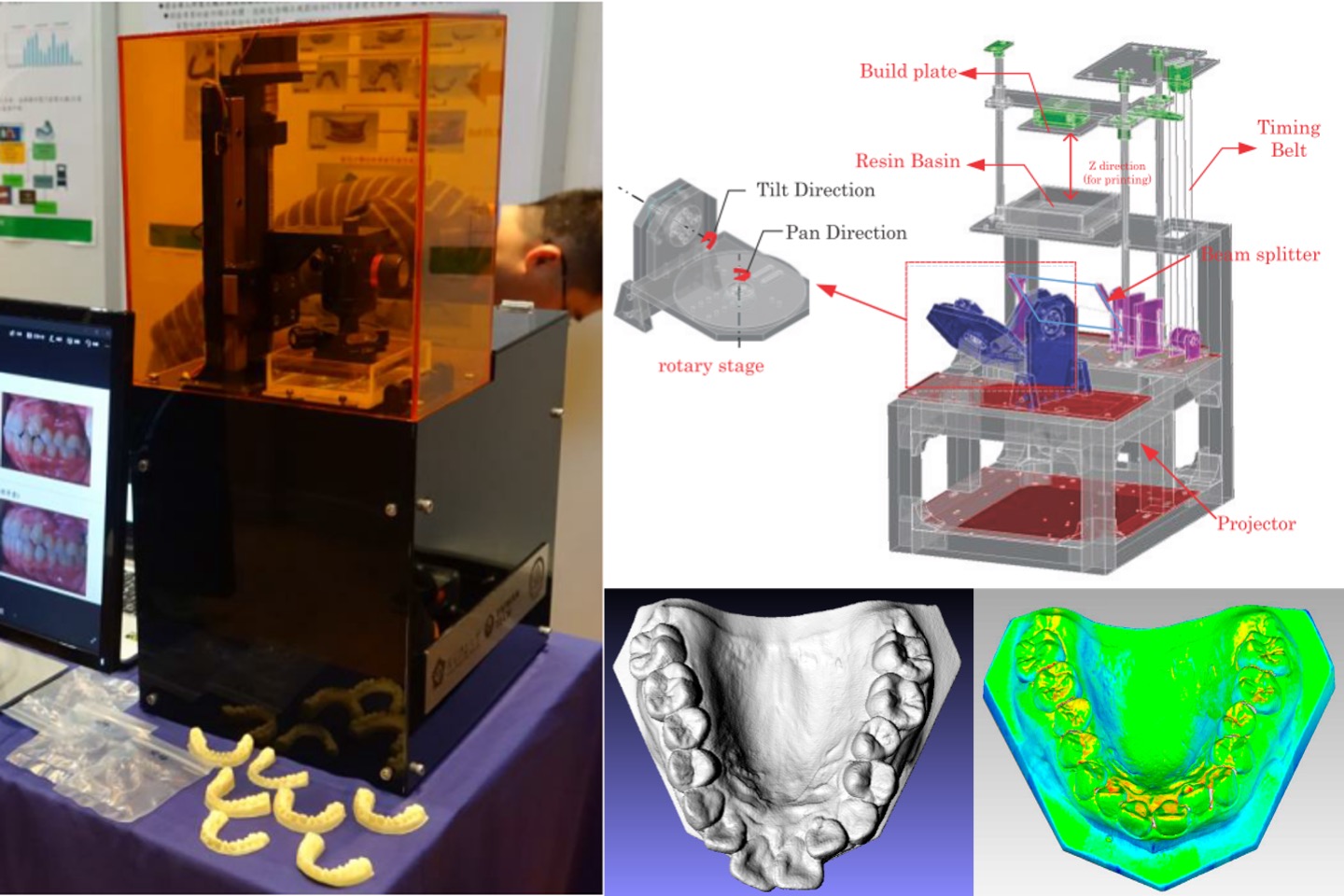

Two-in-one 3D scanner and printer
We have developed a 2-in-1 3D scanning and printing machine that comprise a high-power projector as the main component of the 3D scanner and 3D printer. We use a linear motor to drive the platform to achieve the light-curing 3D printing. It is also equipped with a dual-axis rotation motor device and an industrial camera to carry out automated 3D scanning functions. This device is designed for scanning dental molds, printing dental molds, and tooth braces-related applications.
Y. L. Liu, H. T. Yau, R. S. Lin, Y. J. Chen, T. H. Lin, and J. Y. Jeng, “A two-in-one system of structured light scanner and light cured printer,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.
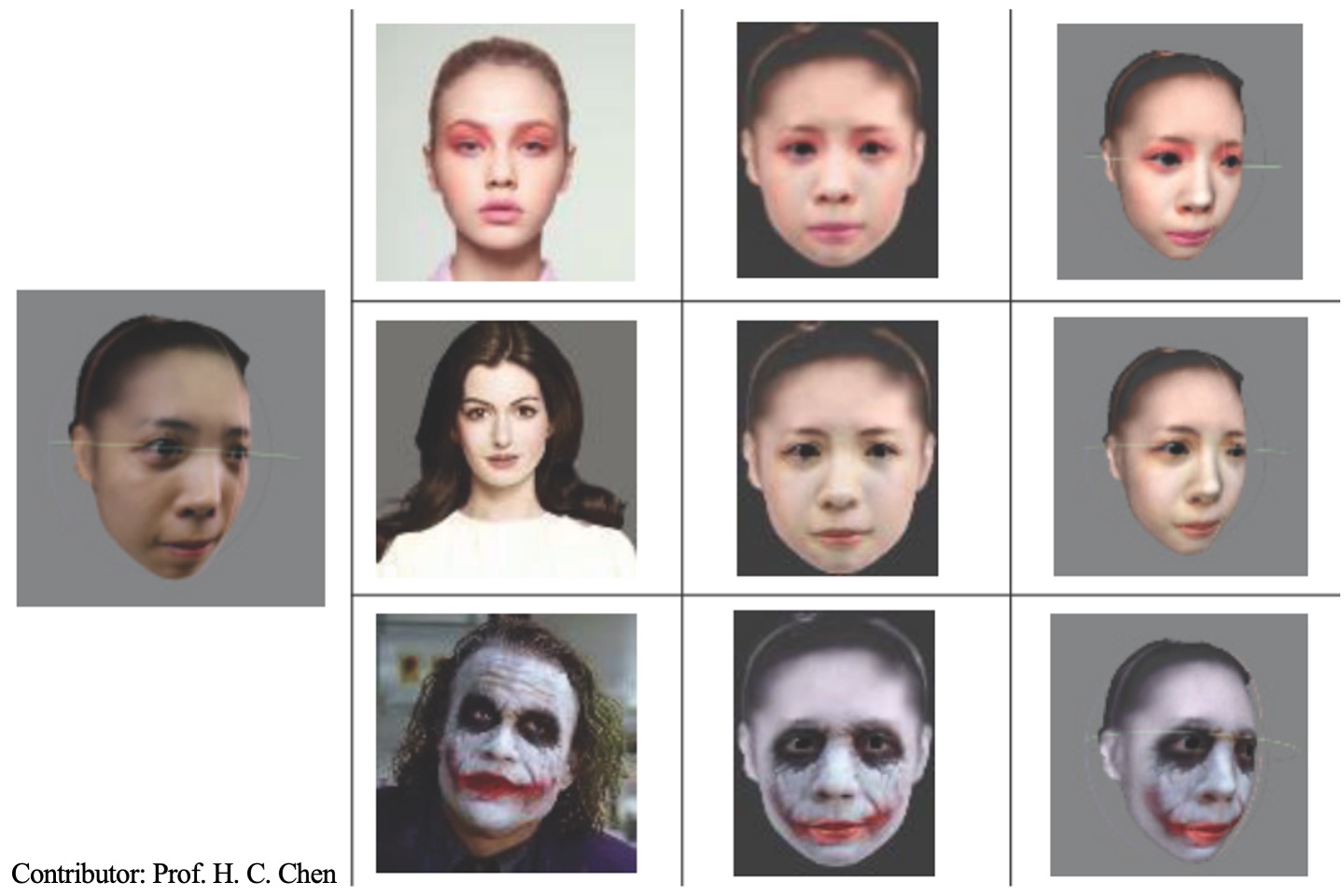


Digital cosmetic coloring system for 3D facial images
This study aims to develop a 3D-automatic facial makeup system, which is able to simulate make-up 3D-model and print 3D-model based on the selected reference image. We utilize affine transformation to establish the geometrical relationship between the reference image and the scanned 3D model, then perform a computer-simulated makeup 3D model.. Finally, this model is printed again by a color 3D printer under a proper color manager engine of our makeup system.
M. H. Lin, Y. P. Pi, H. S. Chen, P. L. Sun, and T. H. Lin, “Digital cosmetic coloring system for 3D facial images,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 16’), Dec. 7-9, 2016 Fukuoka, Japan.
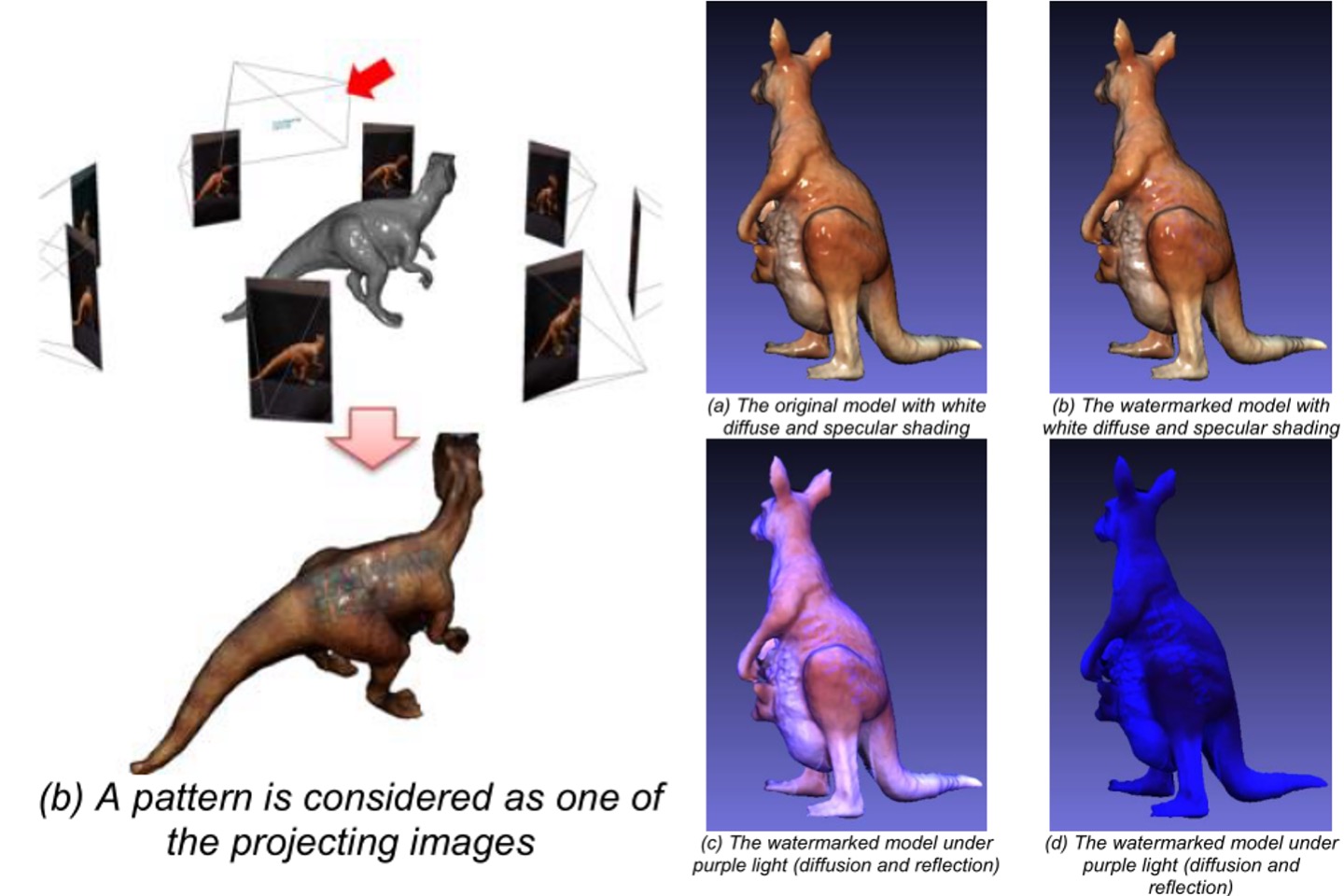

Hidden watermark of 3D models by just noticeable color difference
A watermark is a subtle pattern on images or documents to prevent counterfeiting. For color 3D models, it is feasible for add watermarks on either texture images or vertex colors, as well. We propose a hidden watermark method by superimposing a just noticeable difference pattern on 3D color models. The color difference on the watermark is too small to be noticed and it will be enlarged under specific lighting conditions in the computer graphics environment. This idea is very similar to the anti-counterfeit label on most banknotes. Thus, the watermark is almost invisible when rendering under formal white lights, but visible under violet lights.
T. H. Lin, “Hidden watermark of 3D models by just noticeable color difference,” Electronic Imaging 2016, Poster, Feb. 14-18, 2016, San Francisco, USA.

Multi-camera real-time 3D foot shape acquisition
We utilized 6 depth cameras (passive/stereoscopy) with specific projection stripes to capture the appearance of 3D feet in real time.

3D Color slicing and blending
We optimize the color bleding of color 3D printing slicing, which is able to adapt to various forms of models. It supports file formats such as texture mode and vertex color, and takes into account the manifold problem. It is suitable for powder bed Jet-binding and photo-curing mode 3D printing.
2015Y’ achievements
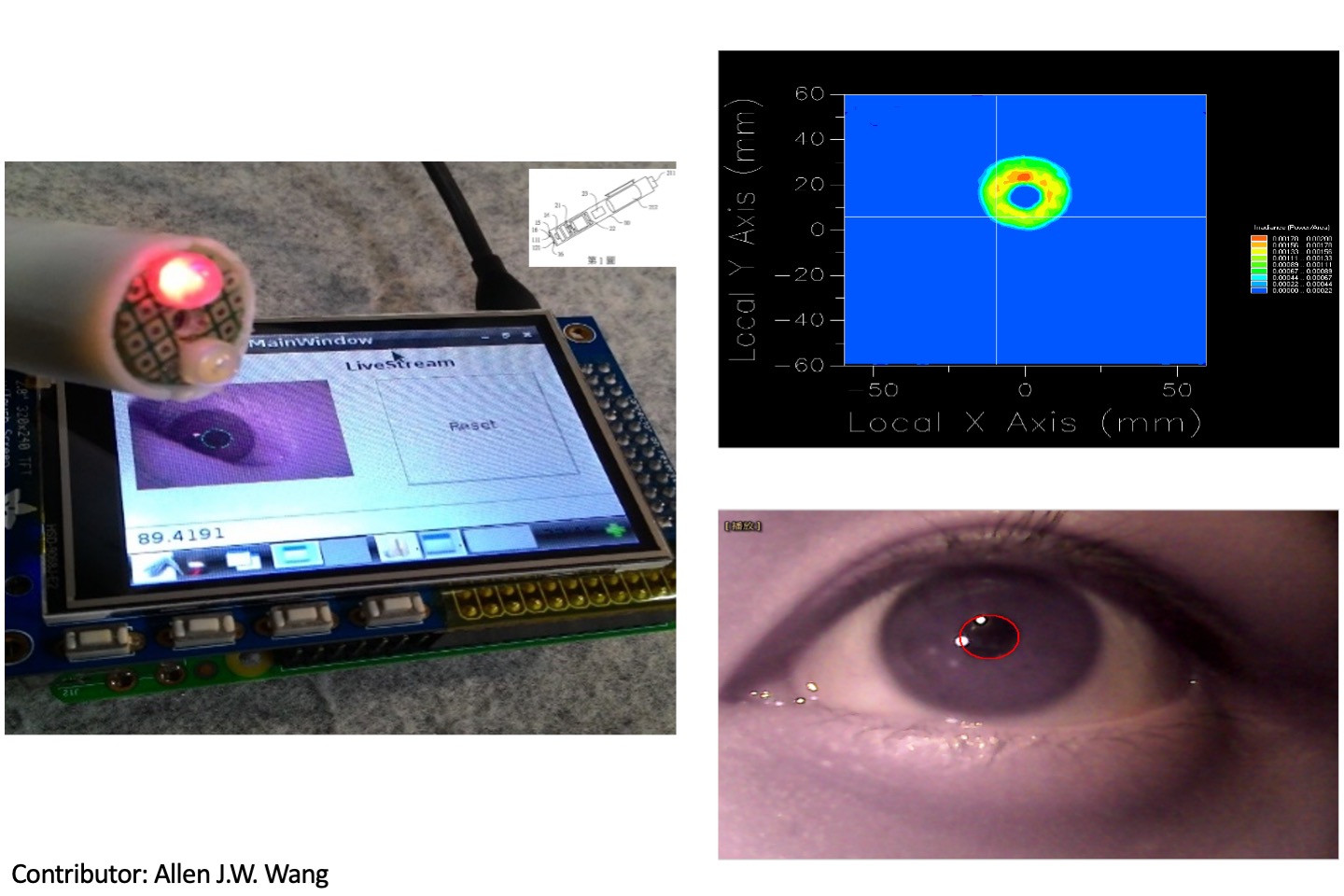

Pupil size detection
We developed a pupil size detection device as well as the pen shape. The front of this device equipped with a miniature camera and tiny light bulb. With a special optical design for the light bulb, camera lens, and an embedded system, we can use image analysis technology to detect and extract the position and size of the pupil, and its computing efficiency can achieve real-time. This will assist hospital nursing staff in observing patients in the front end.
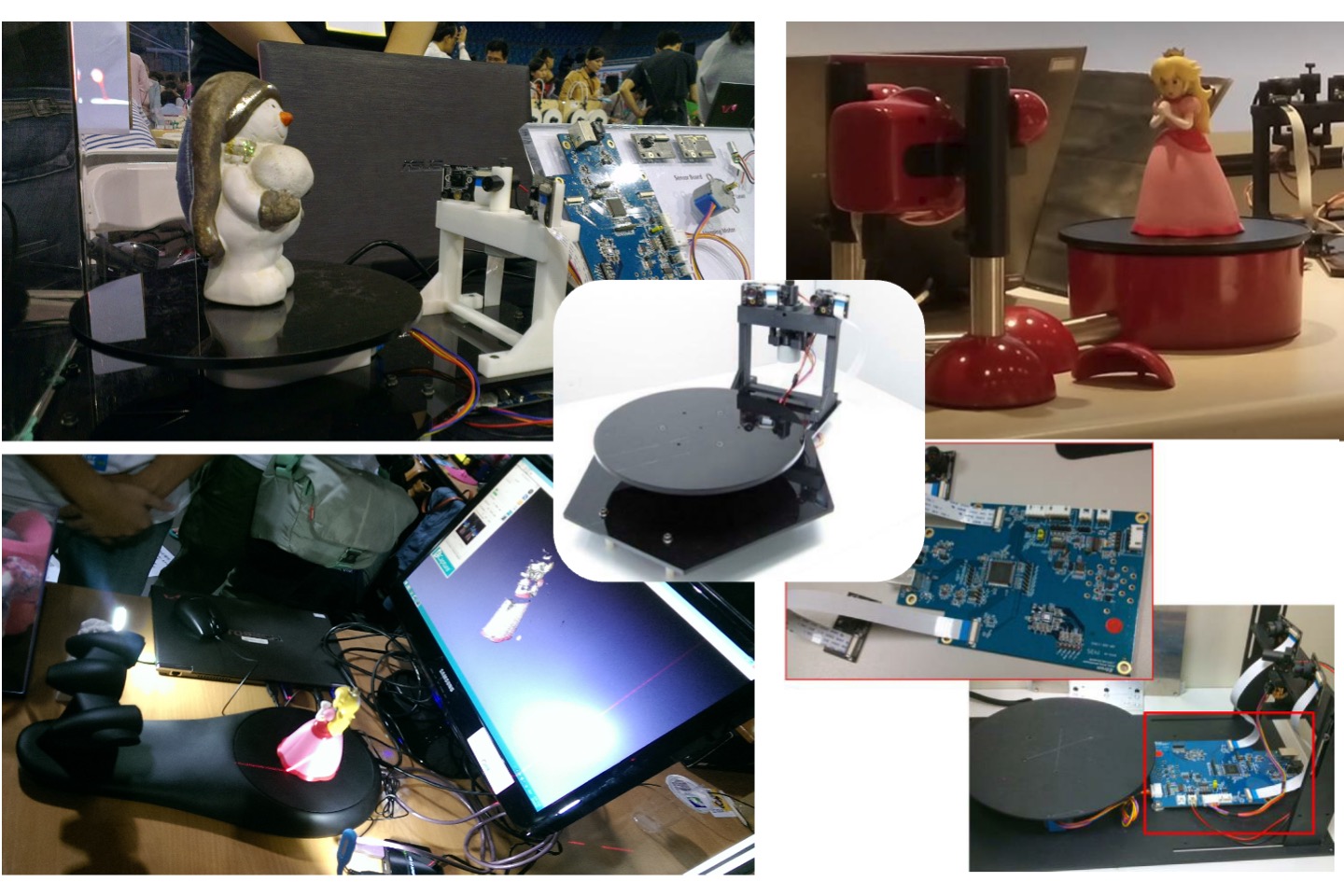


DIY Color 3D scanner (Cloud Funding)
We converted our owned 3D scanning technology into a DIY assembly kit. In this kit, we used a lot of Maker elements. For example, the gear structure and other mechanical components were created through 3D printing and laser cutting machines. We have also developed an assembly manual to guide students, and integrate with our self-developed core algorithm, they can assemble a low-cost and high-quality automatic color 3D scanner.

Study on Generating Binary Colors for Monochrome 3D Intraoral Laser Scanner
Nowadays, the intraoral scanner has become more and more popular for orthodontic treatment. However, most of current intraoral scanners can’t automatically recognize the difference between the crown and gingiva. This is a very important information for dentists to operate the orthodontics. In this paper, we present an intensity compensation method to separate the crow and gingiva. Based on the laser scanner, we analyze the energy decay due to the geometry of teeth and laser distance. Then we correct it according to a plane surface to reduce the geometrical effect, and the estimated lighting energy can actually represent the material property to separate the crown and gingiva.
Y. L. Liu, Y. C. Chen, T. H. Lin, and P. C. Hu, “Study on generating binary colors for monochrome 3D intraoral laser scanner,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 15’), Poster, Dec. 9-11, 2015, Otsu. Japan.

Developing a Quality Normal Map Acquisition Device Based on LED Array
Nowadays, 3D models with various textures, such as diffusion, bump and normal maps, are used for representing high quality visualization. To emphasize the surface details, normal maps are usually the most important. This study focuses on how to general normal map from a self-fabricated device. A normal map indicates the local surface geometry which is stored as R-G-B pixels to represent local [x, y, z] vectors. Therefore, we propose a practical solution to directly retrieve image channels with corresponding lighting sources to synthesize a quality normal map.
C. H. Wang, Y. L. Liu, and T. H. Lin, “Developing a quality normal map acquisition device based on led array,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 15’), Poster, Dec. 9-11, 2015, Otsu. Japan.

Slicing and Halftoning Algorithm for High Quality Color 3D Printing
We utilized high translucent printable materials to simulation the printed model. We focus on rebuild surface color for 3D models by voxelizatoin. We propose four methods to evaluate the overall quality. From simulation data, the hybrid method is much close to our expectation. This method induces better color boundary, and the inside color are more vivid than the other methods, says the color is close to the original color. For a CMYW 3D printer, we have to dither the tone color into halftone color with CMYW palette. It also proves that our solution can satisfy a smooth quality and acceptable efficiency. In the future, if there is any new demand or technological progress in 3D printing, the proposed method would be expanded to match the new characteristics.
C. I. Lin, Y. P. Sie, T. H. Lin, and P. L. Sun, “Slicing and halftoning algorithm for high quality color 3D printing,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 15’), Poster, Dec. 9-11, 2015, Otsu. Japan.

Color Correction Operations for 3D Scanning Images
We implemented the polynomial regression for correcting the color information and luminance distortion of 3D scanned models. Additionally, the evaluations of 3D luminance correction for 3D scanning image were performed in terms of color difference, luminance curve plot and contrast ratio.
K. L. Chan, H. Y. Hsiao, T. H. Lin, and H. S. Chen, “Evaluation of Color correction operation for 3D scanning models,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 15’), Oral, Dec. 9-11, 2015, Otsu. Japan.
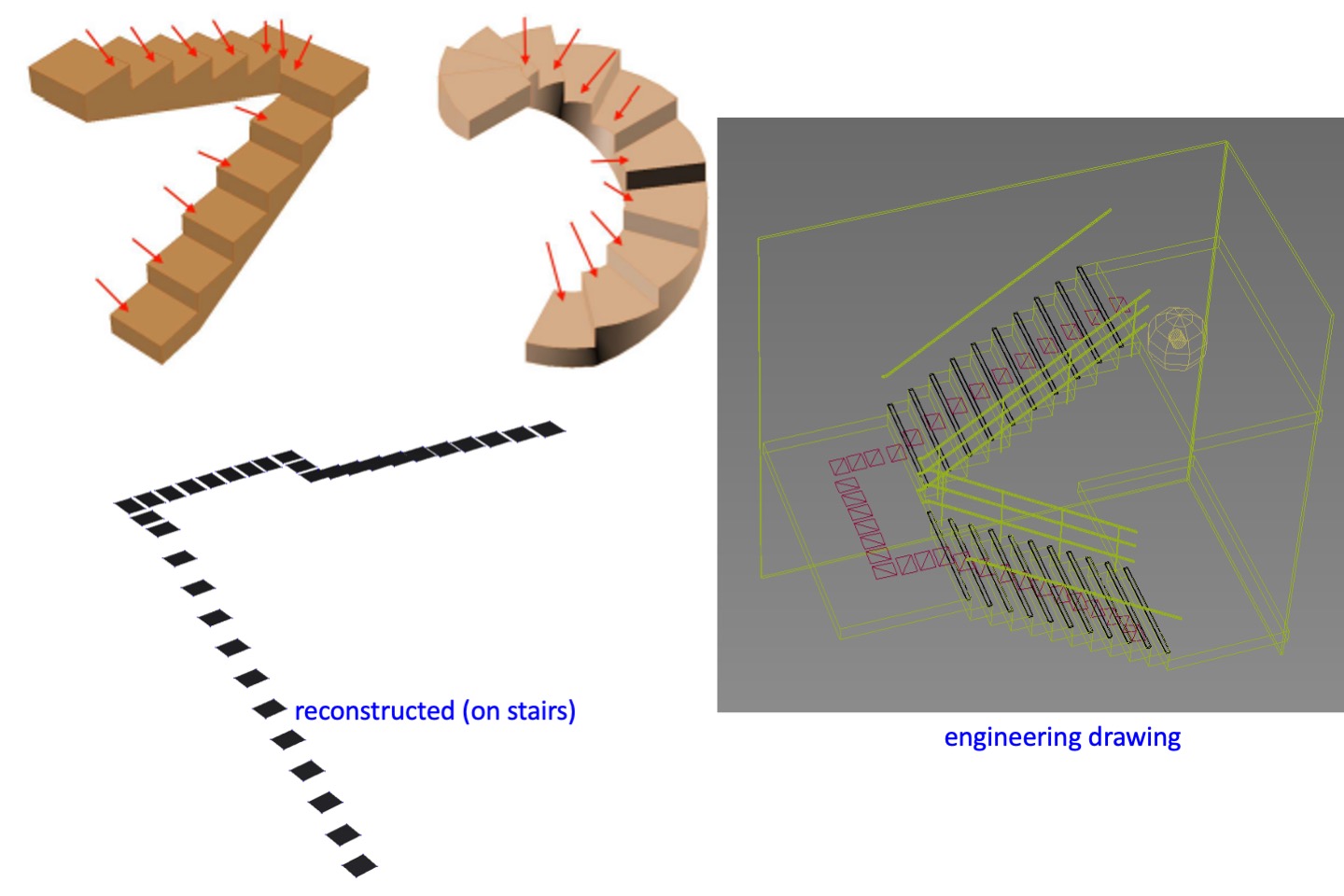

Stair measurement for creating track of lift chair (image 3D)
Stair lifts are one kind of elevators commonly used in low-rise buildings and are often used as barrier-free space tools. Its track must be laid along the stairs, which is often not easy to measure accurately. In order to solve the 3D reconstruction of the staircase, we use image 3D reconstruction. Through a self-designed specific calibration plate, we can measure and 3D coordinates between each staircase, and use this information to assist the construction of the staircase model, and then go one step further. It achieves the goals of track planning and advance design, and avoids frequent construction modifications caused by inaccurate measurements.
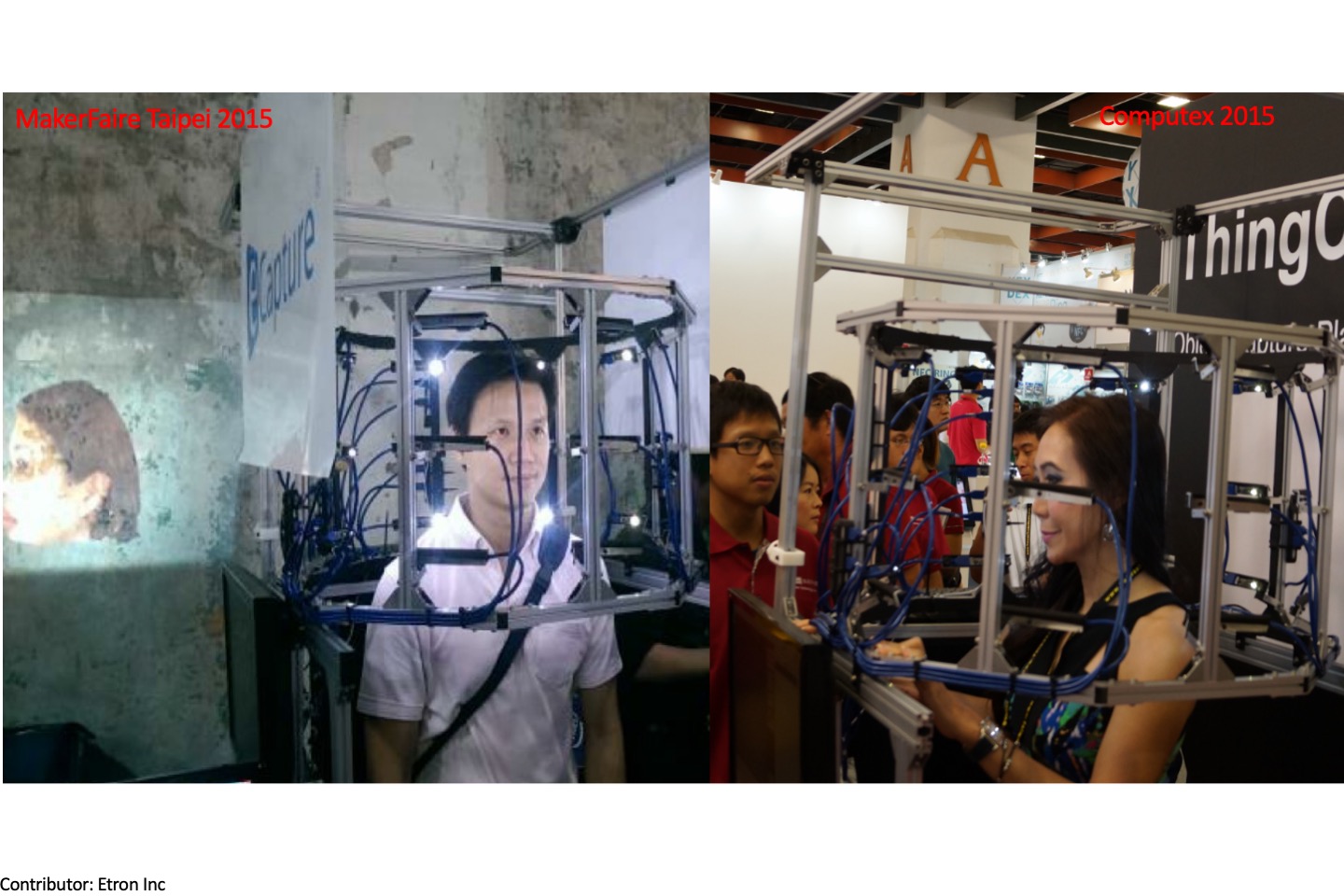


Multi-stereo-camera array for 3D real-time photography
We utilized 24 stereo cameras (Etron Inc), which are arranged and distributed in a dome shape. These 24 stereo cameras are synchronized through high-speed USB and can record up to 15fps. Therefore, we can capture a certain moment of 3D models/people/animals and record them, save data as 3D models immediately.


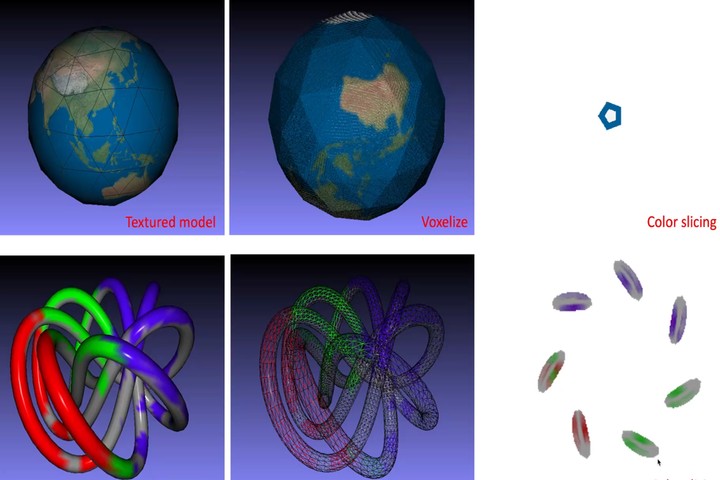
Voxel-based and Segment-based 3D slicing algorithm for Color 3D printing
This technology mainly develops the 3D slicing software for color 3D printers. Since the color is only recorded on the surface of 3D models, different 3D printing methods require different cutting modes. We have developed 3D slicing for FDM (fused deposition modeling, as line segmented color interpolation) and voxel-based 3D slices (Powder binder , voxel color mixing).
2014Y’ achievements


Portable 3D scanner (Steroscopy)
This technology utilized a depth camera (Etron Inc), stereoscopy type, and a tablet computer to continuously capture depth images (as well as triangular meshes), and through the patch stitching of continuous depth and 3D images, finally a complete 3D model can be obtained.
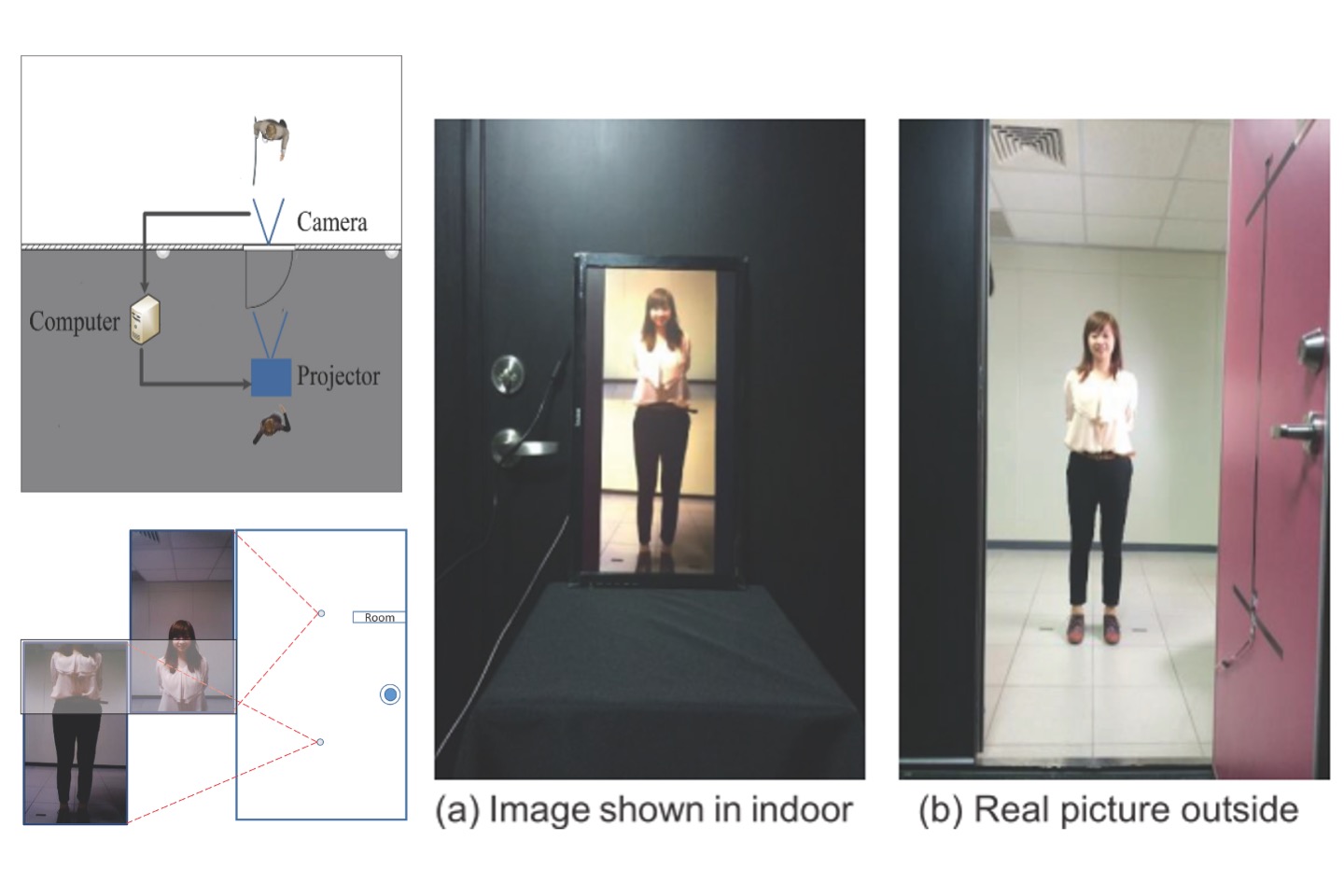

Security Door
This paper presents a practical “security door” to create an illusion of seeing outdoor view through the indoor. This illusion is achieved by transferring information from two cameras which are disposed at outdoor area, and then their images are cast on the indoor by a display.
H. F. Wang, C. C. Lan, J. Y. Huang, T. H. Lin, H. S. Chen, “Security Door,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 14’), Oral, Dec. 2014, Niigata, Japan.

Study of realistic color painting for 3D models
This paper discusses a practical solution of color texture mapping. In this paper, we try to map the high quality color texture, particularly from physical measurement, on the 3D teeth model in order to construct a realistic 3D teeth model. Traditionally, the 3D model from 3D scanners is not good at both geometry resolution and color quality. To improve the appearance of 3D model, we use a painting tool to paint a 3D scanned model by the measured colors. In the result, several realistic teeth models are compared to different RGB measurements.
C. C. Lan, H. F. Wang, T. H. Lin, P. C. Hu, H. S. Chen, “Study of realistic color painting for 3D models,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop (IDW 14’), Poster, Dec. 2014, Niigata, Japan.
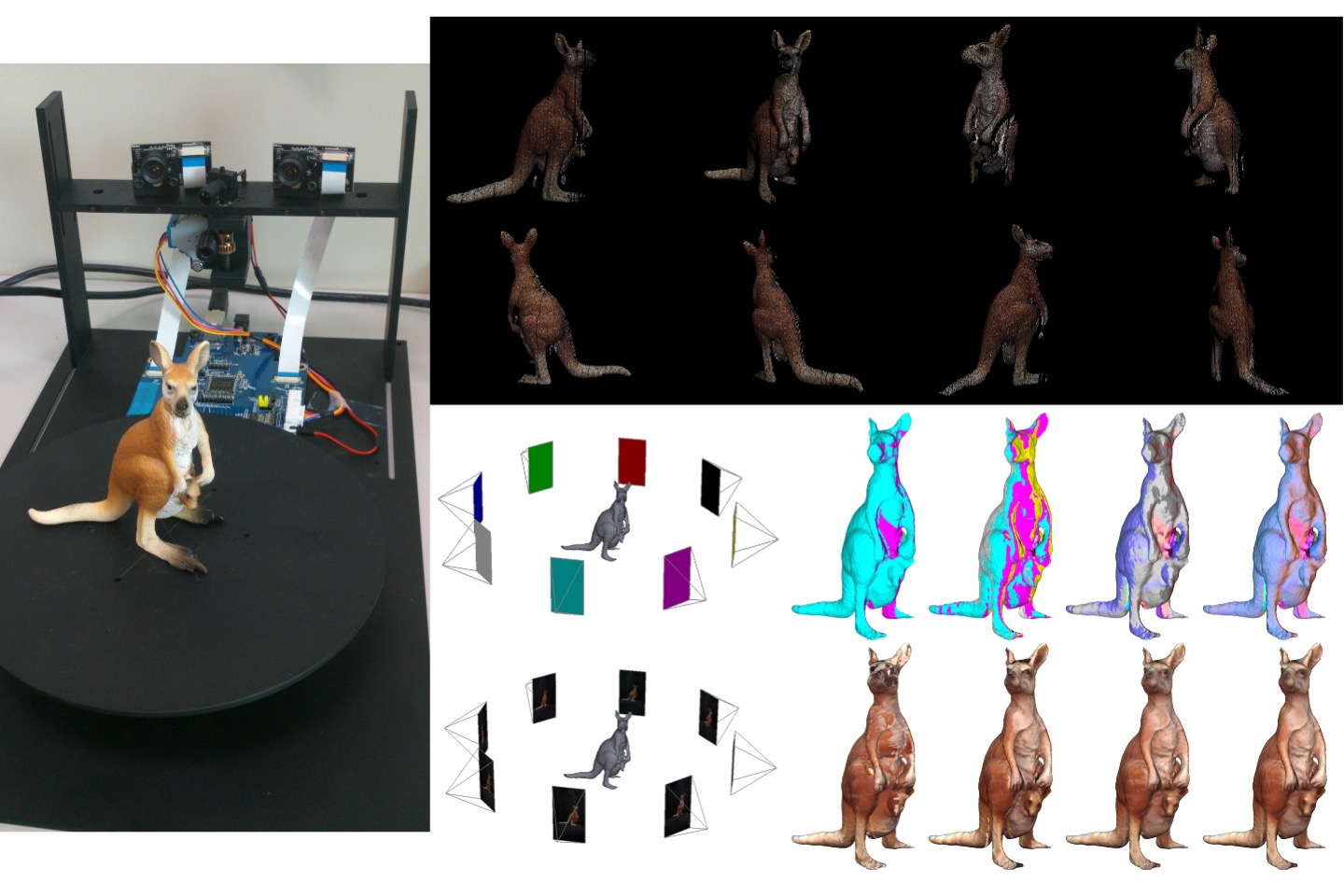

Multiview texture blending technology
For color texture processing, we integrate relationship between the constructed 3D model and the camera coordinate. We colorize each vertex or each triangle mesh on the model through 3D projection. This problem involves many aspects such as: data type, spatial occlusion/interference of meshes, consideration of the visibility of points and surfaces, and multi-view edge seam issues. Since each camera face may see the same surface on a model, there are concluded to be multiple possibilities when determining the model color. Therefore, hybrid mapping methods are developed, as well as light source uniformity correction (solved on the front end) and other methods to solve the problem. The experimental results show that from right to left: the weighted blending map in the visible view direction, the average blending map in the visible view direction, the most frontal direction map, and the photo order priority decision map.
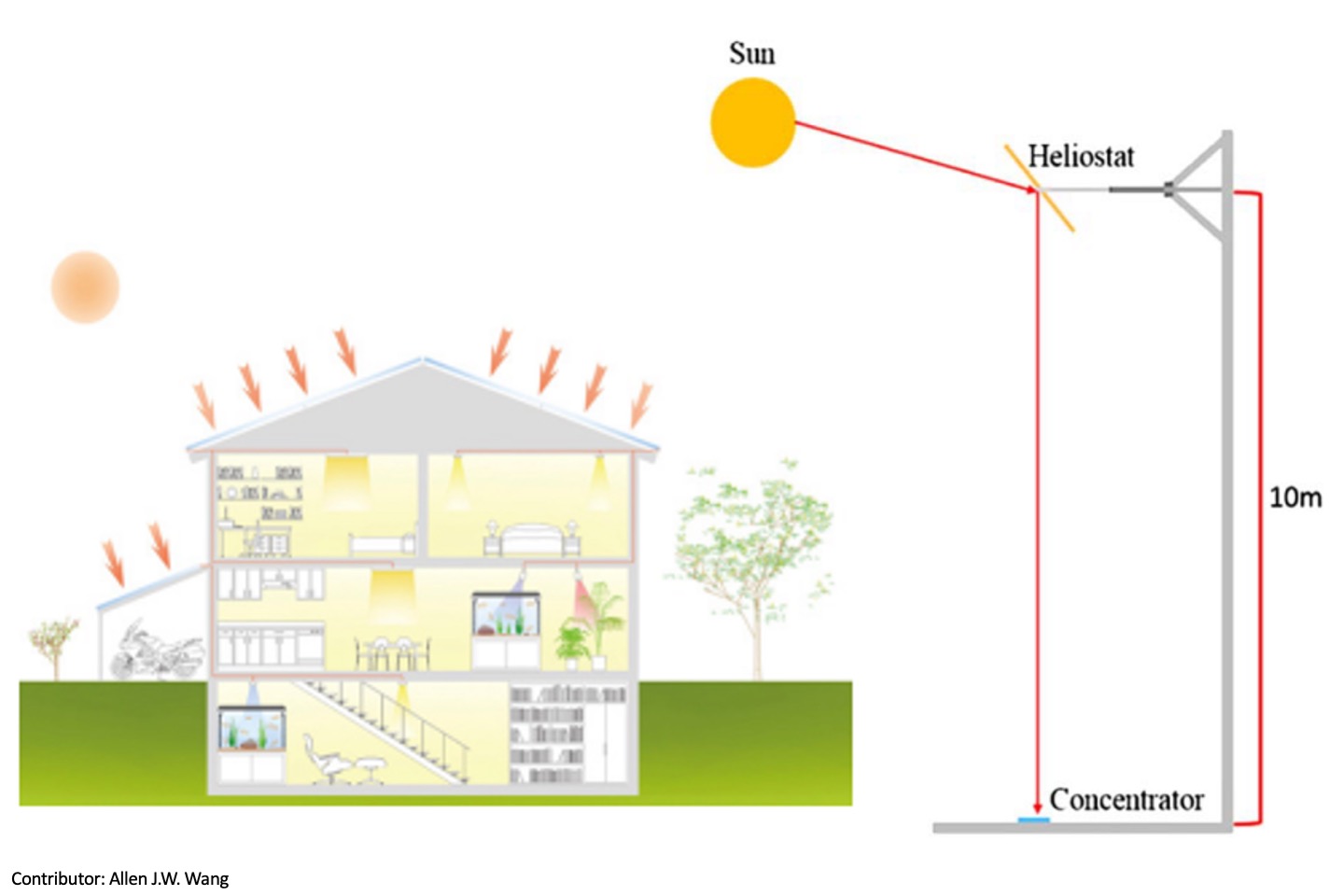

Heliostat design for the daylighting system
The daylighting system is designed to guide sunlight into buildings for illumination. It has the best illumination performance when sunlight vertically impinges on the collector of the daylighting system, while it has low performance when sunlight impinges obliquely. To overcome the problem, this paper investigates the design of a heliostat that reflects sunlight vertically onto a daylighting system. This study proposes 3×3 mirror matrix heliostat, which is different from the traditional heliostat with one single mirror. With the heliostat, the system efficiency increases as high as 3.32 times.
C. H. Chang, H. C. Hsiso, C. M. Chang, C. Y. Wang, T. H. Lin, Y. Y. Chen, Y. L. Lai, C. J. Yen, K. Y. Chen, and A. J. W. Whang*, “Heliostat design for the daylighting system,” Applied Optics, 53(29), pp. H165–H169, 2014.
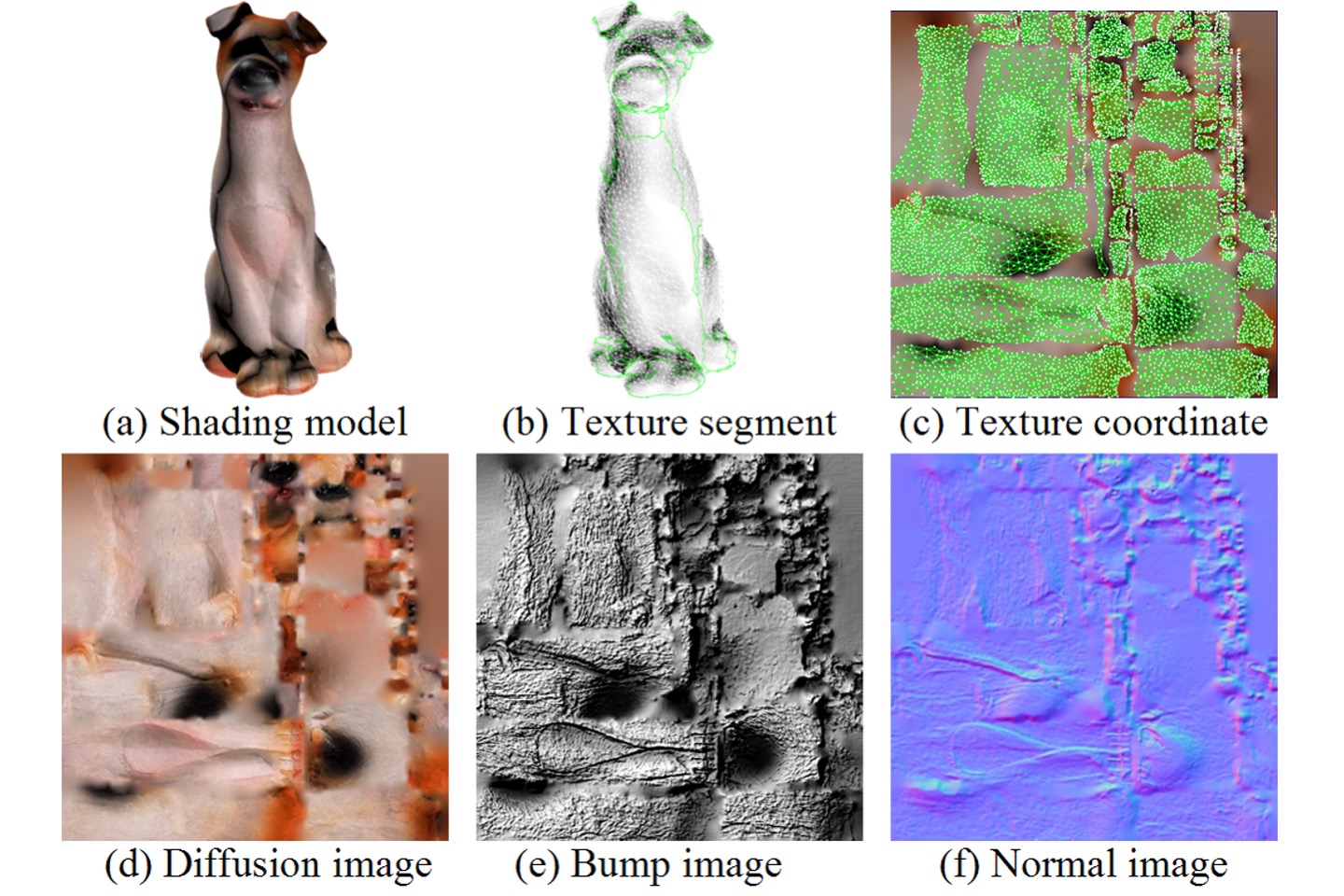

Study on realistic texture mapping for 3D models
This paper discusses the comparison of the visual appearances of 3D texture models. In this paper, we collected ten 3D digital models and each model is illustrated by three types of texture maps, says diffusion, bump and normal maps. All of these models are created by the image-based modeling method. In most cases, the normal map will improve the visual reality of 3D model appearance. However, the bump map and normal map are generated by software and may fail in specific conditions. Nevertheless, it is worth for improving the quality in rendering a 3D model.
T. H. Lin, C. C. Lan, C. H. Wang, and C. H. Chen, “Study on realistic texture mapping for 3D models,” International Conference on Information Science, Electronics and Electrical Engineering (ISEEE 2014), Oral, April 26-28, 2014, Sapporo, Japan.
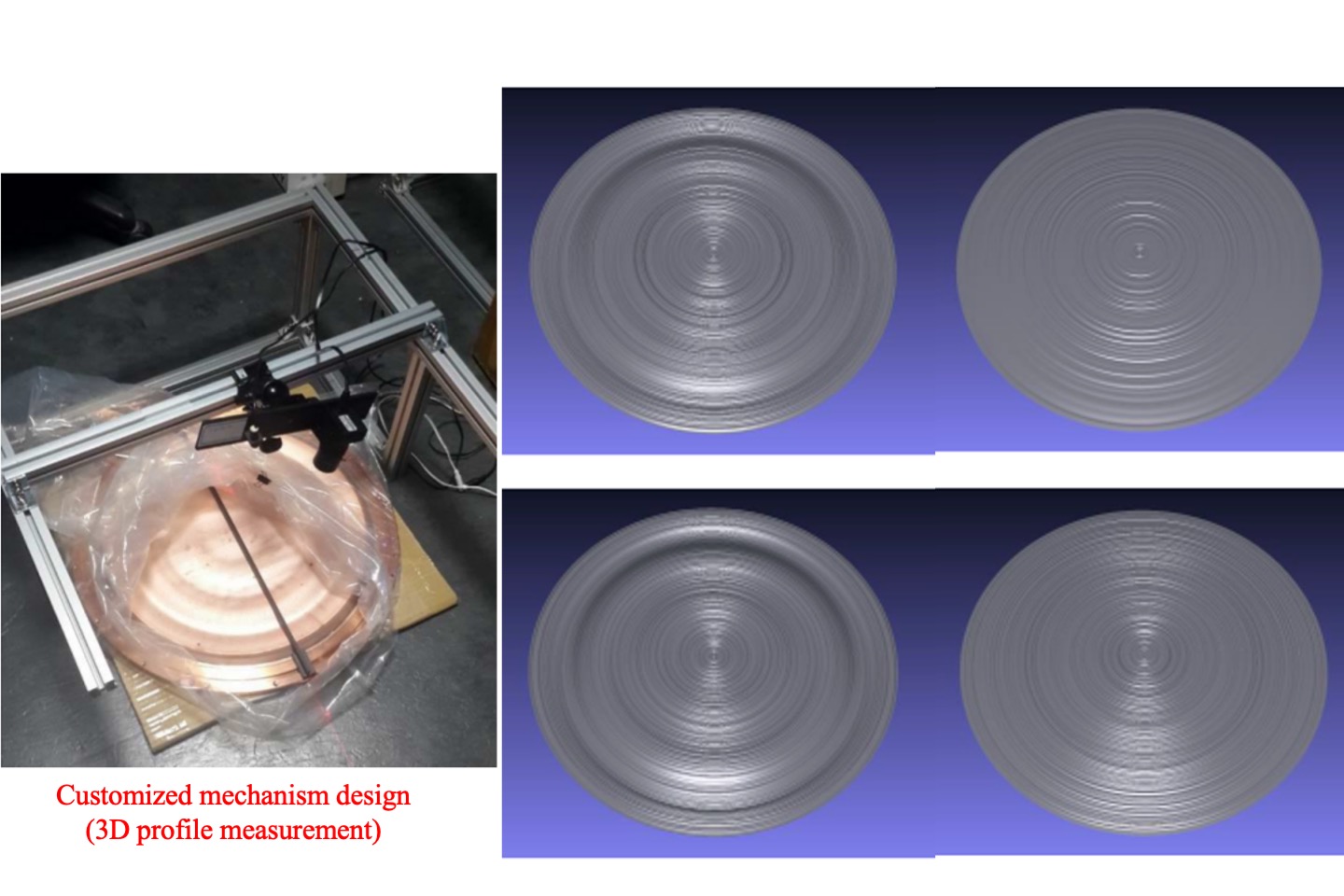


Profile and 3D surface measurement for sputtering Targets
A customized 3D scanning service for industrial companies. This kind of material is the mainly used in IC-manufacturing which is extemely expansive. To avoid wasting during processing, our device can monitor the profile to assist for optimized manufacturing parameters.
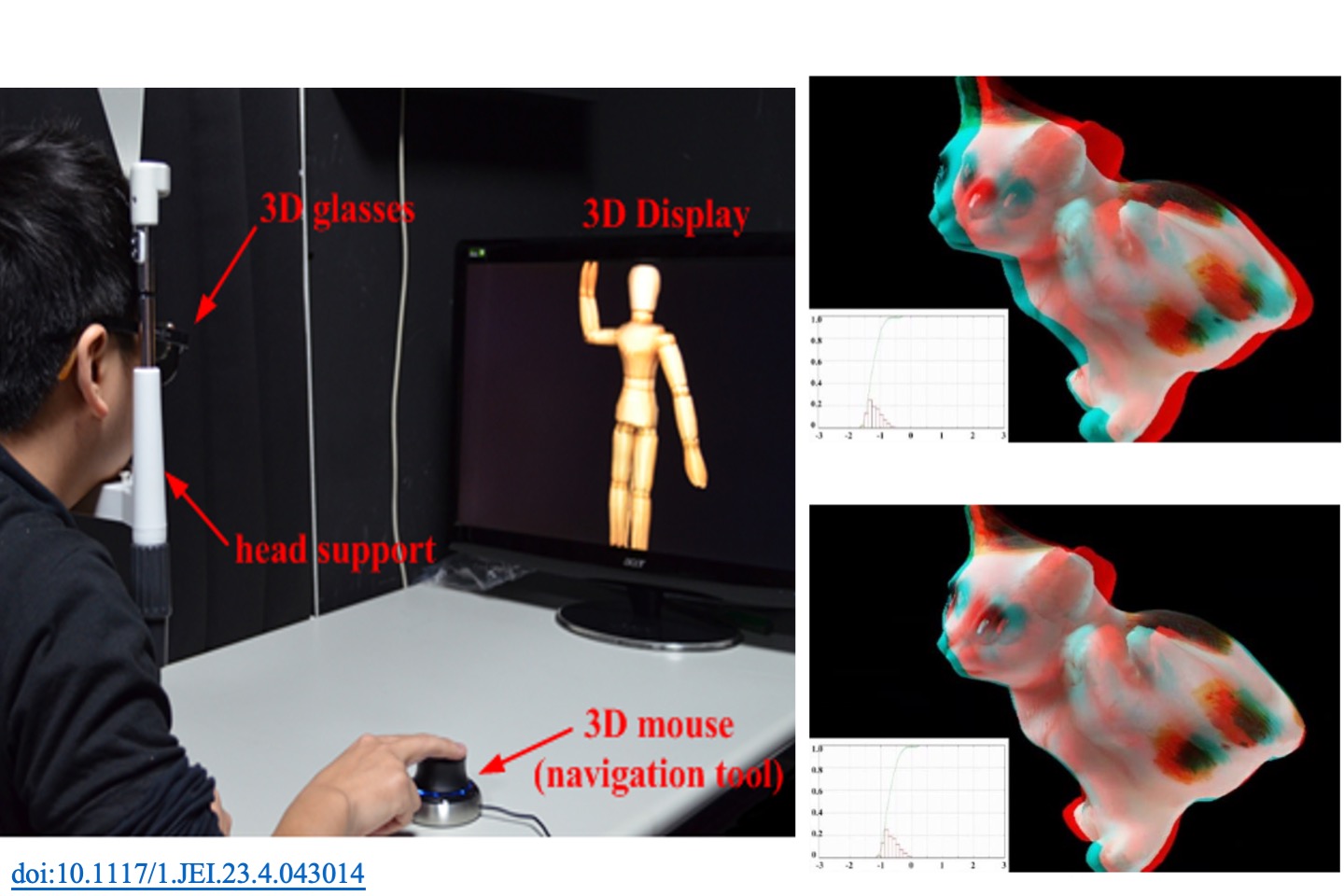

Perceived depth analysis for view navigation of stereoscopic three-dimensional models
This paper addresses how to define and control the perceived depth when rendering a single stereoscopic three-dimensional (3-D) model. In most 3-D manipulation software, the control of view navigation is the most important feature needed to visualize 3-D scenes of good quality. In a stereoscopic 3-D situation, however, this becomes more complex. We used two factors, parallax range and average parallax, to quantify the 3-D effect of rendering a 3-D model. After an experiment using subjective questionnaires, the fusional limit and depth perception of 22 subjects were regressed as paraboloid functions of parallax range and average parallax. Then, the comfort region, which is defined according to these parameters, was used again for developing an auto-adjustment algorithm for stereoscopic view navigation. This algorithm iteratively adjusts the parameters of a virtual stereo camera and simultaneously restrains parallax range and average parallax within a comfortable region. Finally, by using questionnaires and critical fusion frequency tests, we verified that this algorithm can significantly improve the comfort index of a user in customary operations.
T. H. Lin, S. Z. Hu, “Perceived depth analysis for view navigation of stereoscopic 3D models,” Journal of Electronic Imaging, 23(4), 043014, 2014.
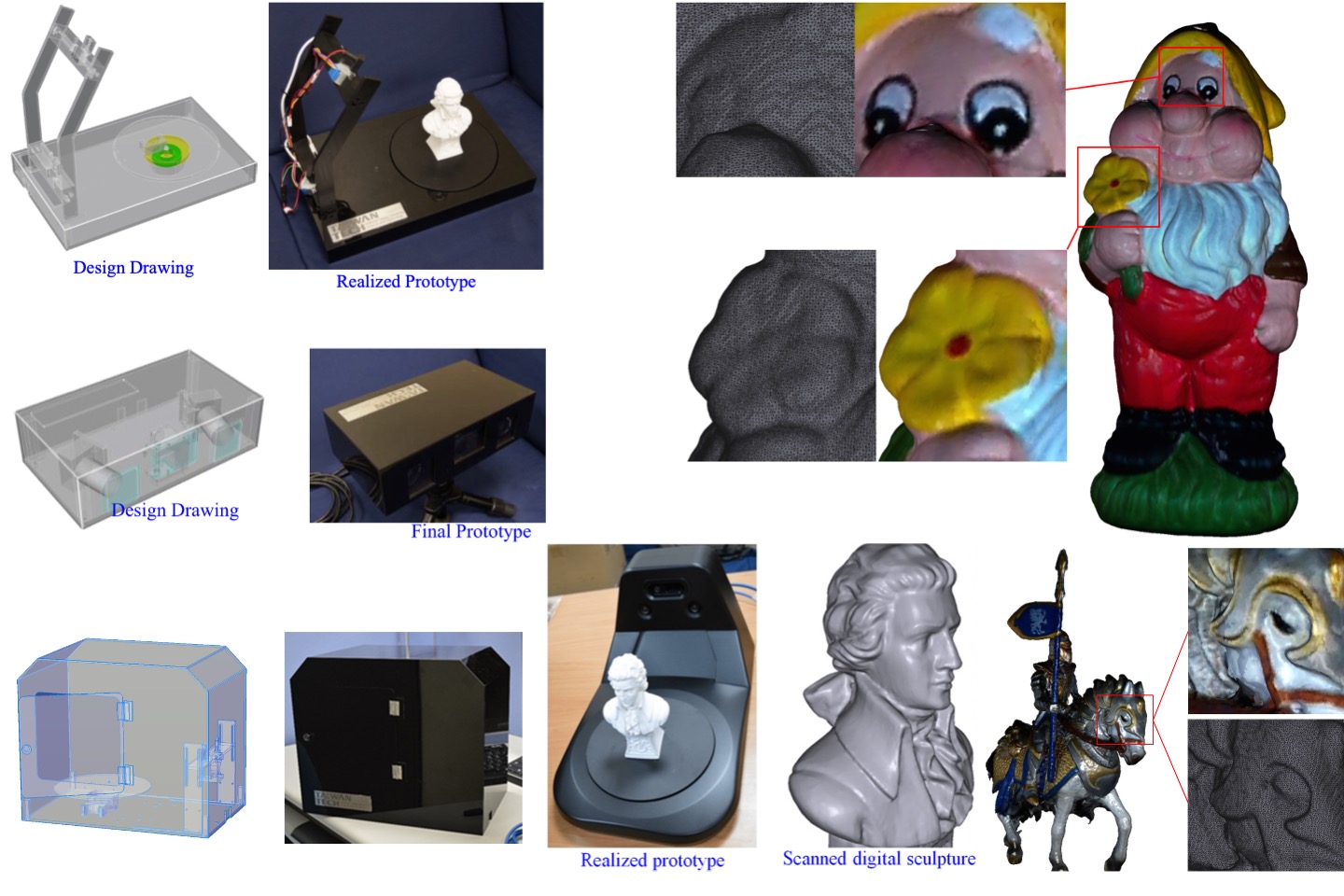

Commercial 3D scanner development (stereo-based)
In response to the needs of many customers, we have commercialized our 3D scanning technology into several prototypes, including independent scanning module and automatic scanning module, which can achieve one-click scanning. And completed the cross-platform window interface program development (wxWidget), which can operate normally in windows / macOS / Jetson / Raspberry PI / Ubuntu environment.
2013Y’ achievements


3D Reconstruction of Intricate Objects using Planar Cast Shadows
3D reconstruction for intricate objects such as mesh structures or translucent materials is a challenging task. One way to form the shape of an intricate object is to probe its silhouette. We propose a 3D reconstruction system based on planar cast shadows and the shape from silhouette algorithm. Our work focuses on simplifying the calibration procedure and equalizing the numbers of effective pixels of shadows in all captured images. With this design, the spatial resolution is improved and it is able to carve intricate shapes.
T. H. Lin, H. T. Chang, S. J. Hu, “3D Reconstruction of Intricate Objects using Planar Cast Shadows,” ACM SIGGRAPH 2013, Poster, July 2013, Anaheim, CA, USA.


Color appearance enhancement projection system – Augmented Projection
The main purpose of AR projection applications using projectors and CCDs is to enhance the color and style of physical images. We have developed an augmented projection device with a feedback mechanism, which includes a projector and a camera. We solved the problem of spatial correction and used the camera to capture the actual image. After calculation, the image to be overlaid was accurately projected back into the physical image. We can use such a device to achieve image processing of real objects: for example, we can enhance the contrast of real images, increase the brightness of colors, strengthen outlines, etc. It can also be used to correct the style of paintings for exhibitions, such as solving the problem of desaturated colors in portraits.
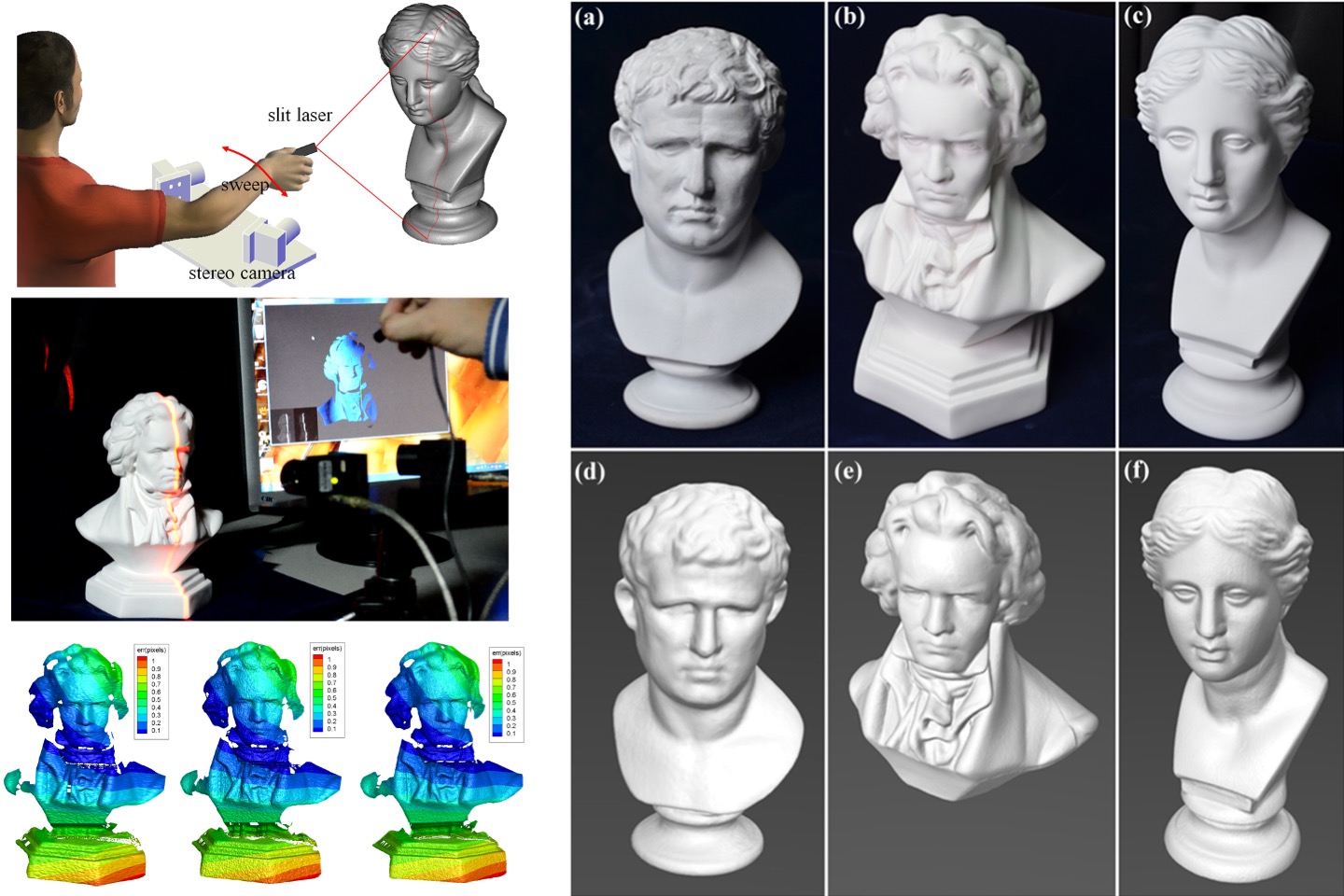


Resolution adjustable 3D scanner based on stereo cameras
This paper addresses a stereo-based 3D scanner system, which is able to acquire various resolution range data. The system consists of stereo cameras and one slit laser. In each stereo image pair, we cast one laser stripe on the surface of object, and analyze their disparities for determining their depth values. Utilizing a super-sampling filter, the sub-pixel features are generated for enhancing the native resolution of CCD component. In this system, we use one slit laser for sweeping the surface of objects and generating correspondences under the epipolar constrain. Since the correspondences are generated by the positions of the cast stripes, their resolution is controllable.
T. H. Lin, “Resolution adjustable 3D scanner based on stereo cameras,” Asia Pacific Signal and Information Processing 2013, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, Oct. 2013.
2012Y’ achievements
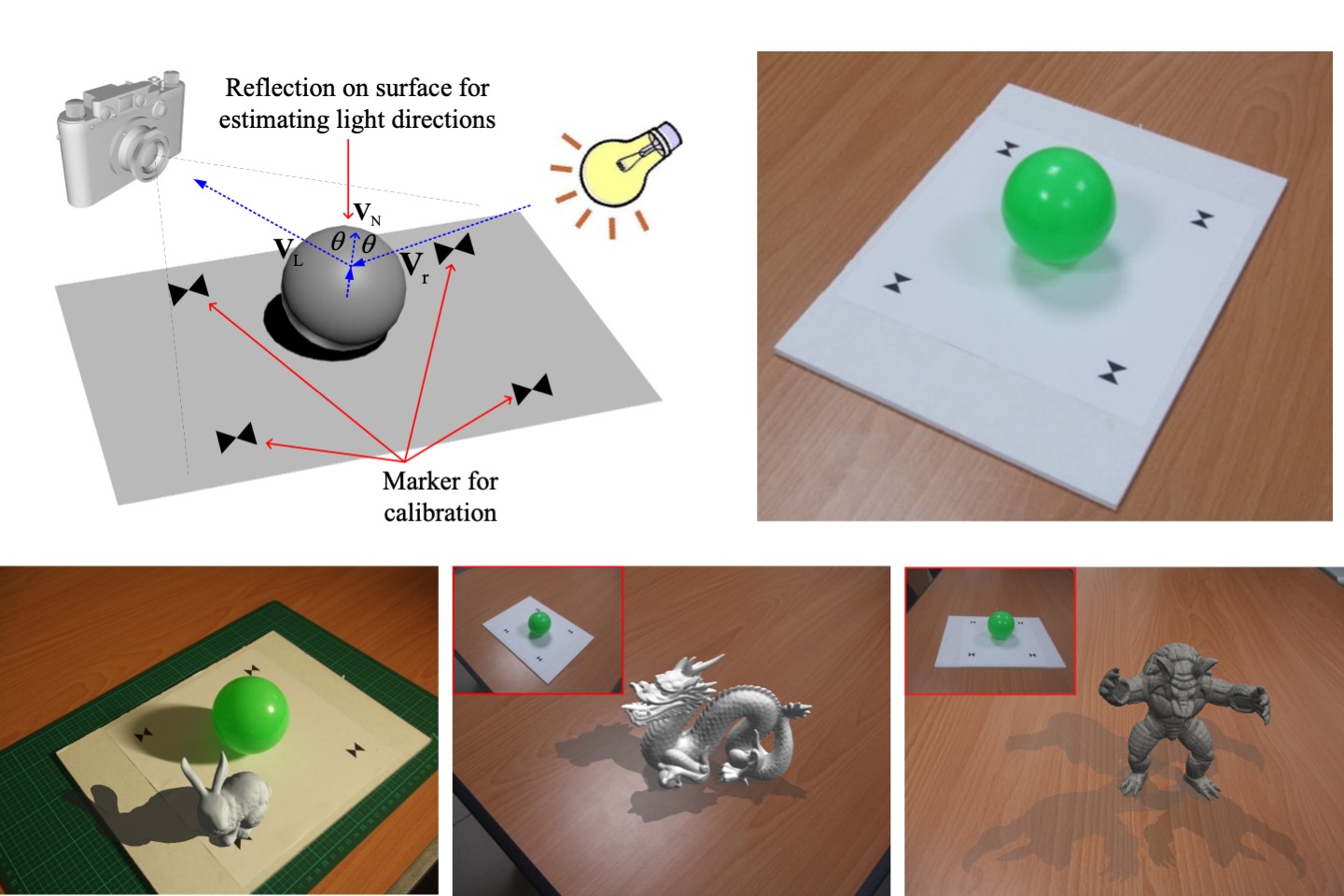

Argumented 3D objects based on illumination distribution estimation
We developed an algorithms capable to calculate environment light distribution. This technology mainly integrates computer vision correction technology for images. It is assumed that the light sources are all point lights and only one reflection is considered. Through self-made calibration board, we estimated the “direction” and “relative size” of the light source. This method can easily obtain the relative relationship between the camera and the current ambient light. We were able to calculate multiple lights and verify it with augmented reality. We can combine virtual objects into the captured image and render a realistic effect.
T. H. Lin, “Image Synthesis from Illumination Estimation,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop 2012, Poster, Dec. 4-7, 2012, Kyoto, Japan.
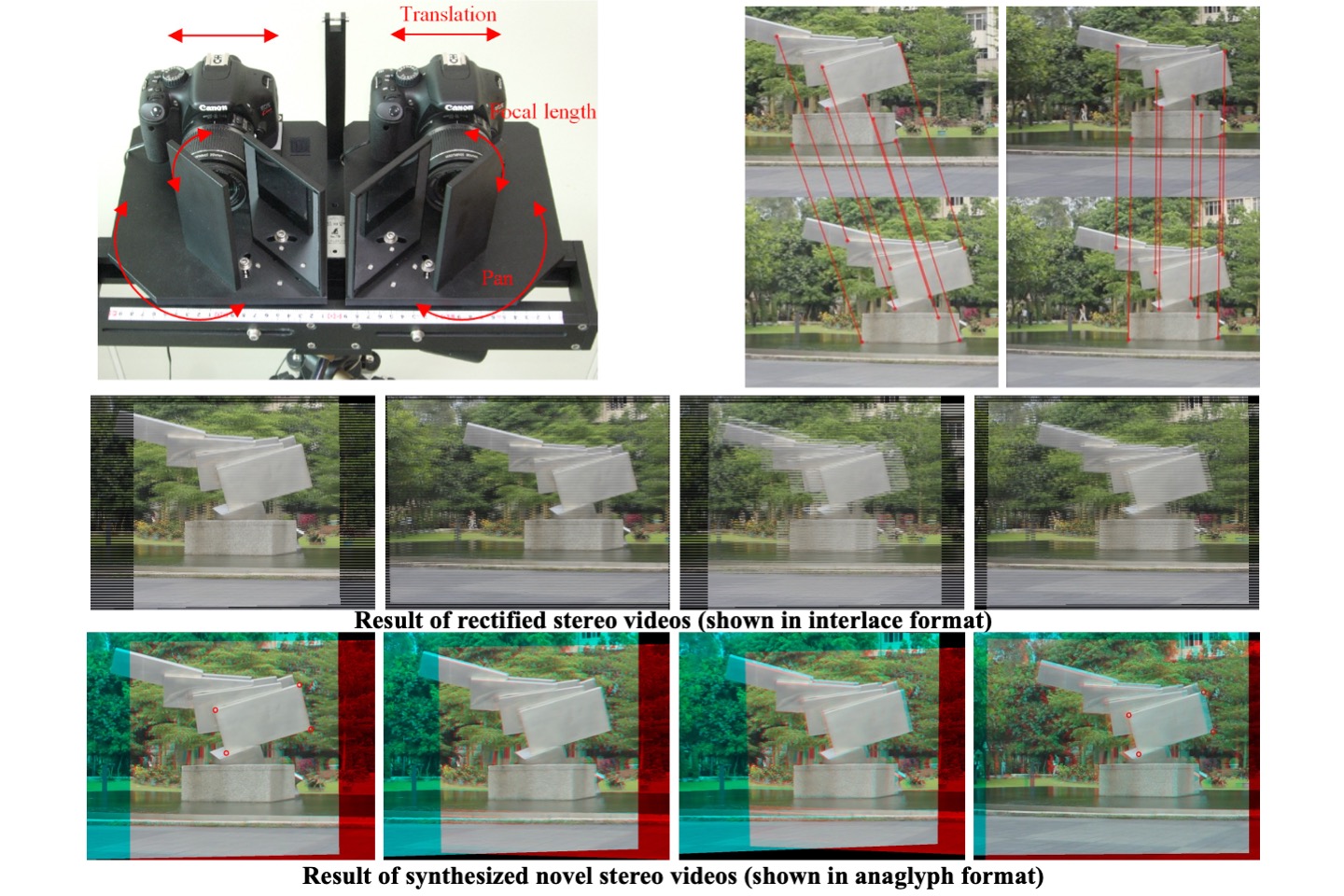

Stereo Video Rectification by Using Interpolated Homography Matrixes
This paper addresses a rectification method for stereo videos which are captured with varying physical parameters. Our method linearly interpolates homography matrixes by decomposition of the rectification matrixes of key frames. The result shows our method can rectify stereo videos and has smoother transition effects than the traditional methods.
T. H. Lin, “Stereo Video Rectification by Using Interpolated Homographics,” Proceedings of IDW/AD, International Display Workshop 2012, Poster, Dec. 4-7, 2012, Kyoto, Japan.
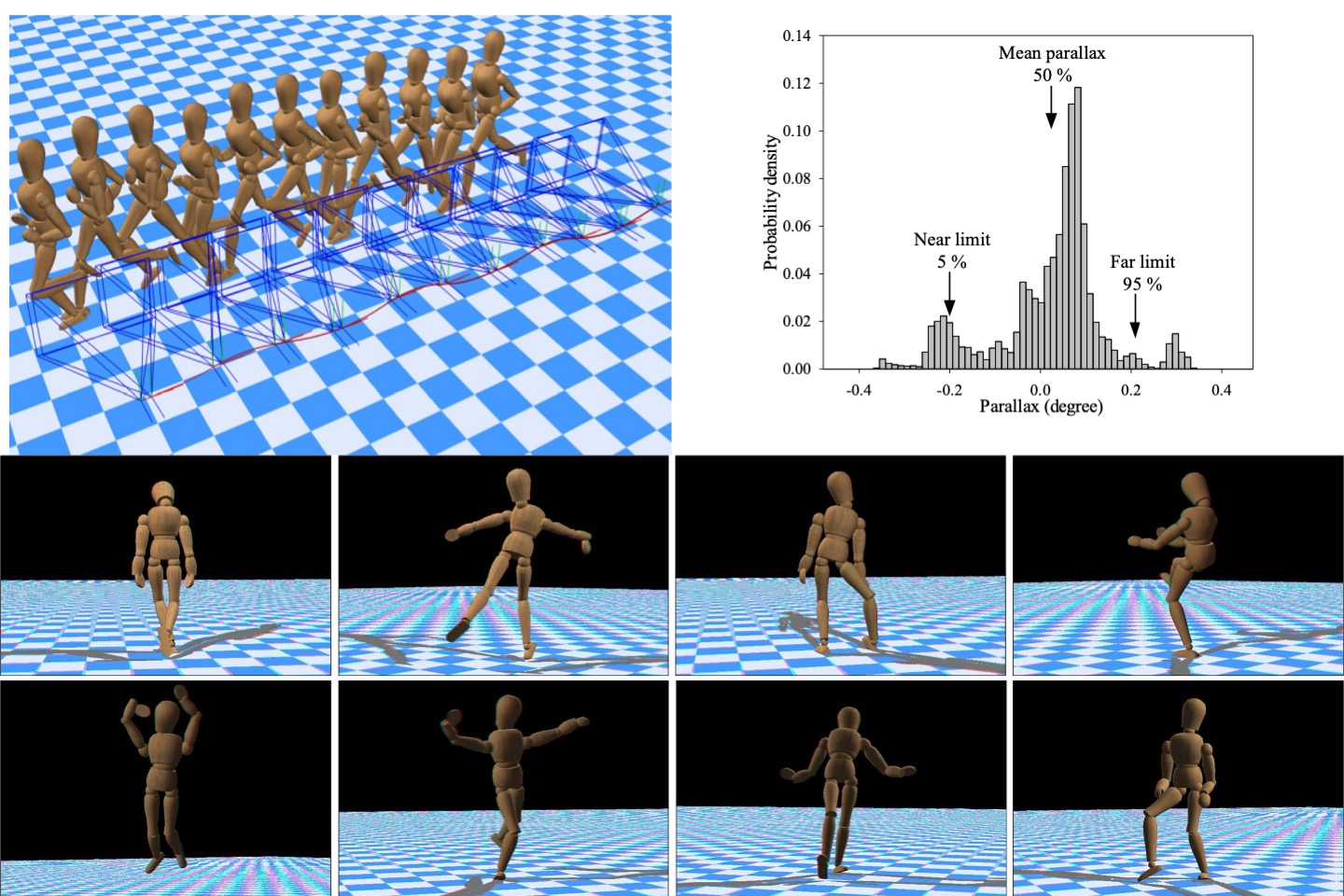

Controlling Depth Perception of Stereoscopic Images under Given Constraints
This paper addresses a practical method for controlling depth perception by adjusting stereo camera parameters. We use 3D graphic models and motion capture data to simulate various action scenarios. The goal is to keep an appropriate 3D effect for the interested character who has a specific motion. This method analyses the parallax distribution for every frame, and the temporal change is also considered for smooth transition between successive frames.
T. H. Lin, “Controlling Depth perception of stereoscopic images under given constraints,” World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science 2012 (WCECS2012), Oral, Oct. 24-26, 2012, San Francisco, USA.
Views: 674

